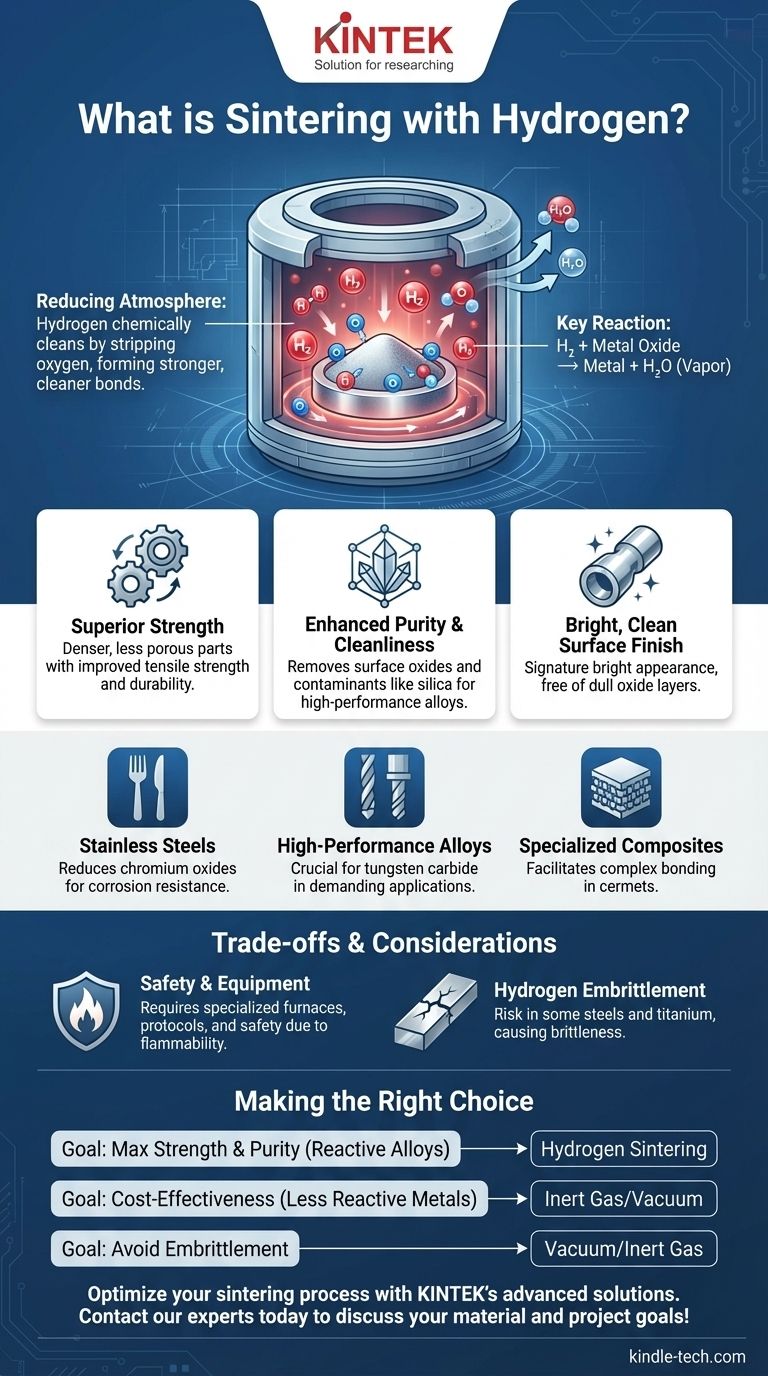
In short, sintering with hydrogen is a high-temperature manufacturing process that uses a hydrogen-rich atmosphere to bond powdered materials together. Unlike sintering in air or with inert gases, hydrogen actively functions as a chemical cleaning agent, reducing surface oxides and removing impurities from the materials. This results in parts with superior mechanical strength, higher purity, and a characteristically bright, clean surface finish.
The core purpose of using hydrogen in sintering is to create a powerful reducing atmosphere. This environment chemically strips oxygen from the metal particles, allowing for the formation of stronger, cleaner metallic bonds than are possible in less reactive atmospheres.

How Hydrogen Transforms the Sintering Environment
To understand the value of hydrogen sintering, you must first understand the role of the furnace atmosphere. The gases surrounding the parts during heating dictate the chemical reactions that will occur on the material's surface.
Creating a Reducing Atmosphere
A "reducing" atmosphere is one that actively removes oxygen. Hydrogen (H₂) is highly reactive, especially at high temperatures, and it aggressively seeks out oxygen atoms to bond with.
This is the direct opposite of an "oxidizing" atmosphere (like open air), which would add an oxide layer to the hot metal, preventing the particles from bonding effectively.
The Chemical Reaction of Oxide Reduction
Nearly all metal powders have a thin layer of metal oxide on their surface. During hydrogen sintering, the hydrogen gas reacts with these oxides (e.g., iron oxide, chromium oxide) to form water vapor (H₂O).
This water vapor is then safely vented from the furnace, effectively scrubbing the surfaces of the individual powder particles clean on a microscopic level.
Preventing Further Oxidation
By flooding the furnace chamber with high-purity hydrogen, virtually all ambient oxygen is displaced. This ensures that no new oxides can form on the metal surfaces as they are heated, preserving the material's integrity throughout the entire process.
The Tangible Benefits of Hydrogen Sintering
This chemical cleaning process translates directly into measurable improvements in the final product. The primary benefits are directly linked to the removal of oxide barriers between the powder particles.
Superior Mechanical Strength
By eliminating the oxide layers, the metal particles can form direct, robust metallic bonds with one another. This results in a denser, less porous final part with significantly improved tensile strength, hardness, and overall durability.
Enhanced Purity and Cleanliness
Beyond just reducing oxides, the reactive hydrogen atmosphere can also help strip away other contaminants, such as residual silica. This leads to a final alloy of higher purity, which is critical for high-performance applications.
A Bright, Clean Surface Finish
The signature "bright" finish of hydrogen-sintered parts is a direct visual confirmation of the process's effectiveness. This brightness is the appearance of the pure metal surface, completely free of the dulling oxide layers that would form in other atmospheres.
Common Materials and Applications
Hydrogen sintering is essential for materials where performance and purity are non-negotiable.
Stainless Steels
This is a very common application. Hydrogen is crucial for reducing the tough chromium oxides on the surface of stainless steel powders, which is essential for achieving proper bonding and maintaining the material's corrosion resistance.
High-Performance Alloys
Materials like tungsten carbide and other advanced alloys are used in demanding applications like cutting tools and wear-resistant components. These materials require the high-purity, oxygen-free environment that only hydrogen or a high vacuum can provide to reach their maximum performance potential.
Specialized Ceramic-Metal Composites
Certain advanced materials, known as cermets, blend the properties of ceramics and metals. Hydrogen sintering is often used to facilitate the complex bonding required to create these specialized parts with unique physical characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, hydrogen sintering is not the universal solution. A trusted technical advisor must point out the significant operational trade-offs.
Safety and Equipment
Hydrogen gas is highly flammable and requires specialized furnaces, rigorous safety protocols, and advanced monitoring systems to handle safely. This represents a significant investment in both equipment and training.
Operational Cost
High-purity hydrogen gas and the specialized equipment needed to manage it are typically more expensive than alternatives like nitrogen-based atmospheres or vacuum sintering.
Material Compatibility
A critical consideration is hydrogen embrittlement. In certain metals, particularly some steels and titanium alloys, hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the material's structure, causing a severe loss of ductility and making the part brittle. This risk must be carefully evaluated for the specific alloy being processed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal sintering atmosphere is determined entirely by your material, budget, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength, density, and purity for reactive alloys: Hydrogen sintering is often the superior technical choice for materials like stainless steel and tungsten carbide.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for less reactive metals: An inert nitrogen atmosphere or a vacuum furnace can often provide sufficient quality with lower costs and fewer safety complexities.
- If you are working with materials susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement: You must prioritize vacuum or inert gas atmospheres to preserve the material's essential mechanical properties.
Ultimately, choosing the correct furnace atmosphere is a critical decision that directly controls the quality and performance of your final sintered components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature bonding of powdered materials in a hydrogen-rich atmosphere. |
| Primary Benefit | Creates a reducing environment that removes surface oxides and impurities. |
| Key Outcomes | Superior mechanical strength, enhanced purity, bright surface finish. |
| Ideal Materials | Stainless steels, tungsten carbide, high-performance alloys. |
| Main Consideration | Higher operational cost and safety requirements; risk of hydrogen embrittlement in some alloys. |
Need to optimize your sintering process for maximum strength and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions for laboratory and industrial applications. Our expertise in furnace atmospheres, including hydrogen sintering, can help you achieve the superior material properties your high-performance components demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and project goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory vacuum drying oven play in processing nanoparticle powder samples? Protect Sample Integrity
- What are the applications of vacuum deposition? Create High-Performance Coatings for Your Products
- Why are high-temperature testing furnaces over 2000°C needed for SiC cladding? Validate Gen IV Nuclear Safety
- What are the byproducts of plastic pyrolysis? Turning Waste into Valuable Resources
- What is the purpose of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in catalyst post-processing? Preserve Activity & Pore Structure
- How does multi-stage vacuum distillation facilitate the removal of zinc and cadmium from crude magnesium?
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- How does sintering temperature affect hardness? Optimize for Maximum Material Strength



















