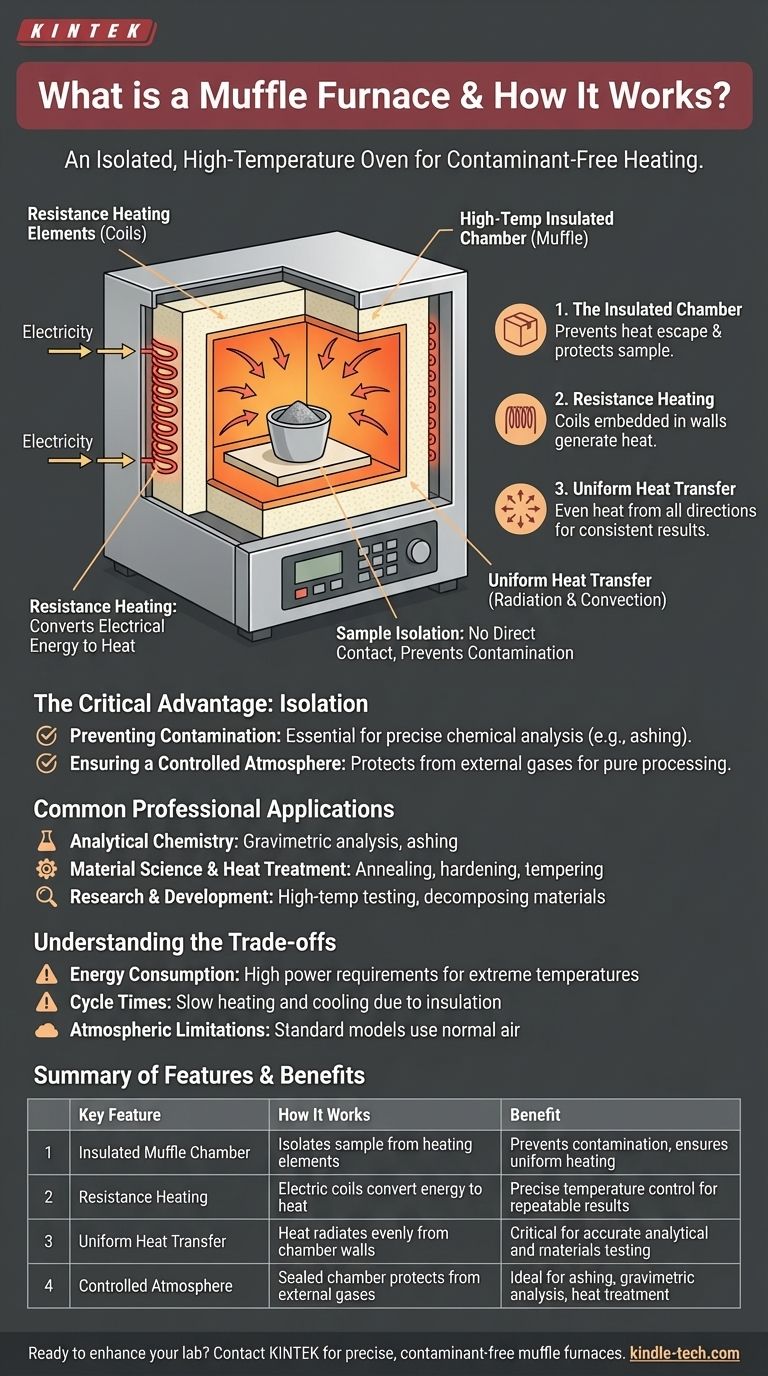
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that completely isolates the material being heated from the heating elements and any external contaminants. This is achieved by placing the sample within a specialized chamber, or "muffle," which ensures that heat is transferred indirectly and uniformly without any cross-contamination.
The defining principle of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but its use of an isolated chamber (the "muffle") to heat a sample uniformly and without any contact from the direct heat source.

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves High, Controlled Heat
A modern muffle furnace's operation is straightforward and elegant, based on a few key principles of energy transfer and insulation.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The heart of the furnace is the muffle, which is essentially a box or chamber made of high-temperature insulating material. This thick-walled chamber separates the interior workspace from the exterior environment and the heating elements.
This design serves two purposes: it prevents heat from escaping, making the furnace energy-efficient, and it protects the sample inside.
The Principle of Resistance Heating
The heat itself is generated by high-temperature heating coils or resistor wires, typically embedded within the insulated walls of the furnace. When electricity passes through these coils, their resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat.
This process is known as resistance heating and is governed by the law of conservation of energy.
Uniform Heat Transfer
The generated heat warms the inner chamber. The energy is then transferred to the workpiece or sample inside primarily through radiation and convection.
Because the sample isn't in direct contact with the coils, it receives heat evenly from all directions, ensuring temperature uniformity that is critical for laboratory and industrial processes.
The Critical Advantage: Isolation
The true value of a muffle furnace lies in its ability to isolate the sample. This characteristic was even more critical in historical models that used coal or wood, but it remains essential today.
Preventing Contamination
By separating the sample from the heating elements, the furnace guarantees that no particles from the coils can flake off and contaminate the material.
In chemical analysis, such as ashing, this ensures that the only material left is the true ash of the sample, without any external impurities.
Ensuring a Controlled Atmosphere
The sealed nature of the chamber provides a highly controlled environment. It protects the contents from any substances or gases present in the outside air, allowing for pure thermal decomposition or heat treatment.
Common Applications in a Professional Setting
Muffle furnaces are standard equipment in many laboratories and are valued for their versatility and precision.
Analytical Chemistry
They are widely used for gravimetric analysis, where a substance is heated until it reaches a constant weight. A common application is burning off filter paper or driving volatile compounds out of a sample.
Material Science and Heat Treatment
Engineers and material scientists use muffle furnaces for processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering metals. The precise temperature control allows for a material's properties to be altered in a highly repeatable manner.
Research and Development
These furnaces are indispensable for testing how materials behave under extreme temperatures, decomposing organic matter, and performing high-temperature melting of minerals and metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's important to understand the practical limitations of a standard muffle furnace.
Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures of 1200°C requires a significant amount of electrical energy. While they are designed to be efficient for their class, they are still high-power devices.
Cycle Times
The same thick insulation that holds heat in so effectively also means the furnace cools down slowly. This can create a bottleneck in processes that require rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Atmospheric Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere inside the chamber. For processes requiring a vacuum or a specific inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), a more specialized and expensive type of furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The primary benefit of a muffle furnace is its ability to deliver clean, uniform heat.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical analysis (ashing/gravimetry): The key is the furnace's ability to provide a clean, contaminant-free environment for complete combustion.
- If your primary focus is materials testing or metallurgy: You need the furnace's precise temperature control and uniformity to ensure repeatable heat-treatment results.
- If your primary focus is general high-temperature lab work: The furnace serves as a reliable and safe workhorse for heating samples without direct exposure to heating elements.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is an indispensable tool for any process demanding high-temperature heating in a meticulously controlled and clean environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | How It Works | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Insulated Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample from heating elements | Prevents contamination and ensures uniform heating |
| Resistance Heating | Electric coils convert energy to heat | Precise temperature control for repeatable results |
| Uniform Heat Transfer | Heat radiates evenly from chamber walls | Critical for accurate analytical and materials testing |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Sealed chamber protects from external gases | Ideal for ashing, gravimetric analysis, and heat treatment |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable muffle furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for precise temperature control and contaminant-free heating. Whether you're in analytical chemistry, materials science, or R&D, our solutions ensure accurate and repeatable results. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application and achieve superior thermal processing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- At what temperature does ceramic melt? A Guide to Ceramic Heat Resistance
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnace? Achieve Absolute Purity and Control in Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab



















