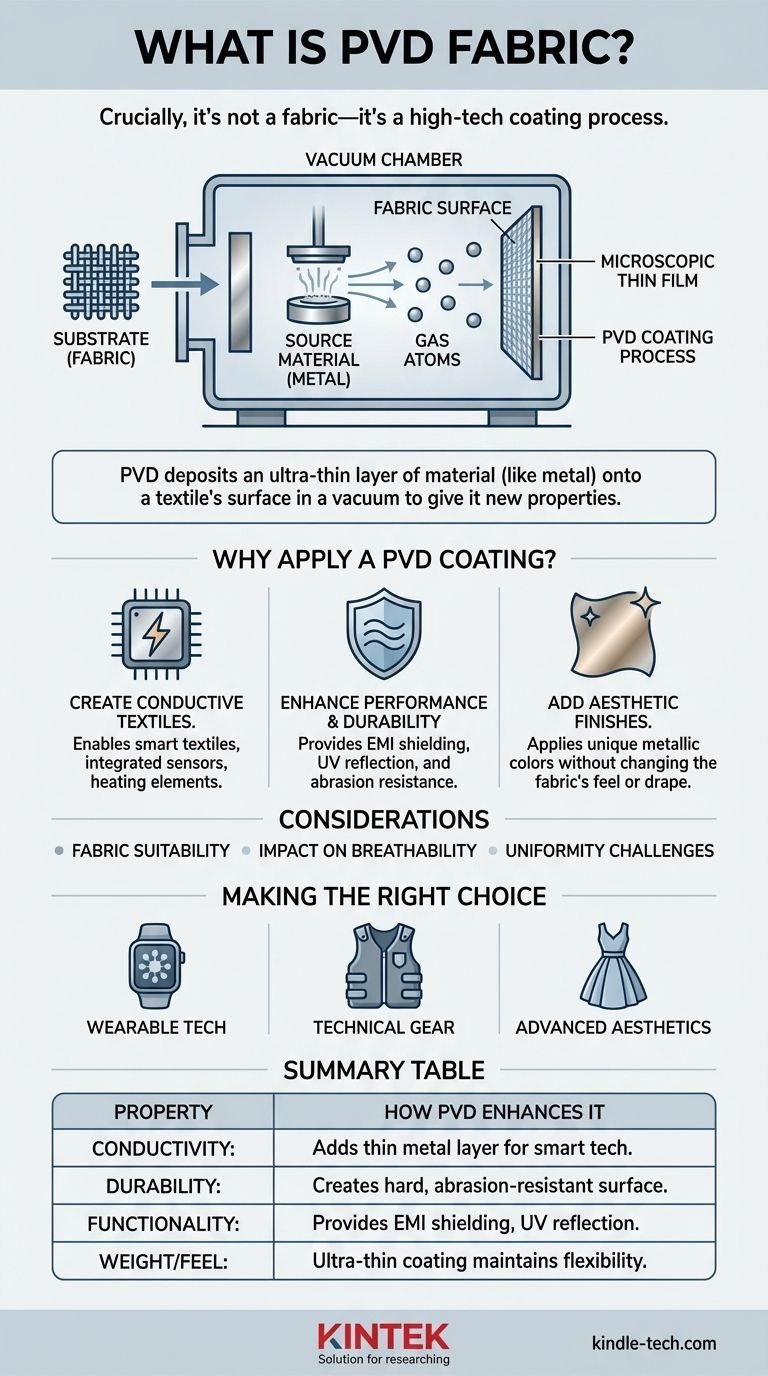
Crucially, there is no such thing as "PVD fabric." The term refers to a standard fabric or textile that has been treated with a high-tech coating process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). This process deposits an ultra-thin layer of material, often metal, onto the fabric's surface to give it entirely new properties.
The key takeaway is that PVD is not a type of material but a vacuum-coating process. When you hear "PVD fabric," you should think of a conventional textile that has been enhanced with a microscopic film to improve its performance or function.
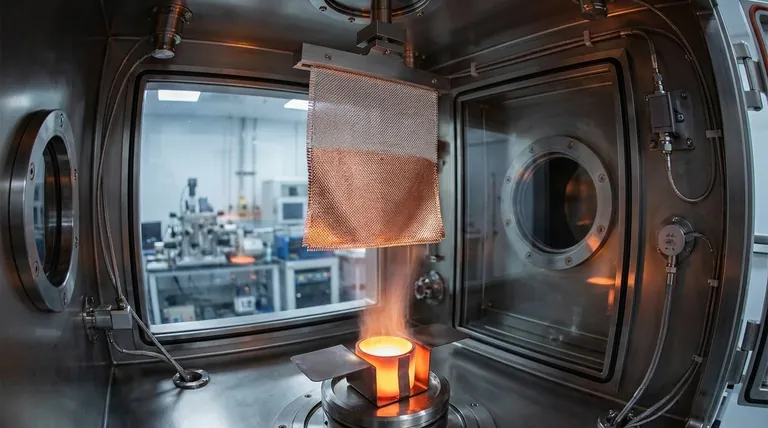

What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
Physical Vapor Deposition is a sophisticated manufacturing process used to apply very thin, durable coatings to a wide range of surfaces, from microchips to medical implants. When applied to textiles, it transforms them into high-performance materials.
The Core Concept: Vaporization in a Vacuum
The PVD process begins by placing the base material, or substrate (in this case, the fabric), into a vacuum chamber.
A solid source material, such as a metal like titanium, aluminum, or copper, is also placed inside. This source material is then vaporized, turning it from a solid into a gas of individual atoms or molecules.
The Deposition Process
Once vaporized, these atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and land on the surface of the fabric.
As they settle, they condense back into a solid state, forming a tightly bonded, uniform, and extremely thin film across the entire surface of the textile, even coating individual fibers.
Why a Vacuum is Essential
The process must occur in a high vacuum to prevent the vaporized atoms from colliding with air particles like oxygen or nitrogen.
This contamination-free environment ensures the deposited film is pure and adheres strongly to the substrate, resulting in a high-quality, durable coating.
Why Apply a PVD Coating to Fabric?
Applying a PVD coating fundamentally changes the fabric's properties without significantly altering its weight or flexibility. This opens up a world of possibilities for advanced textiles.
Creating Conductive Textiles
One of the most common applications is depositing a thin layer of conductive metal, like copper or silver, onto a non-conductive fabric.
This effectively turns the fabric into a circuit board, allowing for the creation of "smart textiles" with integrated sensors, heating elements, or wiring for wearable electronics.
Enhancing Performance and Durability
PVD coatings can add a range of performance attributes. For example, a metallic coating can provide excellent EMI shielding (blocking electromagnetic interference) for technical applications or UV reflection for performance apparel.
These coatings are also highly durable and resistant to abrasion, significantly extending the life of the base fabric.
Adding Aesthetic Finishes
PVD can also be used for purely decorative purposes. It allows for the application of a wide spectrum of colors with a metallic luster that cannot be achieved with traditional dyes.
Because the coating is so thin, it often doesn't change the feel or "drape" of the fabric, maintaining its original comfort.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, the PVD process has specific requirements and limitations that are important to understand. It is an industrial process that adds complexity and cost to the final product.
Fabric Suitability
Not all fabrics are suitable for PVD coating. The material must be able to withstand being in a vacuum environment and may need to tolerate a minor increase in temperature during the process.
Impact on Breathability
While the coatings are microscopic, a dense metallic layer can reduce a fabric's natural breathability. The specific coating material and its thickness must be carefully chosen to balance performance with comfort.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly uniform coating on a complex, three-dimensional surface like a woven textile can be challenging. The process must be precisely controlled to ensure every fiber receives an even layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding PVD-coated fabrics is about recognizing them as engineered materials designed for a specific purpose.
- If your primary focus is wearable technology: PVD is the key process for integrating electronics directly into clothing by creating flexible, durable conductive paths.
- If your primary focus is technical or protective gear: PVD adds critical functions like thermal regulation, EMI shielding, or antimicrobial surfaces without adding bulk.
- If your primary focus is advanced aesthetics: PVD provides a method for creating unique, metallic color effects that are far more durable than traditional printing or dyeing.
Ultimately, PVD is a transformative technology that turns ordinary textiles into advanced materials engineered for a specific function.
Summary Table:
| Property | How PVD Coating Enhances It |
|---|---|
| Conductivity | Adds a thin metal layer, enabling smart textiles and wearable tech. |
| Durability | Creates a hard, abrasion-resistant surface that extends fabric life. |
| Functionality | Provides EMI shielding, UV reflection, and unique aesthetic finishes. |
| Weight/Feel | Ultra-thin coating maintains the fabric's original flexibility and comfort. |
Ready to engineer the next generation of smart textiles?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for innovative PVD coating processes. Whether you're developing wearable technology, protective gear, or high-performance fabrics, our solutions can help you achieve precise, durable, and functional coatings.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your textile innovation projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- What were the 4 factors that affect the rate of evaporation? Master Control for Lab & Industrial Processes
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage



















