PVD colour is a high-performance finish created through a vacuum coating process called Physical Vapor Deposition. This technique bonds an ultra-thin film of specialized metal alloys, such as titanium nitride or chromium, to a surface at the molecular level. The result is a durable, corrosion-resistant coating that provides a range of attractive, high-gloss colours.
PVD is not a paint, powder coat, or traditional plating. It is a sophisticated surface modification process that enhances an object's durability, wear resistance, and appearance while being more environmentally friendly than conventional methods.

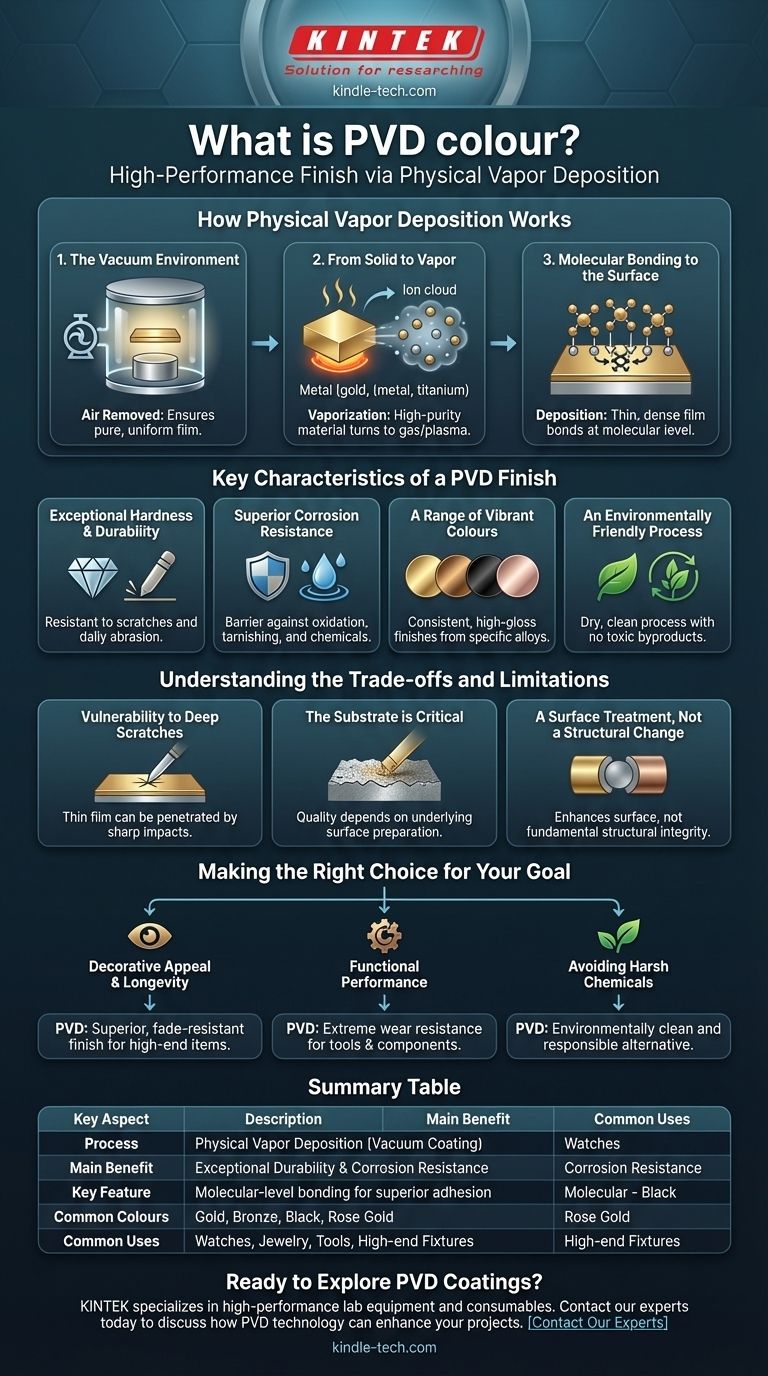
How Physical Vapor Deposition Works
Understanding the PVD process reveals why it creates such a resilient and high-quality finish. The entire operation takes place within a specialized vacuum chamber.
The Vacuum Environment
First, the object to be coated (the substrate) is placed in a vacuum chamber. Removing the air is critical to ensure the coating material can travel without colliding with air molecules, guaranteeing a pure and uniform film.
From Solid to Vapor
A solid, high-purity coating material is then vaporized. This is achieved through physical methods, such as heating or bombarding it with ions, which turns the solid metal directly into a gas or plasma.
Molecular Bonding to the Surface
The vaporized metal atoms travel across the vacuum chamber and are deposited onto the substrate. This creates an extremely thin, dense, and highly-adhered film that is bonded to the surface at a molecular level, not just layered on top.
Key Characteristics of a PVD Finish
The unique application process gives PVD coatings several distinct advantages over other finishing methods.
Exceptional Hardness and Durability
PVD coatings are remarkably hard and significantly increase the wear resistance of the base material. This makes them highly resistant to scratches and daily abrasion.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
The deposited film is dense and non-porous. This creates a protective barrier that shields the underlying material from oxidation, tarnishing, and damage from chemical exposure.
A Range of Vibrant Colours
The final colour is determined by the specific alloy used in the process. This allows for a wide spectrum of consistent, high-gloss finishes, including gold, bronze, black, and more.
An Environmentally Friendly Process
Compared to traditional electroplating, which involves harsh chemicals and hazardous waste, PVD is a dry, clean process. It produces no toxic byproducts, making it an environmentally responsible choice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly advanced, PVD coatings have specific characteristics that are important to understand. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Vulnerability to Deep Scratches or Impact
The coating itself is extremely hard, but it is also very thin. A sharp impact or a deep, abrasive scratch can penetrate the thin film and expose the substrate material underneath.
The Substrate is Critical
The final quality of the PVD finish is heavily dependent on the quality and preparation of the underlying surface. The coating will replicate any existing imperfections on the base material.
A Surface Treatment, Not a Structural Change
PVD enhances surface properties like hardness and corrosion resistance. However, it does not alter the fundamental structural integrity or strength of the object itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if a PVD-coated product is right for you depends entirely on your priority.
- If your primary focus is decorative appeal and longevity: PVD offers a superior, fade-resistant colour finish for items like high-end fixtures, watches, and jewelry.
- If your primary focus is functional performance: The process is an excellent choice for tools, blades, and industrial components that require extreme wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is avoiding harsh chemicals: The environmentally clean nature of PVD makes it a modern and responsible alternative to traditional coating methods.
Ultimately, choosing a PVD-coated product means investing in a sophisticated finish that delivers a powerful combination of aesthetic quality and surface resilience.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (Vacuum Coating) |
| Main Benefit | Exceptional Durability & Corrosion Resistance |
| Key Feature | Molecular-level bonding for superior adhesion |
| Common Colours | Gold, Bronze, Black, Rose Gold |
| Common Uses | Watches, Jewelry, Tools, High-end Fixtures |
Ready to explore PVD coatings for your laboratory or manufacturing needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether you are developing new products or require durable coatings for your tools and components, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD technology can enhance your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















