At its core, plasma torch gasification is an extreme thermal destruction process that uses superheated, electrically charged gas—or plasma—to break down hazardous waste. Operating at temperatures hotter than the surface of the sun, it doesn't just burn waste; it causes molecular dissociation, breaking materials down into their basic elemental components. These elements then reform into a combustible synthesis gas and a non-hazardous, glass-like solid.
Plasma gasification should not be viewed merely as waste disposal, but as a process of waste conversion. Its fundamental value lies in its unique ability to transform highly dangerous materials into two distinct and potentially valuable byproducts: a clean-burning fuel gas and an inert, commercially usable slag.
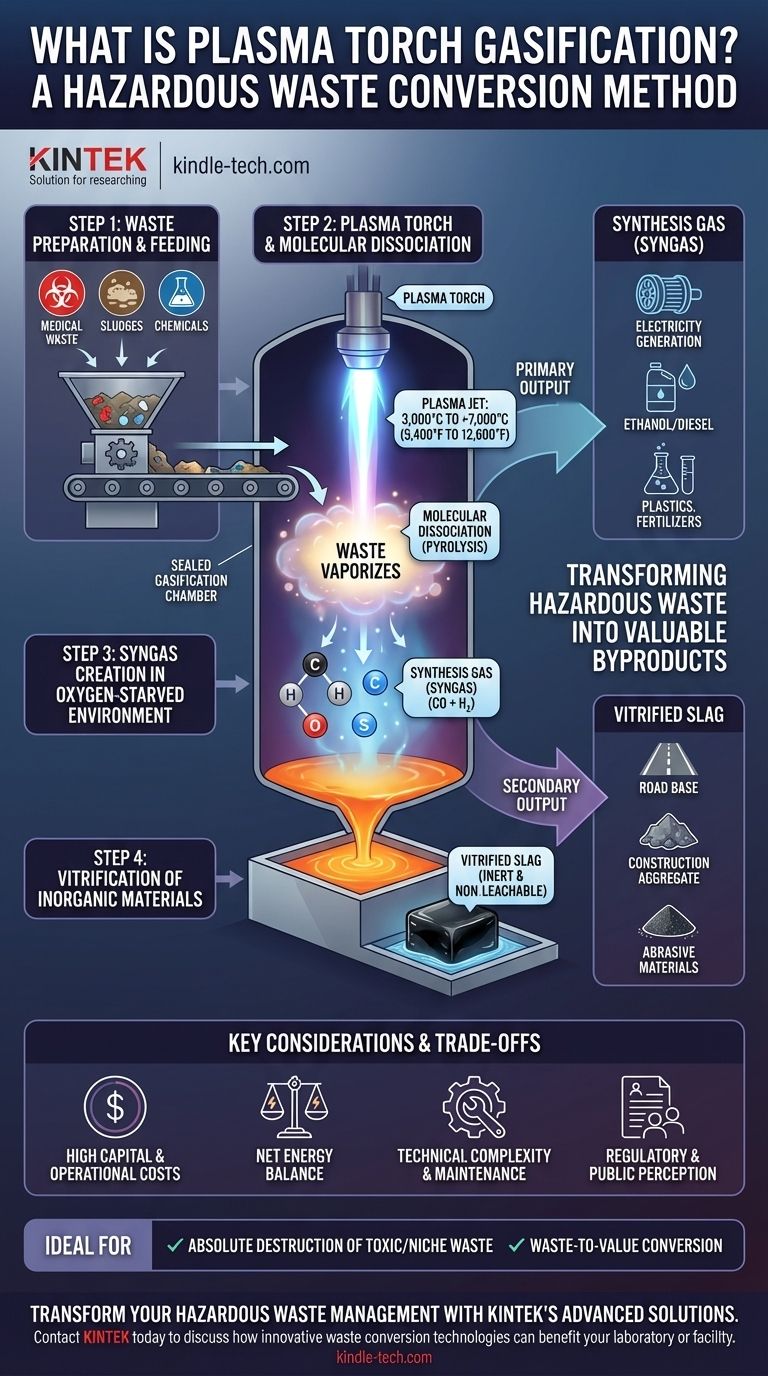
How Plasma Gasification Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand its application, it’s crucial to visualize the process. It is a highly controlled, multi-stage engineering system far removed from simple incineration.
Step 1: Waste Preparation and Feeding
Waste materials, which can range from medical waste to industrial sludges and chemical agents, are often pre-processed (shredded or mixed) for a consistent feed. This material is then fed into the sealed gasification chamber.
Step 2: The Plasma Torch and Molecular Dissociation
This is the heart of the system. A plasma torch passes a high-voltage current through a stream of gas (like air or nitrogen), creating a column of plasma—the fourth state of matter.
This plasma jet, with temperatures ranging from 3,000°C to over 7,000°C (5,400°F to 12,600°F), is directed at the waste. The intense energy instantly vaporizes the organic materials and breaks down their chemical bonds, a process known as pyrolysis.
Step 3: Syngas Creation in an Oxygen-Starved Environment
The reactor is kept at very low oxygen levels. This prevents combustion (burning) and instead forces the dissociated elements—primarily carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—to recombine into a mixture called synthesis gas, or syngas.
Syngas is composed mainly of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂), both of which are combustible fuels.
Step 4: Vitrification of Inorganic Materials
Any inorganic materials in the waste stream, such as metals, glass, and minerals, melt under the extreme heat. This molten material collects at the bottom of the reactor. When drained and cooled, it forms a hard, black, glass-like rock called vitrified slag.
Analyzing the Outputs: From Hazardous Waste to Byproducts
The success of plasma gasification is measured by the quality and utility of its outputs. The goal is to eliminate the original hazard completely.
The Primary Output: Synthesis Gas (Syngas)
Syngas is a valuable fuel. It can be cleaned and then used in several ways:
- Burned in a gas turbine or engine to generate electricity.
- Converted into liquid fuels like ethanol or diesel through chemical processes.
- Used as a chemical feedstock for manufacturing plastics and fertilizers.
This creates a waste-to-energy pathway, turning a disposal cost into a potential revenue stream.
The Secondary Output: Vitrified Slag
The slag's most important property is that it is inert and non-leachable. The vitrification process traps heavy metals and other inorganic toxins within the glass matrix, preventing them from ever dissolving and contaminating soil or groundwater.
This inert slag passes stringent environmental tests and can often be sold for use as construction aggregate, road base, or in abrasive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While technologically impressive, plasma gasification is not a universal solution. Its implementation requires a careful analysis of its significant costs and complexities.
High Capital and Operational Costs
This is the single greatest barrier to adoption. Plasma gasification facilities are extremely expensive to build due to the sophisticated reactors, plasma torches, and gas handling systems. Operational costs are also high, driven primarily by the immense electricity consumption of the plasma torches.
Net Energy Balance
A critical question for any project is its net energy balance. The system must generate more energy from the syngas than the plasma torches consume to be considered a true net-energy producer. This balance depends heavily on the energy content of the waste feedstock.
Technical Complexity and Maintenance
These are not "set-it-and-forget-it" systems. They require highly skilled operators and a rigorous maintenance schedule. The electrodes in the plasma torches, for instance, are consumable components that require regular replacement.
Regulatory and Public Perception
Because it is a thermal process, plasma gasification can sometimes be incorrectly grouped with incineration by the public and regulators. This can lead to "Not In My Back Yard" (NIMBY) opposition and a lengthy, complicated permitting process.
Is Plasma Gasification the Right Solution for Your Goal?
Deciding on this technology requires aligning its unique capabilities with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is the absolute destruction of highly toxic or niche waste (like PCBs, asbestos, or chemical weapons): Its ability to achieve complete molecular dissociation makes it arguably the most effective and safest destruction technology available.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective volume reduction for general hazardous materials: The high cost of plasma gasification may make advanced incineration a more pragmatic choice, provided the resulting ash can be managed and landfilled safely.
- If your primary focus is establishing a circular economy or a waste-to-value stream: This technology excels by converting a hazardous liability into tangible assets (energy and building materials), but it demands significant upfront investment and a long-term, stable supply of suitable waste.
Ultimately, plasma gasification represents a powerful, albeit costly, tool for transforming the world's most challenging waste streams from an environmental liability into a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature (3,000°C - 7,000°C) plasma breaks down waste molecularly in an oxygen-starved environment. |
| Primary Output | Synthesis gas (syngas: CO + H₂), a combustible fuel for electricity or chemical production. |
| Secondary Output | Vitrified slag, an inert, non-leachable solid usable in construction. |
| Ideal For | Absolute destruction of highly toxic waste (e.g., PCBs, asbestos) and waste-to-energy conversion. |
| Key Challenge | High capital/operational costs and significant electricity consumption. |
Transform your hazardous waste management with KINTEK's advanced solutions.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK understands the critical need for safe, efficient, and sustainable disposal of hazardous materials. Plasma gasification technology offers a powerful path to not only eliminate dangerous waste but also convert it into valuable resources like clean energy and reusable materials.
If you are evaluating advanced disposal methods for toxic or hard-to-treat waste streams, our expertise can help you assess if this high-tech solution aligns with your operational and sustainability goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how innovative waste conversion technologies can benefit your laboratory or facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty



















