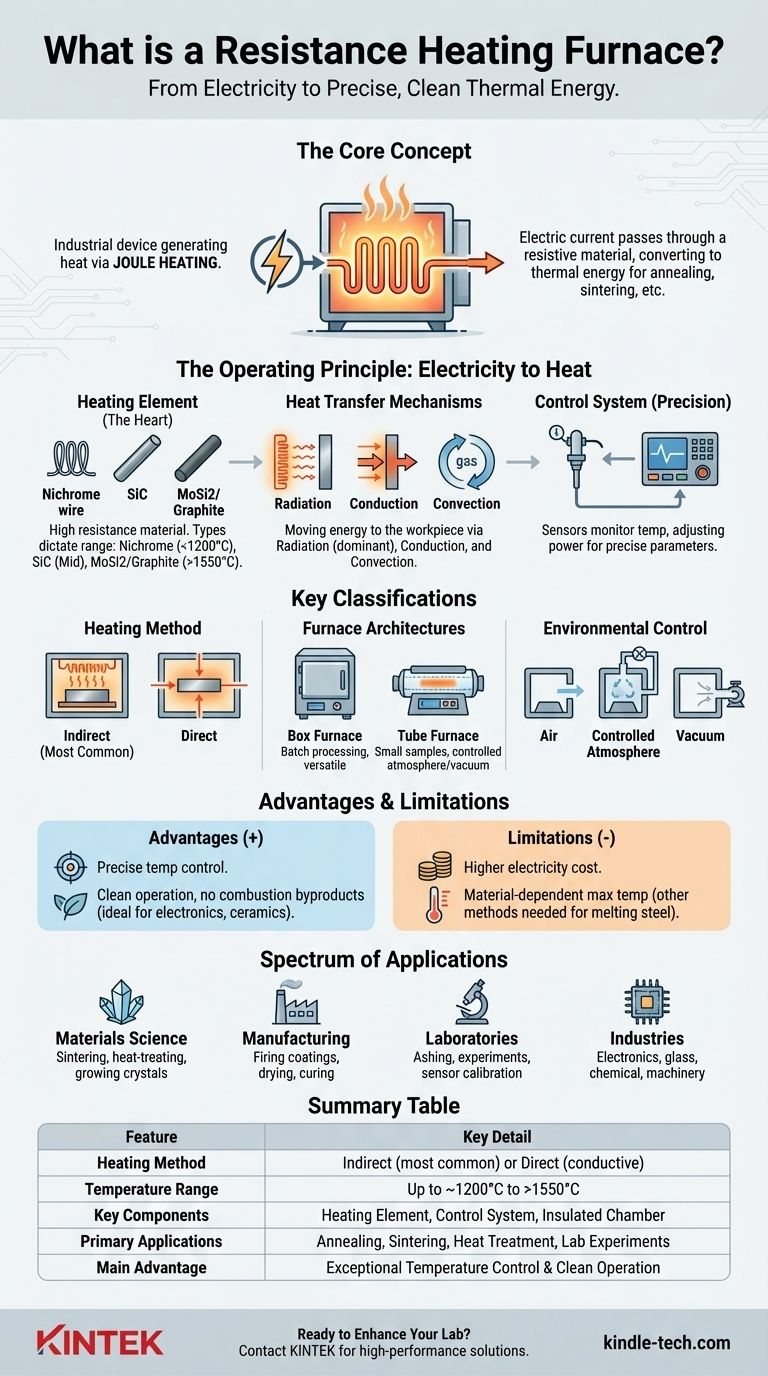
At its core, a resistance heating furnace is an industrial or laboratory device that generates heat by passing an electric current through a purpose-built resistive material. This process, known as Joule or resistive heating, converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy, which is then transferred to a workpiece or material through conduction, convection, and radiation to perform processes like annealing, sintering, or heat treatment.
A resistance furnace leverages the simple physical principle of electrical resistance to create a highly controllable, clean, and precise high-temperature environment. Its versatility makes it a foundational tool across scientific research and industrial manufacturing.

The Operating Principle: From Electricity to Heat
The function of a resistance furnace is elegant in its simplicity. It's built around a few key components working in concert to deliver controlled thermal energy.
The Heating Element: The Heart of the Furnace
The central component is the heating element, a material chosen for its high electrical resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. When electric current is forced through this element, its resistance causes it to heat up significantly.
Common materials for heating elements dictate the furnace's performance and temperature range. These include nichrome resistance wire for lower temperatures (up to ~1200°C), silicon carbide (SiC) rods for mid-range temperatures, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or graphite for very high-temperature applications (approaching and exceeding 1550°C).
Heat Transfer: Moving Energy to the Workpiece
Once generated, the heat must be transferred to the material being processed. This occurs through three primary mechanisms:
- Radiation: The hot element emits thermal radiation that is absorbed by the workpiece. This is the dominant mode of heat transfer at high temperatures.
- Conduction: Heat travels directly from the element to any components it touches, and through the furnace's internal atmosphere to the workpiece.
- Convection: In furnaces with a gaseous atmosphere (like air or nitrogen), circulating gas currents carry heat from the element to the workpiece.
The Control System: Ensuring Precision
A sophisticated temperature control system is essential. It uses sensors like thermocouples to monitor the internal temperature and adjusts the electrical power supplied to the heating elements, ensuring the process stays within precise, predefined parameters.
Key Classifications of Resistance Furnaces
Resistance furnaces are not a monolithic category. They are classified based on their heating method, physical structure, and the environment they create.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The most fundamental distinction is how the heat is generated relative to the workpiece.
- Indirect Heating: This is the most common type. Current is passed through a dedicated heating element, which then heats the workpiece.
- Direct Heating: In this less common configuration, the electric current is passed directly through the workpiece itself, causing it to heat up from within. This method is only suitable for materials that are electrically conductive.
Common Furnace Architectures
The physical shape of the furnace is designed around its intended application.
- Box Furnace: Resembling a large oven, this design offers a spacious chamber for processing batches of materials or irregularly shaped parts. It is a versatile workhorse in many labs and workshops.
- Tube Furnace: This design features a cylindrical tube (often made of ceramic or quartz) surrounded by heating elements. It is ideal for processing small samples, growing crystals, or for experiments requiring a tightly controlled atmosphere or vacuum.
Environmental Control
Many material processes are sensitive to oxygen or other reactive gases. Resistance furnaces can be designed to manage this.
- Air Atmosphere: The simplest design, operating in ambient air.
- Controlled Atmosphere: The furnace chamber can be sealed and purged with inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation.
- Vacuum: The chamber can be evacuated to create a vacuum, which is critical for certain high-purity metal and ceramic processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Like any technology, resistance furnaces have distinct advantages and limitations that define their ideal use cases.
The Primary Advantage: Control and Cleanliness
Because they are powered by electricity, resistance furnaces offer exceptionally precise temperature control. They produce no combustion byproducts, making them a very clean source of heat that prevents contamination of the workpiece. This combination is critical for sensitive electronics, technical ceramics, and metallurgical research.
The Main Limitation: Operating Cost and Temperature
The primary drawback is the cost of electricity, which can make them more expensive to operate for large-scale industrial processes compared to fuel-fired furnaces. Furthermore, while capable of high temperatures, they have material-dependent ceilings; other technologies like induction or arc furnaces are required for melting steel and other ultra-high-temperature tasks.
A Spectrum of Applications
The versatility of resistance furnaces makes them indispensable across numerous fields, including:
- Materials Science: Sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals (annealing, hardening), and growing crystals.
- Manufacturing: Firing coatings, drying powders, and curing composites.
- Laboratories: Ashing samples, conducting high-temperature experiments, and calibrating sensors.
- Industries: Electronics, glass, chemical, machinery, and building materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the material, process, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or batch heat treatment: A box resistance furnace offers the most versatility for various sample sizes and processes, typically operating below 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is experiments in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum: A tube furnace provides the ideal contained environment for processing sensitive materials or for continuous-flow applications.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or material synthesis (>1500°C): A specialized furnace with advanced silicon molybdenum or graphite elements is required for processing technical ceramics and other refractory materials.
Ultimately, the resistance furnace is a foundational technology in modern science and industry, enabling innovation through the precise and clean application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (most common) or Direct (for conductive materials) |
| Temperature Range | Up to ~1200°C (nichrome) to >1550°C (graphite/MoSi2) |
| Key Components | Heating Element, Control System, Insulated Chamber |
| Primary Applications | Annealing, Sintering, Heat Treatment, Lab Experiments |
| Main Advantage | Exceptional Temperature Control & Clean Operation (No Combustion Byproducts) |
Ready to Enhance Your Lab's Capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a full range of resistance heating furnaces tailored for materials science, research, and industrial manufacturing. Whether you need a versatile box furnace for batch processing or a precise tube furnace for controlled atmosphere work, our solutions deliver the reliability and accuracy your experiments demand.
Let us help you find the perfect furnace for your specific application. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















