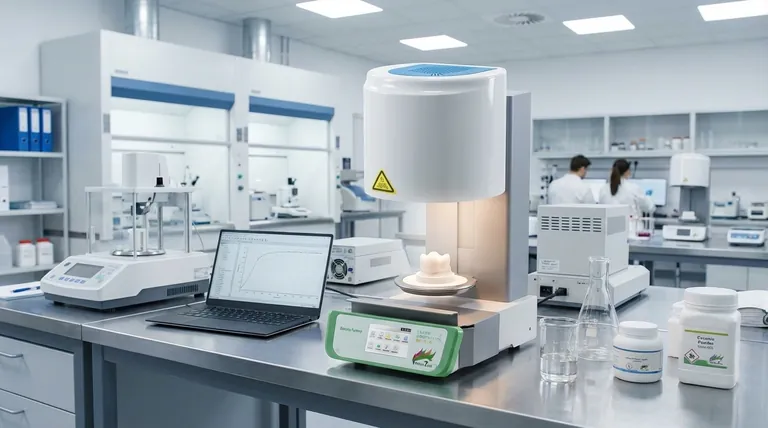
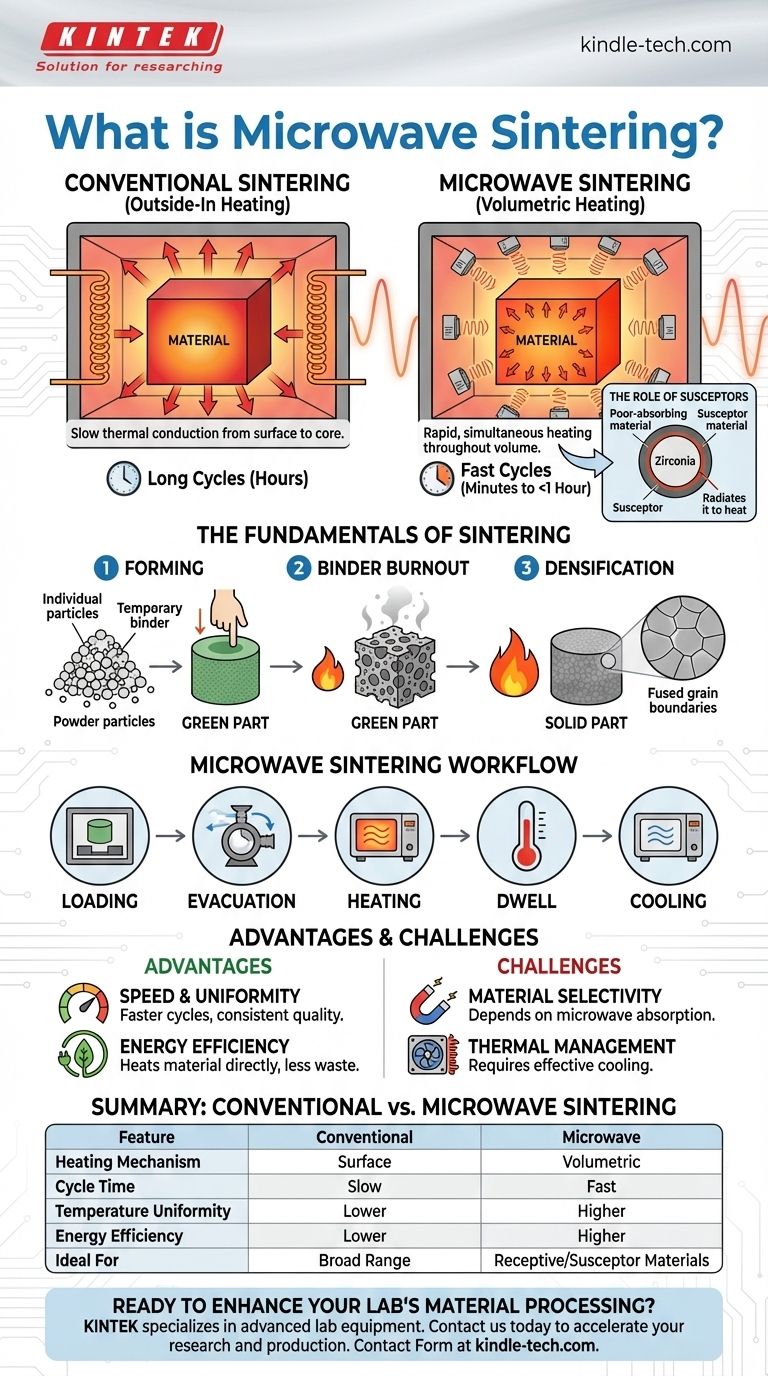
Microwave sintering is an advanced thermal process that uses microwave energy to heat and compact a powdered material into a solid, dense object. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside-in, microwaves generate heat directly within the material itself, enabling significantly faster and more uniform processing. For materials that do not naturally absorb microwave energy, such as certain ceramics like zirconia, a secondary "susceptor" material is used to absorb the energy and transfer it as heat.
The crucial difference between conventional and microwave sintering lies in the heating mechanism. Instead of relying on slow thermal conduction from a material's surface, microwave sintering provides rapid, volumetric heating from within, leading to faster cycles and more uniform density.

The Fundamentals of Sintering
To understand microwave sintering, one must first grasp the core principles of sintering itself. It is a foundational process in powder metallurgy and technical ceramics.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is the process of forming a solid mass of material by applying heat and sometimes pressure. Crucially, this is done without melting the material to the point of liquefaction.
The goal is to heat the powder to a temperature where the atoms in the individual particles become mobile enough to diffuse across the boundaries, fusing the particles together.
The Goal: Fusing Particles
Imagine a box of loose sand. Sintering transforms this into a solid piece of sandstone. It works by dramatically reducing the porous spaces between the powder particles.
This process is essential for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum, which are difficult or impractical to process using traditional casting methods.
The Three-Stage Process
The general sintering process, whether conventional or microwave, typically involves three key stages:
- Forming: A blend of the primary powder and a temporary bonding agent (like wax or a polymer) is compressed into the desired shape, often called a "green part."
- Binder Burnout: The green part is heated to a temperature high enough to burn away or evaporate the temporary bonding agent, leaving behind a fragile, porous structure of the primary powder.
- Densification: The temperature is raised further, just below the material's melting point. At this stage, the particles fuse together, the structure shrinks, and the part becomes dense and solid.
How Microwave Sintering Changes the Game
Microwave sintering follows the same fundamental goal as conventional sintering but revolutionizes the heating stage with a completely different energy delivery mechanism.
From Surface Heating to Volumetric Heating
A conventional furnace works by radiation and convection, heating the surface of the part first. That heat must then slowly conduct its way to the core, creating a temperature gradient between the outside and inside.
A microwave furnace works by coupling an electromagnetic field with the material's microstructure. This interaction generates heat simultaneously throughout the entire volume of the part, ensuring a much more uniform temperature profile.
The Role of Susceptors
Not all materials interact with microwaves. This is known as their microwave receptivity.
For materials like monoclinic zirconia that are poor microwave absorbers, a susceptor is used. A susceptor is a material that strongly absorbs microwave energy and converts it to thermal heat, which is then transferred to the target material via radiation and conduction.
The Microwave Sintering Workflow
The process inside a microwave furnace is highly controlled and typically follows these steps:
- Loading: The green parts are loaded into the heating cavity, often surrounded by or placed on susceptor materials.
- Evacuation: The furnace chamber is often evacuated to a vacuum state to prevent oxidation and ensure a controlled atmosphere.
- Heating: The microwave source is activated, rapidly and uniformly raising the material's temperature to the target.
- Dwell: The material is held at the peak sintering temperature for a specific period to allow for complete atomic diffusion and densification.
- Cooling: The microwave source is deactivated, and the now-solid part is cooled back to room temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is critical for proper application.
Advantage: Speed and Uniformity
Volumetric heating is dramatically faster than surface heating via conduction. This can reduce sintering cycles from many hours to less than one hour, significantly increasing throughput. The uniform heating also reduces internal stresses and the risk of cracking.
Advantage: Energy Efficiency
By heating only the material (and the susceptor, if used) instead of the entire furnace chamber, microwave sintering can be significantly more energy-efficient than conventional methods.
Challenge: Material Selectivity
The effectiveness of the process is entirely dependent on the material's ability to absorb microwave energy. This requires careful material characterization and, in many cases, the design of a suitable susceptor system.
Challenge: Thermal Management
The rapid heating achieved with microwaves also presents a challenge for cooling. The system must be designed to manage this thermal load effectively, sometimes requiring auxiliary cooling systems to control the cooling rate and prevent thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your material, production needs, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid production and high throughput: Microwave sintering is an excellent choice, as its dramatically shorter heating cycles can significantly boost productivity.
- If your primary focus is processing non-microwave-receptive materials like zirconia: You must use a susceptor-based microwave system to effectively convert microwave energy into the necessary thermal heat.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and uniformity: The volumetric heating of microwaves minimizes thermal gradients, reducing internal defects and leading to a more homogenous final product.
By understanding its principle of volumetric heating, you can leverage microwave sintering to achieve faster and more uniform results for a wide range of advanced material applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Sintering | Microwave Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Surface heating via conduction/convection | Volumetric heating from within the material |
| Cycle Time | Slow (hours) | Fast (minutes to <1 hour) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Lower (gradients from surface to core) | Higher (simultaneous heating) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (heats entire chamber) | Higher (heats material directly) |
| Ideal For | Broad range of materials | Microwave-receptive materials or those using a susceptor |
Ready to enhance your lab's material processing capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including solutions for efficient thermal processes like sintering. Our expertise can help you achieve faster cycle times, superior uniformity, and reduced energy consumption for your ceramics and powder metallurgy projects.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our sintering solutions can benefit your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















