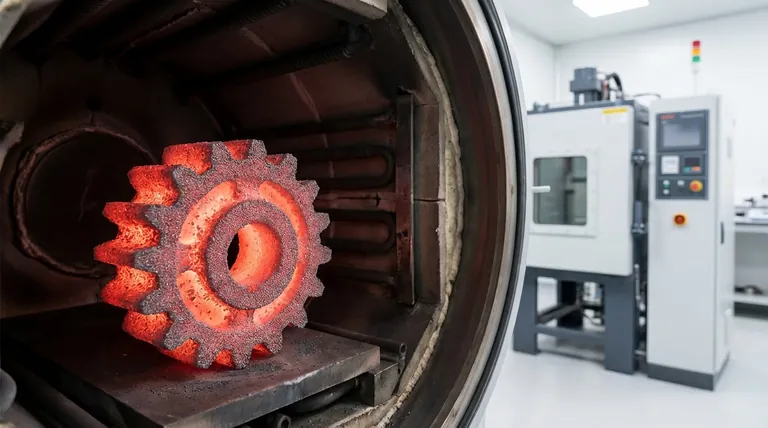
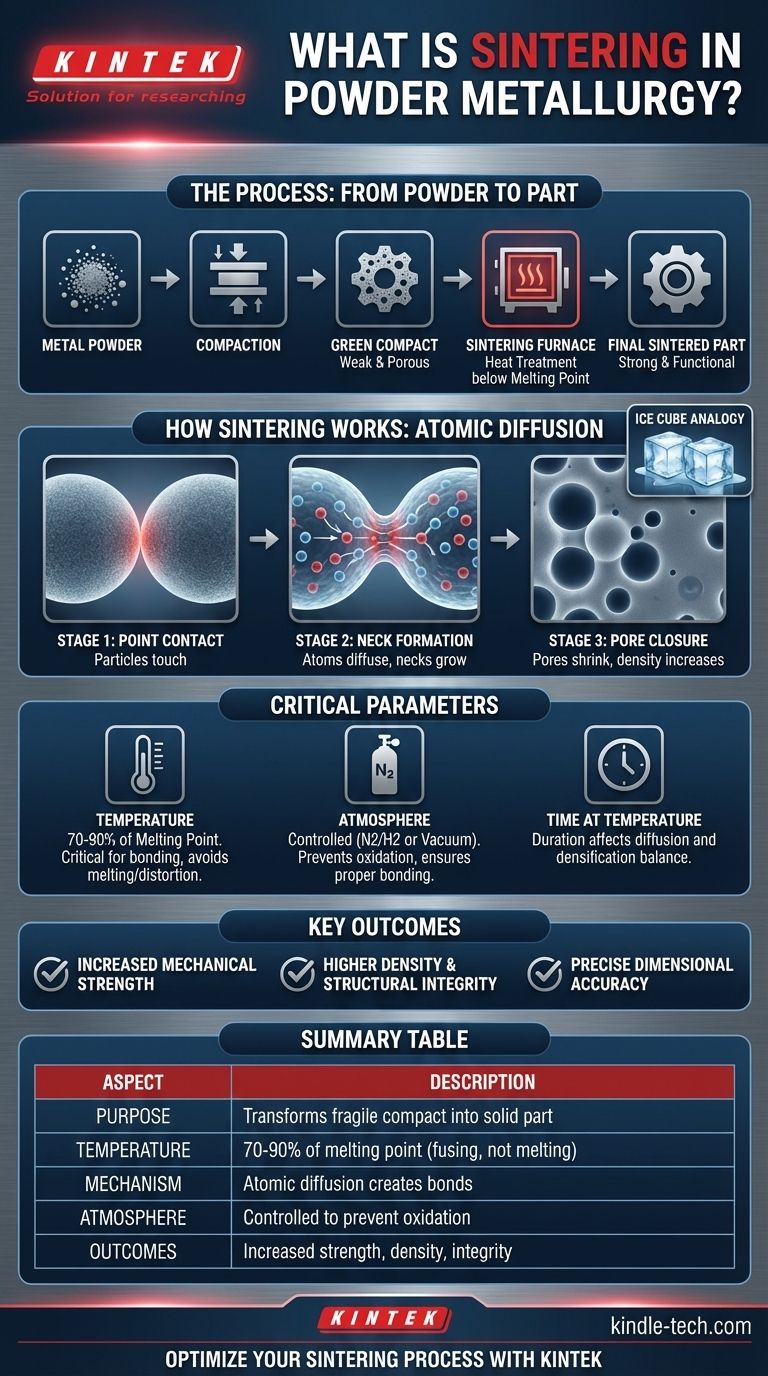
In powder metallurgy, sintering is a critical heat treatment process. It involves heating a compacted metal powder part, known as a "green compact," to a high temperature just below its melting point. This thermal energy causes the individual metal particles to fuse, creating strong bonds that give the component its final strength, density, and structural integrity.
The core purpose of sintering is to transform a fragile, pressed powder shape into a solid, functional metal part. It achieves this by bonding the metal particles together through atomic diffusion, fundamentally converting a collection of grains into a unified engineering material without ever melting it.

The Role of Sintering in the Powder Metallurgy Process
Powder metallurgy is a multi-step manufacturing method. Sintering is the crucial step that provides the final properties to the component after it has been initially shaped.
From Initial Shape to "Green Compact"
The process begins by pressing metal powders into a desired shape using a die. The resulting part is called a "green compact."
This green compact holds its shape but possesses very low mechanical strength. It is often brittle and porous, making it unsuitable for any functional application in this state.
The Sintering Transformation
The green compact is then placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace for sintering. The high temperature, typically 70-90% of the metal's melting point, energizes the atoms.
This energy drives a process called atomic diffusion, where atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This migration creates metallurgical bonds, or "necks," at the points where the particles touch.
The Goal: Fusing, Not Melting
It is critical that the temperature remains below the material's melting point. Melting would cause the part to lose its precise shape and dimensional accuracy.
Sintering achieves the strength of a solid part while preserving the net-shape or near-net-shape geometry created during the compaction phase.
How Sintering Fundamentally Works
At a microscopic level, sintering is a process of reducing surface energy by bonding particles and minimizing empty space, or porosity.
The Ice Cube Analogy
An excellent way to visualize sintering is to think of ice cubes in a glass. Even at a temperature below melting (0°C or 32°F), ice cubes left in contact with each other will slowly fuse together at their contact points.
Sintering functions on a similar principle, but the process is accelerated dramatically by the high temperatures used for metal powders.
Reducing Porosity and Increasing Density
As the particles bond and the "necks" between them grow, the empty spaces (pores) within the compact begin to shrink and become more rounded.
This reduction in porosity leads to an increase in the part's overall density and strength. A properly sintered part is a solid, coherent mass with significantly improved mechanical properties compared to its green state.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
The success of the sintering process depends on precise control over several key variables. Failure to manage these can lead to defective parts.
The Importance of Temperature Control
The sintering temperature is the most critical parameter. Too low a temperature will result in incomplete bonding and poor strength. Too high a temperature risks melting, distortion, and loss of dimensional tolerance.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Sintering is almost always performed in a controlled atmosphere, such as a nitrogen/hydrogen mix or a vacuum. This is essential to prevent oxidation of the metal powders at high temperatures, which would inhibit proper bonding and degrade the material's properties.
Time at Temperature
The duration the part is held at the peak sintering temperature also influences the final outcome. A longer time allows for more complete diffusion and densification, but it must be balanced against production efficiency and the risk of undesirable grain growth.
The Key Outcomes of Successful Sintering
Applying this knowledge helps in understanding why sintering is essential for achieving specific manufacturing goals.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Sintering is the non-negotiable step that creates the strong, inter-particle atomic bonds necessary for load-bearing applications.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: The sintering cycle must be precisely controlled to manage part shrinkage and achieve the final, desired density without distortion.
- If your primary focus is material properties: Sintering is what transforms a simple powder compact into a finished component with the required hardness, durability, and structural integrity.
Ultimately, sintering is the fundamental process that gives powder metallurgy components their final form and function.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Transforms fragile "green compact" into solid, functional metal part |
| Temperature | 70-90% of metal's melting point (fusing without melting) |
| Mechanism | Atomic diffusion creates bonds between particles |
| Atmosphere | Controlled (nitrogen/hydrogen or vacuum) to prevent oxidation |
| Key Outcomes | Increased strength, density, and structural integrity |
Ready to optimize your powder metallurgy process with precision sintering equipment? KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces and consumables that deliver the exact temperature control and atmosphere management required for successful sintering. Whether you're developing new metal components or improving existing manufacturing processes, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory drying oven contribute to TiO2 synthesis? Unlock Advanced Material Stability & Chemical Bonding
- What is the function of a laboratory magnetic stirrer in photocatalytic degradation? Achieve Kinetic Accuracy
- Why graphite Cannot conduct electricity? Unlocking the Secret of its High Electrical Conductivity
- Is it possible to make fuel from plastic? Turn Waste into Valuable Energy
- What are 3 types of biomass? A Guide to Wood, Waste, and Biofuels for Energy
- What is the purpose of using nitrogen cylinders with booster pumps? Achieve Precise Subsurface Corrosion Simulation
- How does brazing work? Create Strong, Permanent Metal Joints with Metallurgical Bonding
- What is the process of slow heating and low temperature pyrolysis produces? Maximizing Biochar for Carbon Sequestration



















