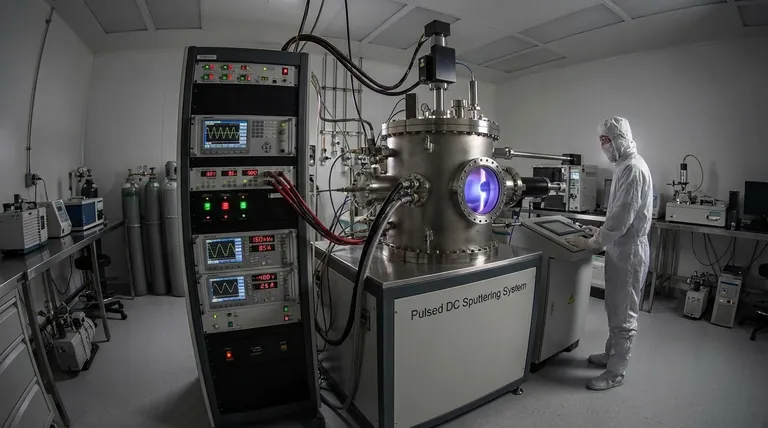
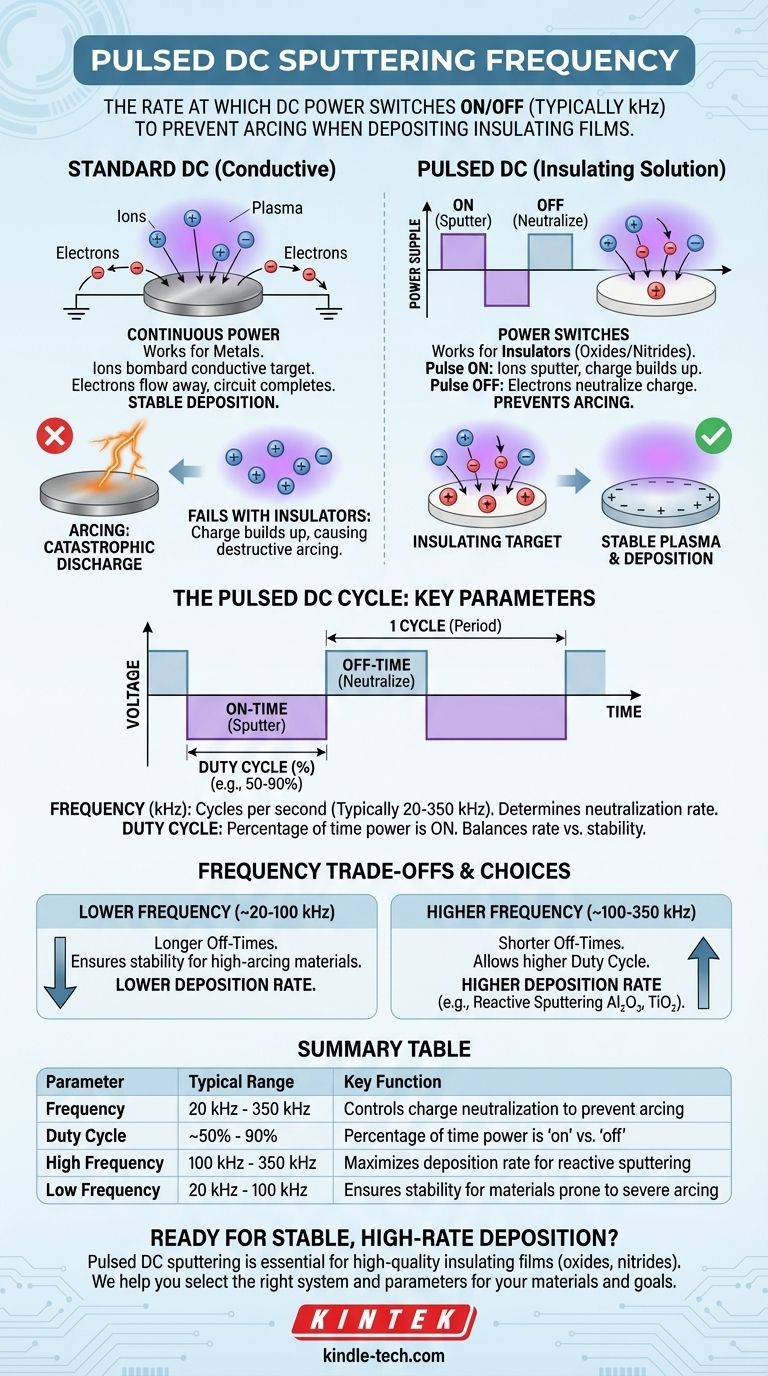
In short, pulsed DC sputtering frequency is the rate at which the DC power supply is switched on and off during the deposition process, typically measured in kilohertz (kHz). This technique is a critical evolution of standard DC sputtering, specifically engineered to deposit insulating or semi-insulating thin films—a task for which simple DC sputtering is ineffective due to a phenomenon called arcing. The frequency of this pulse is a key parameter that controls both the stability of the plasma and the rate of film deposition.
The core problem with sputtering insulating materials is that the target surface accumulates a positive charge, leading to uncontrolled electrical discharges known as arcs. Pulsed DC sputtering solves this by periodically interrupting the voltage, giving electrons from the plasma a moment to neutralize this charge buildup before an arc can form. The frequency determines how often this neutralization occurs.
The Fundamental Problem: Why Standard DC Fails
Standard DC sputtering is a robust and high-rate process, but only for electrically conductive materials like metals. Its physics create an inherent limitation when dealing with insulators.
The Role of a Conductive Target
In standard DC sputtering, a high negative DC voltage is applied to a conductive metal target. Positive ions (like Argon) from the plasma are accelerated into this target, sputtering away material.
Because the target is conductive, it can complete the electrical circuit and dissipate the continuous influx of positive ion charge, allowing the process to run smoothly and indefinitely.
The Insulating Target Dilemma
When you attempt to sputter an insulating (dielectric) material like an oxide or nitride, this process breaks down. The positive ions still bombard the target, but now they become trapped on its surface.
This accumulation of positive charge on the target surface is often called "target poisoning" or "charging." The insulator, by definition, cannot conduct this charge away.
The Consequence: Arcing
As this island of positive charge grows, the local electric field becomes incredibly intense. Eventually, it becomes strong enough to cause a catastrophic breakdown—a violent, high-current electrical discharge known as an arc.
Arcing is highly destructive. It can damage the target, blast large particulates onto your substrate (ruining the film), and destabilize or even extinguish the plasma, halting the deposition process entirely.
Pulsed DC Sputtering: The Engineered Solution
Pulsed DC was developed specifically to overcome the arcing problem. It modifies the continuous DC signal into a series of carefully controlled pulses.
The Core Mechanism: On-Time and Off-Time
A pulsed DC cycle consists of two phases:
- Pulse On-Time: During this phase (typically lasting microseconds), a negative voltage is applied, and sputtering occurs just like in the standard DC process. Positive charge begins to build up on the target.
- Pulse Off-Time (or Reversal): The voltage is then switched off or, in more advanced systems, briefly reversed to a small positive potential. This brief interruption allows the highly mobile electrons in the plasma to flood the target surface and neutralize the accumulated positive charge.
This cycle repeats thousands of times per second, preventing the charge from ever building up enough to trigger an arc.
Defining Frequency and Duty Cycle
Two parameters control this process:
- Frequency: This is the number of full on/off cycles per second, typically ranging from 20 kHz to 350 kHz. It dictates how often the charge neutralization step occurs.
- Duty Cycle: This is the percentage of time the voltage is "on" within one cycle. A 90% duty cycle means the power is on for 90% of the cycle and off for 10%.
Together, frequency and duty cycle determine the duration of the reverse time—the critical window for neutralizing the target.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of frequency is not arbitrary; it involves balancing deposition rate against process stability. While pulsed DC is a powerful solution, it is often compared to RF sputtering, the other primary method for depositing insulators.
Higher Frequencies (~100-350 kHz)
Higher frequencies enable shorter "off-times" while still preventing arcs. This is beneficial because it allows for a higher duty cycle (more time spent sputtering), which in turn yields a higher deposition rate. Most modern reactive sputtering processes for compounds like Al₂O₃ or TiN use high-frequency pulsed DC.
Lower Frequencies (~20-100 kHz)
Lower frequencies may be used for materials that are less prone to severe arcing or in older power supply designs. They typically require a lower duty cycle (longer "off-time") to ensure complete charge neutralization, which results in a lower overall deposition rate.
Pulsed DC vs. RF Sputtering
RF (Radio Frequency) sputtering avoids charging by rapidly alternating the voltage (typically at 13.56 MHz). While effective for all materials, its deposition rates for reactively sputtered compounds are often significantly lower than what can be achieved with modern high-frequency pulsed DC systems. However, RF remains the gold standard for sputtering directly from a highly insulating source target (e.g., sputtering a quartz target).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sputtering parameters depends entirely on your material and performance objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition rate for reactive sputtering (e.g., forming Al₂O₃, TiO₂, Si₃N₄): Use a high-frequency (100-350 kHz) pulsed DC power supply, as this allows you to run a high duty cycle for faster film growth while effectively suppressing arcs.
- If you are experiencing severe arcing with a semi-insulating compound: Start with a mid-range frequency (e.g., 50-100 kHz) and a conservative duty cycle (e.g., 80%) to establish a stable process, then gradually increase both to optimize the rate.
- If you are choosing between technologies for compound films: Favor pulsed DC for its high deposition rates in reactive processes, but choose RF sputtering if you need to sputter directly from a bulk insulating target material.
Ultimately, frequency is the dial that allows you to precisely control the charge neutralization critical for stable, high-quality deposition of insulating films.

Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 20 kHz - 350 kHz | Controls charge neutralization rate to prevent arcing |
| Duty Cycle | ~50% - 90% | Percentage of time power is 'on' vs. 'off' |
| High Frequency | 100 kHz - 350 kHz | Maximizes deposition rate for reactive sputtering |
| Low Frequency | 20 kHz - 100 kHz | Ensures stability for materials prone to severe arcing |
Ready to achieve stable, high-rate deposition of your insulating films?
Pulsed DC sputtering is essential for depositing high-quality oxides, nitrides, and other compound films without destructive arcing. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to optimize your thin-film processes.
We can help you select the perfect sputtering system and parameters for your specific materials and deposition goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the most common type of graphite? Natural Amorphous vs. High-Performance Synthetic
- Is centrifugation or filtration better? A Guide to Choosing the Right Separation Method for Your Lab
- What is the temperature of a pyrolysis reactor? Master Thermal Control for Optimal Product Yields
- What is the difference between filtration and centrifugation? A Guide to Size vs. Density Separation
- What is the most efficient heat transfer system? Optimize Performance for Your Application
- What types of sensitive medical articles can be stored in ULT freezers? Preserve Critical Samples at -80°C
- What is a lab oven used for? A Guide to Precise Heating, Sterilization & Drying
- What is the flow rate of a filter press? Mastering the Dynamic Filtration Cycle



















