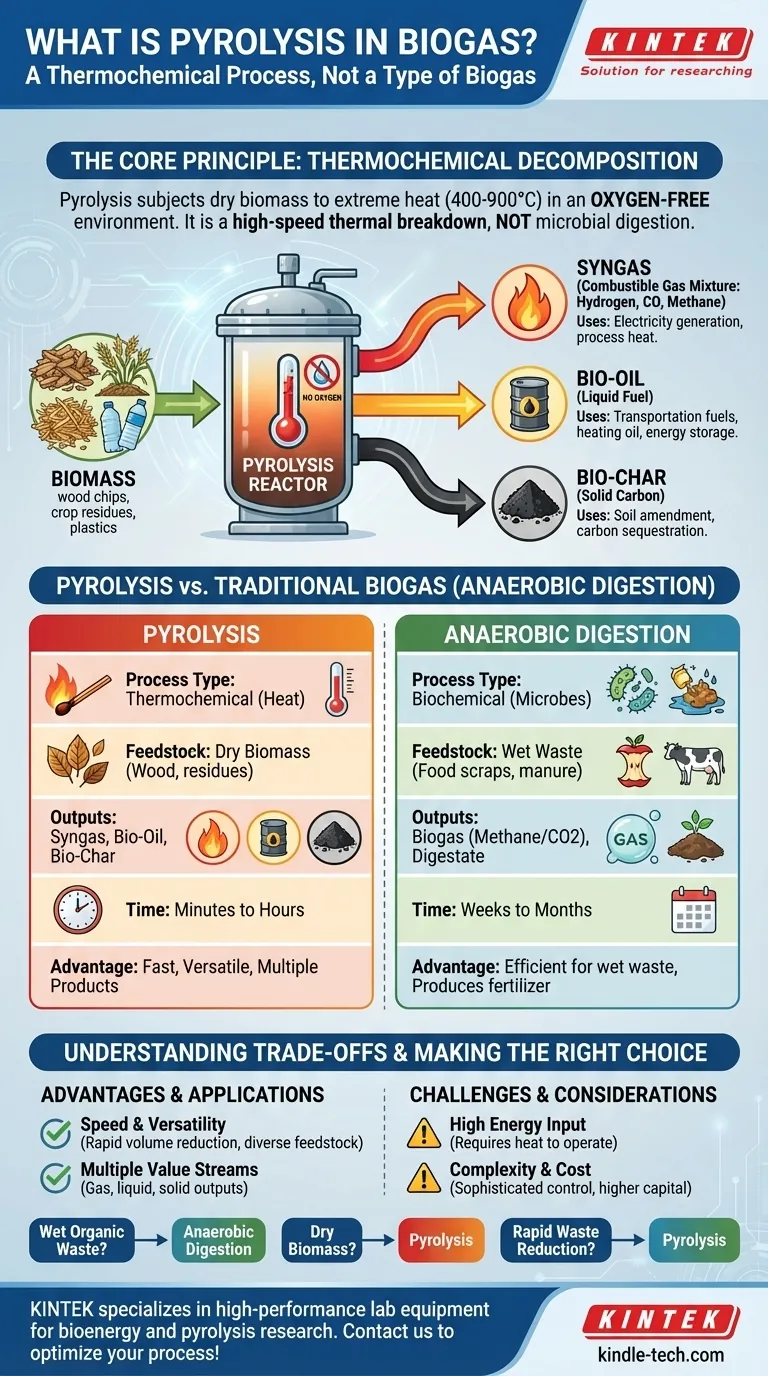
In the context of bioenergy, pyrolysis is not a type of biogas but rather a thermochemical process used to create it. It involves subjecting biomass to extremely high temperatures (400-900°C) in an oxygen-free environment. Instead of burning, the material rapidly decomposes, producing a combustible gas mixture known as syngas (synthesis gas), along with two other valuable byproducts: bio-oil and bio-char.
While often confused, pyrolysis is fundamentally different from the biological process that creates traditional biogas. It is a high-heat, high-speed method of chemical decomposition, not a slow, microbial digestion. Understanding this distinction is critical to evaluating its role in waste-to-energy systems.
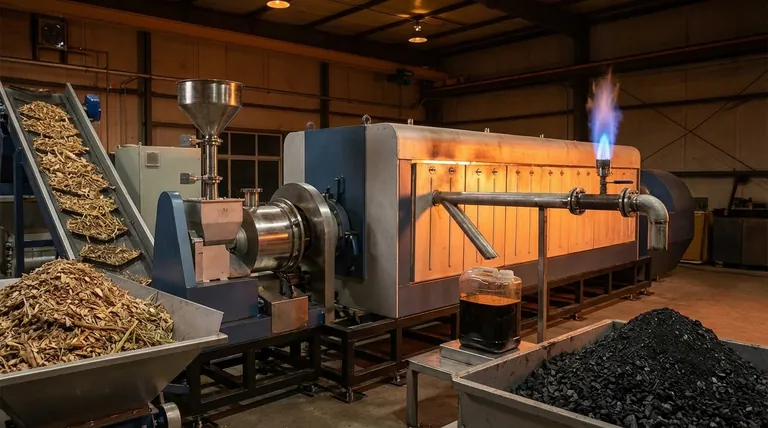

Deconstructing the Pyrolysis Process
Pyrolysis is best understood as a controlled, thermal breakdown of carbon-based materials. The absence of oxygen is the defining characteristic that prevents combustion and instead forces the material to decompose into new, more useful substances.
The Core Principle: Heating Without Burning
Think of pyrolysis as "cooking" biomass at an extreme temperature rather than burning it. By sealing the material in a reactor and removing oxygen, the intense heat breaks down the complex organic polymers into simpler, more energy-dense molecules.
This process aims to preserve as much of the original carbon as possible by converting it into stable gas, liquid, and solid forms, rather than releasing it into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide through combustion.
The Three Key Outputs
The decomposition of biomass via pyrolysis yields a consistent trio of products, each with its own applications.
- Syngas (The "Biogas" Component): This is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This syngas can be captured and used as a fuel for generating electricity or, critically, be redirected to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction itself.
- Bio-oil (Liquid Fuel): Also known as pyrolysis oil, this is a dark, dense liquid that can be refined into transportation fuels or used as a heating oil. It represents a way to store the energy from the biomass in a liquid form.
- Bio-char (Solid Carbon): This stable, charcoal-like solid is rich in carbon. It is a valuable product that can be used as a soil amendment to improve fertility and water retention or as a method for long-term carbon sequestration.
Pyrolysis vs. Traditional Biogas Production
The term "biogas" is most commonly associated with anaerobic digestion, and it's essential to distinguish pyrolysis from this process.
The Fundamental Difference: Heat vs. Microbes
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process. It relies on external energy (heat) to break down materials in minutes or hours.
Anaerobic Digestion is a biochemical process. It uses microorganisms in a wet, oxygen-free environment to slowly digest organic waste over weeks or months.
Feedstock and Output Comparison
The two processes are suited for different types of materials and produce different results.
- Feedstock: Pyrolysis excels at processing dry biomass like wood, agricultural residues, and even plastics or tires. Anaerobic digestion is designed for wet organic waste like food scraps, manure, and sewage sludge.
- Outputs: Pyrolysis creates three distinct products: syngas, bio-oil, and bio-char. Anaerobic digestion primarily produces two: biogas (mostly methane and CO2) and digestate (a nutrient-rich fertilizer).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing pyrolysis involves weighing its unique advantages against its operational complexities.
The Advantage of Speed and Versatility
The primary benefit of pyrolysis is its speed. It can convert large volumes of feedstock in a fraction of the time required for anaerobic digestion. Its ability to process a wide range of dry materials that cannot be digested by microbes is another significant advantage.
The Challenge of Energy Input
Pyrolysis plants require a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain their high operating temperatures. While the syngas produced can be used to offset this, the initial energy investment and thermal efficiency are critical design considerations.
Complexity and Control
Operating a high-temperature, high-pressure reactor demands sophisticated control systems and rigorous safety protocols. This makes the initial capital cost and operational expertise required for pyrolysis considerably higher than for a standard anaerobic digester.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion depends entirely on your feedstock and desired outcomes.
- If your primary focus is processing wet organic waste (e.g., food scraps, manure) for methane production: Anaerobic digestion is the established and more direct technology.
- If your primary focus is converting dry biomass (e.g., wood chips, crop residue) into multiple value streams: Pyrolysis offers superior product diversity with its output of gas, oil, and char.
- If your primary focus is rapid waste volume reduction and feedstock flexibility: The high-speed, versatile nature of pyrolysis makes it a strong candidate for integrated waste management systems.
Ultimately, understanding the core mechanism of each technology is the first step toward designing an effective and efficient bioenergy strategy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Anaerobic Digestion |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Thermochemical (Heat) | Biochemical (Microbes) |
| Feedstock | Dry biomass (wood, crop residues) | Wet waste (food scraps, manure) |
| Primary Outputs | Syngas, Bio-Oil, Bio-Char | Biogas (Methane/CO2), Digestate |
| Processing Time | Minutes to Hours | Weeks to Months |
| Key Advantage | Fast, versatile, multiple products | Efficient for wet waste, produces fertilizer |
Ready to optimize your bioenergy or waste conversion process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for researching and developing pyrolysis and biogas technologies. Whether you're analyzing feedstock, testing syngas composition, or scaling up production, our solutions help you achieve precise control and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique needs in renewable energy and sustainable materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















