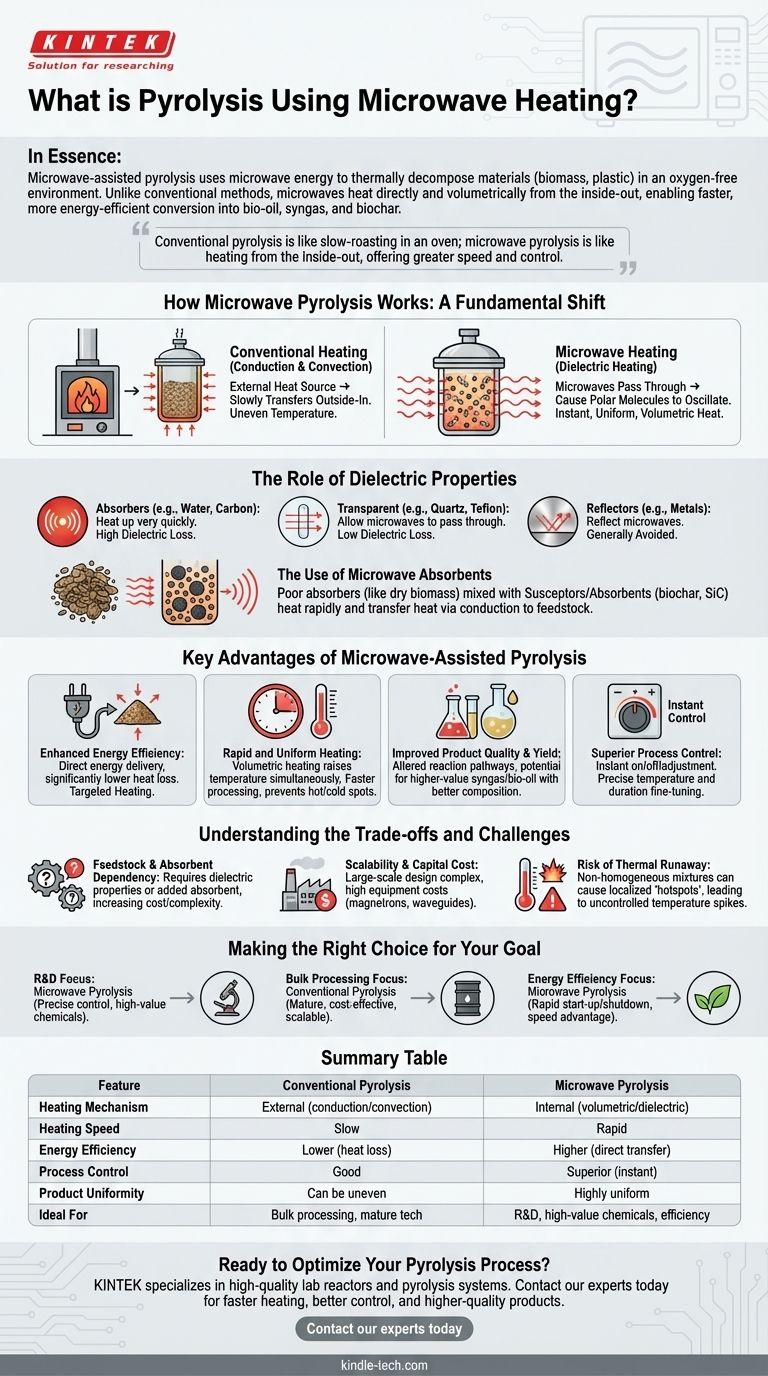
In essence, microwave-assisted pyrolysis is a process that uses microwave energy to thermally decompose materials, such as biomass or plastic, in an oxygen-free environment. Unlike conventional methods that heat the material from the outside, microwaves penetrate the feedstock and heat it directly and volumetrically, leading to faster and more energy-efficient conversion into bio-oil, syngas, and biochar.
The critical difference is the heating mechanism. Where conventional pyrolysis is like slow-roasting in an oven, microwave pyrolysis is like heating from the inside-out, offering greater speed, control, and potential for higher-quality products.

How Microwave Pyrolysis Works: A Fundamental Shift in Heating
Understanding microwave pyrolysis requires moving beyond the idea of simple heating and appreciating its unique interaction with matter. It's a selective and volumetric process, which sets it apart from traditional thermal methods.
Conventional vs. Microwave Heating
Conventional pyrolysis relies on conduction and convection. An external heat source warms the walls of a reactor, and that heat slowly transfers through the feedstock from the outside in. This process is often slow and can lead to uneven temperature distribution.
Microwave pyrolysis, however, uses dielectric heating. Microwaves pass through the material, causing polar molecules within it to rapidly oscillate. This internal friction generates heat instantly and uniformly throughout the material's volume.
The Role of Dielectric Properties
A material’s ability to convert microwave energy into heat is determined by its dielectric properties. Materials are broadly categorized in one of three ways:
- Absorbers: Materials with high dielectric loss (like water or carbon) heat up very quickly.
- Transparent: Materials with low dielectric loss (like quartz or Teflon) allow microwaves to pass through without heating.
- Reflectors: Metals reflect microwaves and are generally avoided.
This selective heating is a core feature of the technology.
The Use of Microwave Absorbents
Many raw feedstocks for pyrolysis, such as dry biomass, are poor microwave absorbers. To solve this, a highly-receptive material, known as a susceptor or absorbent (like biochar, silicon carbide, or graphite), is often mixed with the feedstock.
This absorbent heats up rapidly, and then transfers that heat to the surrounding feedstock via conduction, initiating and sustaining the pyrolysis reaction efficiently.
Key Advantages of Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis
The shift from surface heating to volumetric heating provides several distinct operational advantages that address the core challenges of conventional methods.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Energy is delivered directly to the material being processed, not wasted on heating the large reactor vessel and the surrounding air. This targeting results in significantly lower heat loss and greater overall energy efficiency.
Rapid and Uniform Heating
Volumetric heating raises the entire feedstock to the target temperature almost simultaneously. This rapid heating rate (often orders of magnitude faster than conventional methods) shortens processing times and prevents the formation of hot and cold spots, ensuring a more consistent reaction.
Improved Product Quality and Yield
The fast heating and precise temperature control can alter the chemical reaction pathways. This often leads to a different distribution of final products, potentially increasing the yield of valuable syngas or producing a bio-oil with a more desirable chemical composition, a key solution to the instability and low quality noted in some conventional pyrolysis oils.
Superior Process Control
Microwave power can be turned on, off, or adjusted instantaneously. This gives operators exceptionally precise control over the reaction temperature and duration, allowing them to fine-tune the process to target specific outputs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite its advantages, microwave pyrolysis is not a universal solution. It comes with its own set of technical and economic hurdles that must be considered.
Feedstock and Absorbent Dependency
The process is highly dependent on the dielectric properties of the feedstock. Materials that are transparent to microwaves require the addition of a separate absorbent, which adds cost, complexity, and another step to the process.
Scalability and Capital Cost
Designing large-scale industrial microwave reactors is significantly more complex than building a conventional furnace. The required equipment, such as high-power magnetrons and waveguides, can lead to higher initial capital investment compared to traditional pyrolysis systems.
Risk of Thermal Runaway
While generally providing uniform heating, non-homogeneous mixtures of feedstock and absorbents can create localized "hotspots." These areas can superheat rapidly, potentially leading to thermal runaway—an uncontrolled temperature spike that can damage equipment and compromise process safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a pyrolysis method depends entirely on your project's specific priorities, whether they are research precision, industrial scale, or economic feasibility.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Microwave pyrolysis is an excellent choice for its precise temperature control and ability to selectively produce high-value chemicals.
- If your primary focus is bulk processing of a single, consistent feedstock: Conventional pyrolysis may offer a more mature, cost-effective, and scalable solution for large-volume waste conversion.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and process speed: Microwave pyrolysis presents a compelling advantage, especially for smaller-scale or modular systems where rapid start-up and shutdown are beneficial.
Ultimately, microwave-assisted pyrolysis represents a more sophisticated and controlled approach to thermal decomposition, empowering engineers and scientists to move beyond brute-force heating.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Pyrolysis | Microwave Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | External (conduction/convection) | Internal (volumetric/dielectric) |
| Heating Speed | Slow | Rapid |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (heat loss to reactor) | Higher (direct energy transfer) |
| Process Control | Good | Superior (instant on/off) |
| Product Uniformity | Can be uneven | Highly uniform |
| Ideal For | Bulk processing, mature tech | R&D, high-value chemicals, efficiency |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether you are developing new bio-based materials or scaling up waste conversion, the right lab equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab reactors and pyrolysis systems for researchers and engineers.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can help you achieve faster heating, better process control, and higher-quality products in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















