In essence, sintering metallurgy is a manufacturing process that creates solid, high-strength metal components from fine powders without ever melting the material. It uses a precise combination of pressure and heat to fuse individual metal particles together, forming parts like gears, bearings, and structural automotive components with excellent dimensional accuracy.
Sintering’s core principle is not melting and casting, but solid-state fusion. By heating compacted powder to a temperature just below its melting point, atoms migrate between particles, creating strong metallic bonds and transforming a fragile powder shape into a dense, functional part.
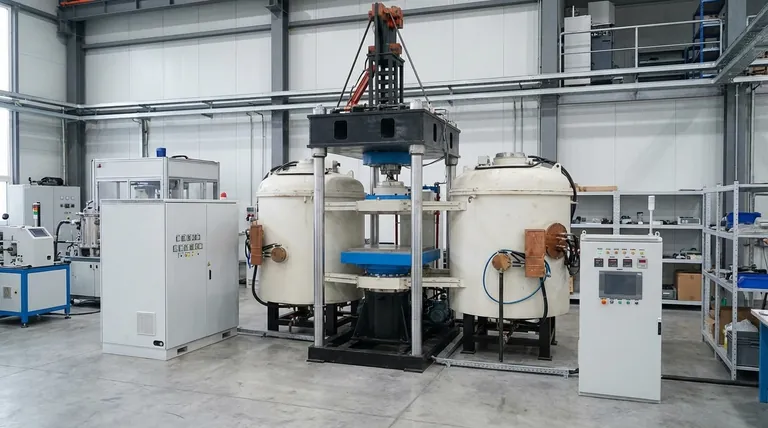

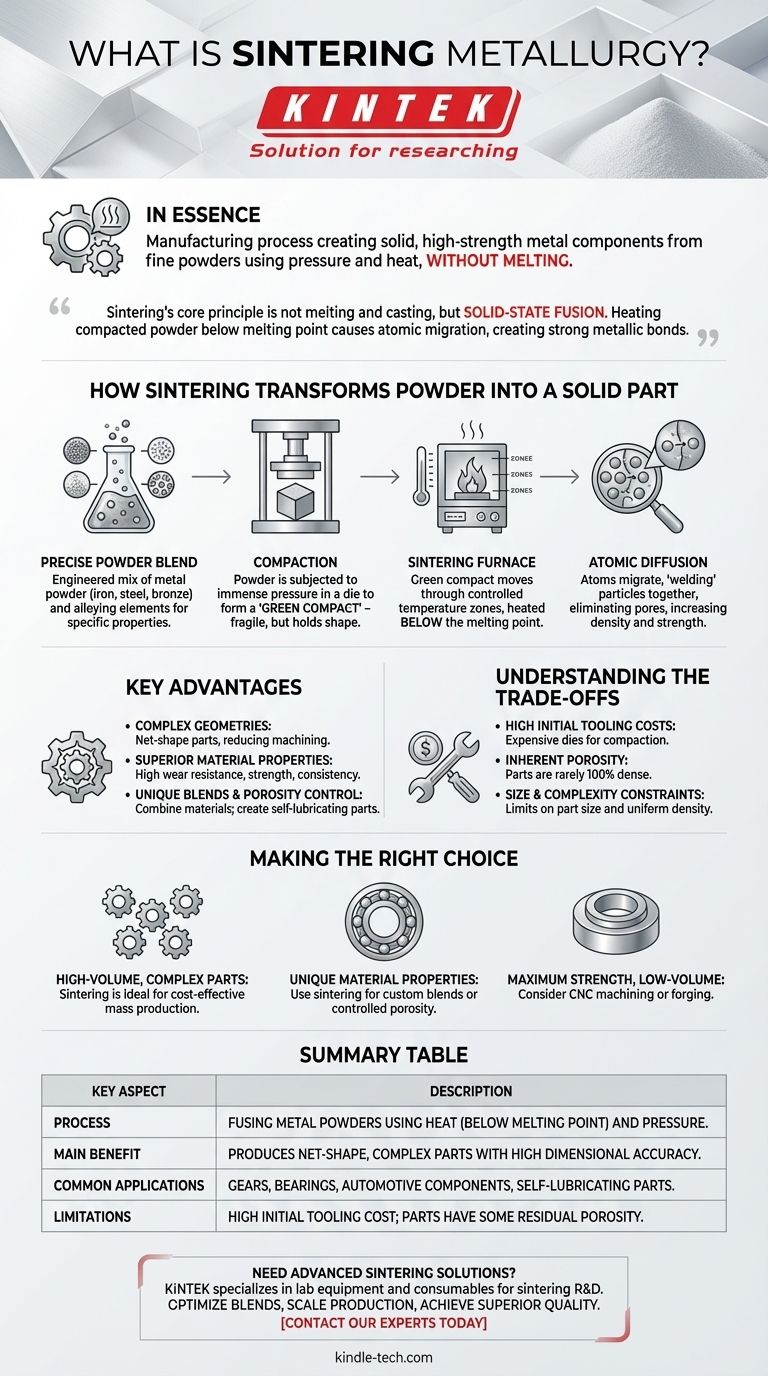
How Sintering Transforms Powder into a Solid Part
The sintering process is a key step within the broader field of powder metallurgy (PM). It is a highly controlled, multi-stage method that reliably turns loose powder into a robust, engineered component.
The Starting Point: A Precise Powder Blend
The process begins with a carefully engineered metal powder. This is often not just one type of metal, but a specific blend of iron, steel, bronze, or aluminum mixed with other alloying elements to achieve desired final properties like hardness or corrosion resistance.
Step 1: Compaction
The metal powder blend is poured into a hardened steel die shaped like the final part. It is then subjected to immense pressure, compacting the loose powder into a cohesive object. This resulting part is known as a "green compact." It is fragile and has low strength but holds its shape accurately.
Step 2: The Sintering Furnace
The green compact is then carefully transported through a long furnace with multiple, precisely controlled temperature zones. The part is heated to a specific sintering temperature, which is always below the melting point of the primary metal.
The Science of Bonding: Atomic Diffusion
At this elevated temperature, the atoms at the surface of the individual powder particles become highly active. They begin to migrate across the boundaries from one particle to another, creating strong, permanent metallic bonds. This process of atomic diffusion effectively "welds" the particles together, eliminating the pores between them and significantly increasing the part's density, strength, and hardness.
Key Advantages of Sintering Metallurgy
Sintering is chosen over other manufacturing methods for several distinct advantages, particularly in high-volume production environments.
Creating Complex Geometries
Sintering excels at producing net-shape or near-net-shape parts. This means the component comes out of the process very close to its final dimensions, drastically reducing or eliminating the need for expensive and time-consuming secondary machining.
Superior Material Properties
The process allows for the creation of parts with excellent wear resistance, high strength, and consistent dimensional accuracy across thousands or even millions of units. This reliability is critical for applications like automotive transmissions and power tools.
Unique Material Blends and Porosity Control
Because the metals are not melted, you can combine materials that would not normally alloy together. Furthermore, the process allows for deliberate control over the final porosity. This is used to create self-lubricating bearings (where pores hold oil) or specialized filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging the limitations of sintering.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies required for the compaction stage are complex and made from extremely hard, wear-resistant steel. This represents a significant upfront investment, making sintering uneconomical for prototypes or very small production runs.
Inherent Porosity
While porosity can be a feature, it can also be a limitation. A sintered part is rarely 100% dense. This residual porosity can make sintered components less suitable than forged or machined parts for applications requiring the absolute maximum tensile strength or fatigue resistance.
Size and Complexity Constraints
There are practical limits to the size of parts that can be produced. Very large components are difficult to compact with uniform density. Likewise, certain complex internal features or undercuts can be impossible to form in the compaction die.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if sintering is the correct approach depends entirely on your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering is an ideal choice for creating thousands of identical, near-net-shape components like gears or sensor housings cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is unique material properties: Use sintering to engineer custom material blends or controlled-porosity parts, such as self-lubricating bushings, that are difficult or impossible to make with other methods.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a low-volume part: A different method like CNC machining from a solid billet or forging will likely be a more suitable and cost-effective path.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage sintering to manufacture robust and intricate metal parts with remarkable efficiency and material control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fusing metal powders using heat (below melting point) and pressure. |
| Main Benefit | Produces net-shape, complex parts with high dimensional accuracy. |
| Common Applications | Gears, bearings, automotive components, self-lubricating parts. |
| Limitations | High initial tooling cost; parts have some residual porosity. |
Need to produce complex, high-strength metal components efficiently? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables essential for sintering and powder metallurgy research and development. Whether you're optimizing material blends or scaling up production, our solutions help you achieve superior part quality and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- Which factor causes the failure of furnace lining? The primary cause is thermal stress and spalling.
- What role does a high-performance vacuum furnace play in the reduction of Magnéli phase titanium oxide?
- What role does the crystallizer perform in magnesium recovery? Master Pure Sublimation and Yield
- What is the use of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Clean, Bright Finish
- What is the role of a laboratory arc melting furnace in Fe-Cu-O melt decopperization? Boost Your Research Precision
- How does a vacuum furnace work? The Key to Clean, High-Purity Heat Treatment
- Why are metal envelopes or containers required for HIP? Achieve 100% Density in Alloy Powder Processing
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep



















