Sintering is a fundamental manufacturing process used to transform powdered materials into a solid, coherent mass using heat and pressure, without melting the material itself. It is widely applied in producing high-strength metal parts, creating traditional ceramics like pottery and porcelain, and enabling the fabrication of complex, custom shapes through 3D printing.
The core value of sintering lies in its ability to create strong, dense objects from powders, especially for materials with extremely high melting points. This solves manufacturing challenges that traditional melting and casting methods cannot address efficiently.

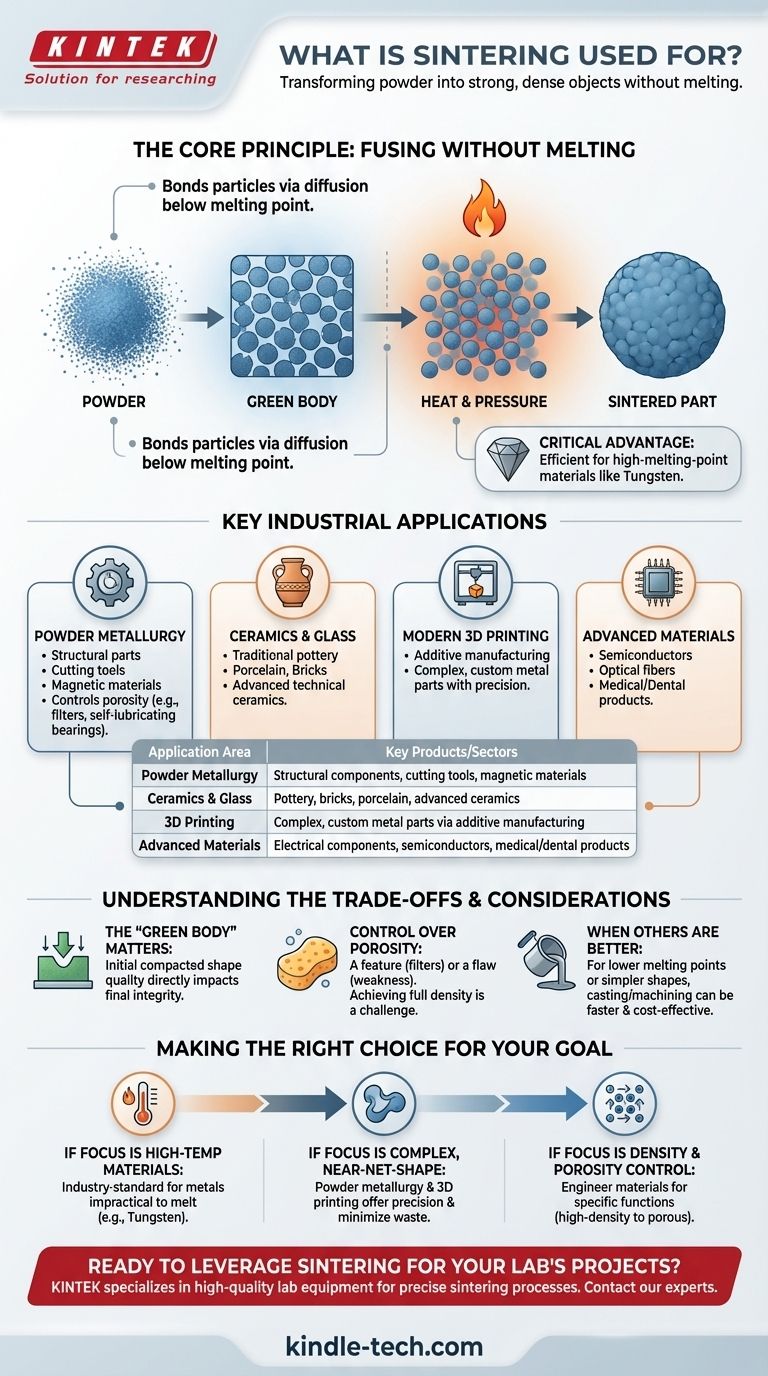
The Core Principle: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal treatment that bonds particles together, dramatically increasing the strength and integrity of the material. This core mechanism provides unique advantages in manufacturing.
How Sintering Works
The process involves heating a compacted powder—often called a "green body"—to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, the atoms in the particles diffuse across their boundaries, fusing the individual particles into a single, solid piece.
A Critical Advantage for Difficult Materials
This ability to fuse material without melting is essential for working with metals that have extremely high melting points, like tungsten. Melting such materials would require enormous energy and specialized equipment, but sintering achieves a similar result much more efficiently.
Key Industrial Applications
From ancient pottery to modern semiconductors, the applications of sintering are vast and varied. It is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and advanced manufacturing.
Powder Metallurgy
This is one of the most common uses of sintering. Metal powders are compressed and sintered to form a huge range of industrial parts, including structural steel components, cutting tools, and magnetic materials.
This technique also allows for precise control over porosity, enabling the creation of specialized products like porous metal filters and self-lubricating bearings that hold oil in their pores.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
Historically, sintering has been used for thousands of years to produce clay pottery, bricks, and porcelain. The firing process in a kiln is a form of sintering that gives these objects their strength and durability. Modern applications extend to advanced ceramics and glass production.
Modern 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Sintering is a key technology in metal 3D printing. A high-power laser sinters powdered metal layer by layer, allowing for the creation of intricate and custom metal forms with exceptional precision and consistency.
Advanced Materials and Components
The process is also crucial for producing highly specialized products. These include electrical components, semiconductors, optical fibers, and various dental and medical products where material purity and precise form are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is a nuanced process. The final properties of a sintered part are highly dependent on the initial steps and process control.
The Importance of the "Green Body"
The initial compacted shape, or "green body," must be formed correctly before sintering. Methods like isostatic pressing, slipcasting, or 3D printing are used to create this initial form, and its quality directly impacts the final product's integrity.
Control Over Porosity
Porosity can be both a feature and a flaw. While essential for products like filters, any unintended residual porosity in a structural part can decrease its strength and durability. Achieving full density is often a primary goal and a key challenge.
When Other Methods Are Better
Sintering is not a universal solution. For materials with lower melting points or for producing simpler shapes, traditional manufacturing methods like casting or machining can be faster and more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering as a manufacturing process depends entirely on the material you are using and the properties you need in the final product.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is the industry-standard method for metals like tungsten that are impractical to melt and cast.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, near-net-shape parts: Powder metallurgy and 3D printing via sintering offer precise control and minimize material waste.
- If your primary focus is controlling material density and porosity: Sintering provides a unique ability to engineer materials for specific functions, from high-density cutting tools to porous, self-lubricating bearings.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and versatile pathway to transform powdered materials into robust, functional components for a vast range of applications.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Products/Sectors |
|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Structural components, cutting tools, magnetic materials |
| Ceramics & Glass | Pottery, bricks, porcelain, advanced ceramics |
| 3D Printing | Complex, custom metal parts via additive manufacturing |
| Advanced Materials | Electrical components, semiconductors, medical/dental products |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's projects?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are in R&D or production, our solutions help you achieve the material density, strength, and complex shapes you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering applications and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















