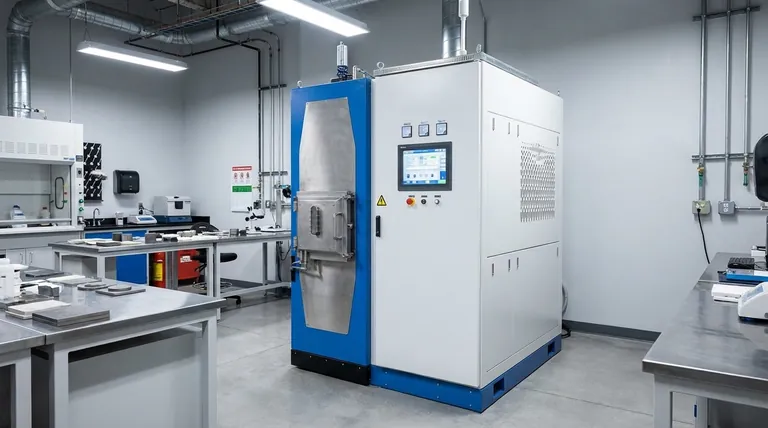
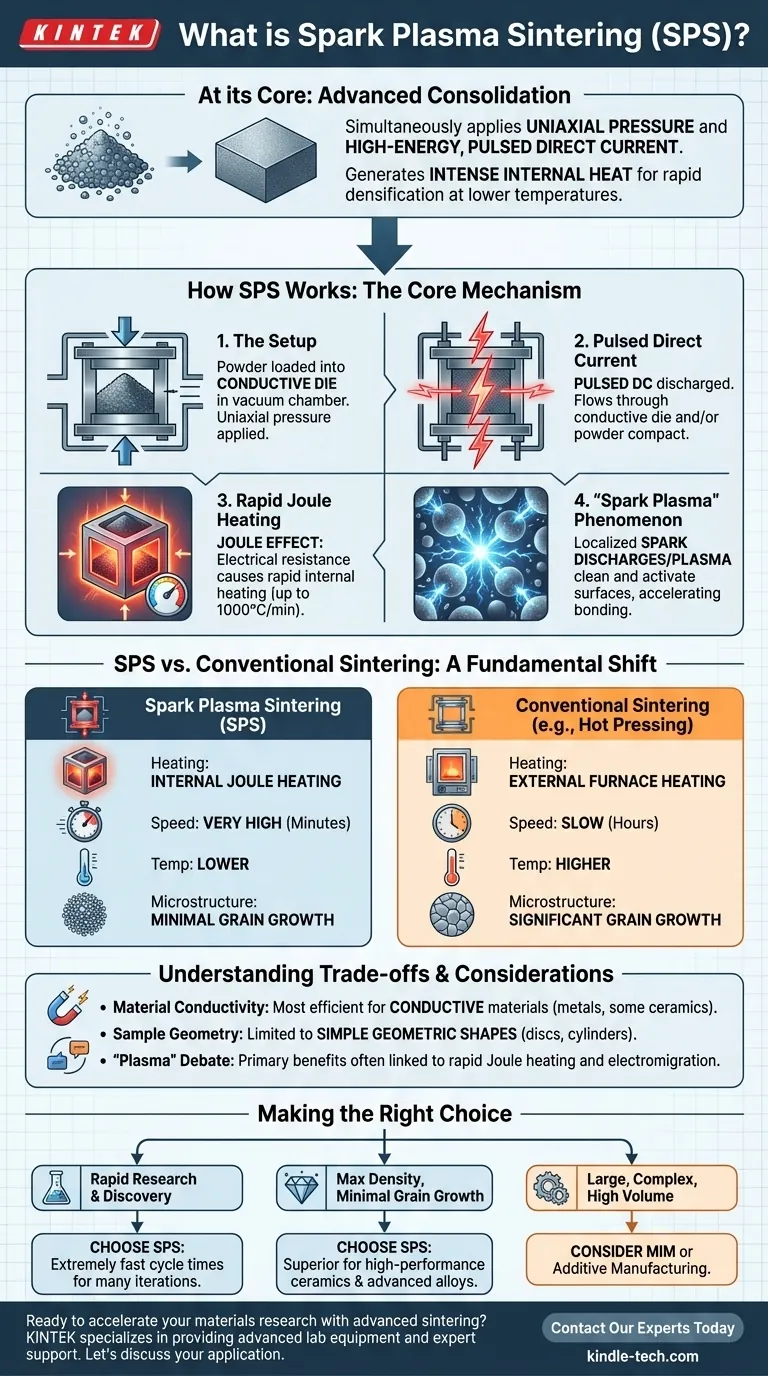
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced sintering technique that consolidates powders into a dense solid by simultaneously applying uniaxial pressure and a high-energy, pulsed direct current. Unlike conventional methods that slowly heat a sample from the outside, SPS passes electricity directly through the sample and its conductive die, generating intense internal heat. This unique combination of pressure and rapid, direct heating allows for densification at lower temperatures and in significantly shorter times, often minutes instead of hours.
The crucial insight is that SPS is not just a faster way to apply heat. It uses an electrical current to directly activate the powder particles, cleaning their surfaces and promoting bonding, which enables densification more efficiently than heat alone ever could.

How Spark Plasma Sintering Works: The Core Mechanism
To understand the power of SPS, we must look at how it combines pressure, current, and heat in a single, rapid process. It is also known as a Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST).
The Setup: Pressure and a Conductive Die
First, the powdered material is loaded into a conductive die, which is typically made of graphite. This entire assembly is placed inside a vacuum chamber and positioned between two electrodes. A mechanical system then applies uniaxial pressure to the powder, pressing it together.
The Key Ingredient: Pulsed Direct Current
Once the chamber is evacuated and pressure is applied, a pulsed direct current (DC) is discharged through the electrodes. This current flows through the conductive graphite die and, if the material itself is conductive, through the powder compact as well.
Rapid Heating via the Joule Effect
The primary heating mechanism is Joule heating. As the electrical current passes through the die and powder, their natural electrical resistance causes them to heat up extremely quickly. This is the same principle that makes a toaster's wires glow.
This direct, internal heating can achieve rates of up to 1000°C per minute, a speed that is impossible with conventional furnaces that rely on slow, external radiation or convection.
The "Spark Plasma" Phenomenon
The name "Spark Plasma Sintering" comes from a theorized effect occurring in the microscopic voids between powder particles. The intense electrical field is believed to generate localized spark discharges or plasma.
This momentary plasma is thought to clean impurities from the particle surfaces and activate them, dramatically accelerating how they bond and fuse together.
SPS vs. Conventional Sintering: A Clear Distinction
SPS is not an incremental improvement; it represents a fundamental shift from traditional sintering methods like hot pressing.
Heating Method and Speed
Conventional hot pressing places a sample in a furnace and heats it externally, a slow process that relies on thermal radiation. SPS uses internal Joule heating, making it orders of magnitude faster and more energy-efficient.
Temperature and Time
Because of the electrical activation and rapid heating, SPS can achieve full densification at temperatures several hundred degrees lower than conventional methods. The entire cycle is often completed in 5 to 20 minutes, compared to many hours for furnace-based sintering.
Impact on Microstructure
The extremely short duration at high temperature is the most significant advantage of SPS. It prevents the growth of coarse grains within the material. This allows for the production of dense, fine-grained materials with superior strength and performance characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material Conductivity Matters
The process is most efficient for electrically conductive or semiconductive materials (metals, some ceramics). For fully insulating powders, all heating comes from the graphite die, making the process function more like a very rapid hot press, where the "spark plasma" effect is negligible.
Sample Geometry is Limited
Due to the use of a rigid die and uniaxial pressure, SPS is generally limited to producing simple geometric shapes, such as discs, cylinders, and rectangular blocks. Complex, three-dimensional parts are not feasible.
The Debate on "Plasma"
Within the materials science community, there is ongoing debate about the extent to which a true plasma is generated. Many experts argue the primary benefits of SPS stem from the rapid Joule heating and electromigration effects, rather than from plasma itself. This distinction does not diminish the technique's effectiveness but is an important point of scientific clarity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if SPS is the correct tool depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid research and material discovery: SPS is an unparalleled tool due to its extremely fast cycle times, allowing for dozens of experimental iterations in a single day.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density with minimal grain growth: The combination of lower temperatures and short hold times makes SPS superior for producing fine-grained, high-performance ceramics and advanced alloys.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing large, complex-shaped parts in high volume: SPS is likely unsuitable; you should consider methods like metal injection molding (MIM) or additive manufacturing.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering empowers the creation of next-generation materials that were previously impossible to fabricate with conventional technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering (e.g., Hot Pressing) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal Joule heating via pulsed DC current | External furnace heating (radiation/convection) |
| Heating Rate | Very high (up to 1000°C/min) | Slow |
| Process Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Typical Temperature | Lower | Higher |
| Grain Growth | Minimal (fine-grained microstructure) | Significant (coarse grains) |
| Ideal For | Conductive/semiconductive powders; R&D; high-performance materials | A wider range of materials; complex shapes |
Ready to accelerate your materials research with advanced sintering?
If your goal is to rapidly develop dense, fine-grained materials with superior properties, Spark Plasma Sintering could be the breakthrough technology for your lab. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to push the boundaries of material science.
Let's discuss how SPS can benefit your specific application. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control


















