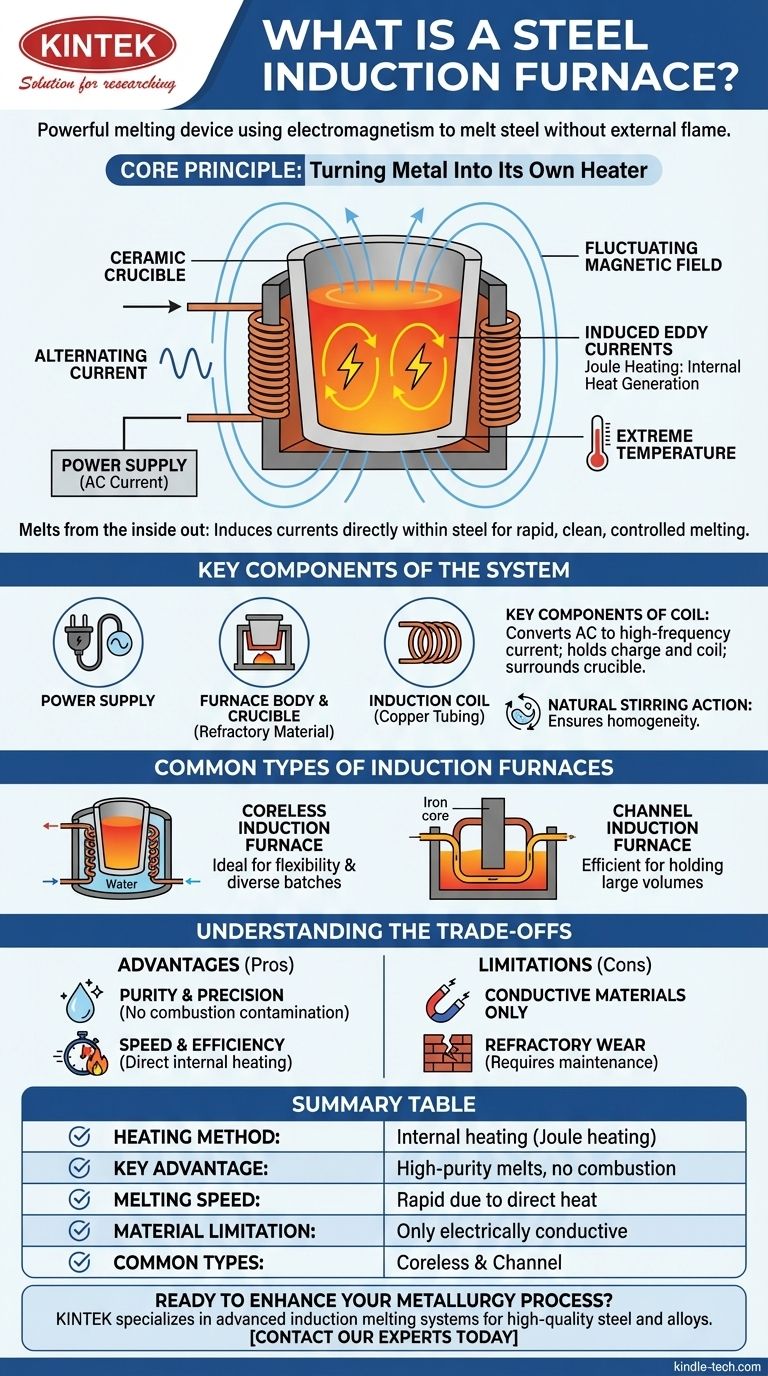
In essence, a steel induction furnace is a powerful melting device that uses the principles of electromagnetism to melt steel and other metals without any external flame or fuel. Instead of heating the outside of a container, it passes a strong alternating current through a copper coil, which creates a fluctuating magnetic field that turns the metal charge itself into the source of heat.
The core takeaway is that induction furnaces melt metal from the inside out. By inducing powerful electrical currents directly within the steel, the furnace achieves rapid, clean, and highly controlled melting, which is essential for producing high-quality alloys with precise compositions.
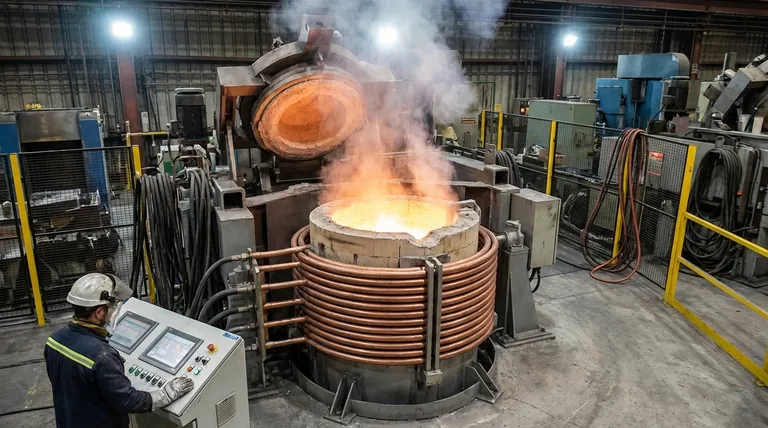

The Core Principle: Turning Metal Into Its Own Heater
An induction furnace operates on a clever application of physics. It doesn't burn fuel; it uses energy to make the metal heat itself.
The Induction Coil
The process begins with a powerful induction coil, typically made of hollow copper tubing. A high-power, variable-frequency alternating current is passed through this coil, which surrounds a non-conductive container called a crucible.
The Electromagnetic Field
This alternating current flowing through the coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around the coil, directly where the solid metal charge (like scrap steel) is placed.
Induced Eddy Currents
The magnetic field passes through the electrically conductive steel, inducing circular electrical currents within the metal itself. These induced currents are known as eddy currents.
Resistance and Heat
The steel has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates friction on an atomic level, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This internal heat rapidly raises the metal's temperature to its melting point and beyond.
Key Components of the System
An induction furnace is more than just a coil. It's an integrated system where each part plays a critical role.
The Power Supply
This is the heart of the furnace. It takes standard three-phase electrical power and converts it into the specific high-amperage, variable-frequency current required to drive the induction coil effectively.
The Furnace Body and Crucible
The furnace structure holds the coil and the crucible. The crucible is a vessel made from highly durable refractory materials that can withstand the extreme temperatures of molten steel.
Natural Stirring Action
A key benefit of the process is that the electromagnetic forces that induce the eddy currents also cause a vigorous stirring action within the molten metal. This ensures a consistent temperature and a homogenous mix of alloying elements.
Common Types of Induction Furnaces
While the principle remains the same, the design can vary based on the application.
Coreless Induction Furnaces
This is the most common design. The crucible containing the charge is placed directly inside the water-cooled coil. It is valued for its flexibility and is ideal for melting a wide range of alloys in various batch sizes.
Channel Induction Furnaces
This type functions more like a transformer. It uses an iron core with a primary coil. A loop of molten metal forms a secondary coil, where the heat is generated in a "channel" and circulates into the main bath. These are extremely efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal for long periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
No technology is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the pros and cons is key to its proper application.
Advantage: Purity and Precision
Because there is no combustion of fuel, there are no byproducts like gas or soot to contaminate the metal. This makes induction furnaces ideal for producing high-purity steels and specialty alloys with exact chemical compositions.
Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated directly within the charge material, not transferred from an external source. This results in very high melting rates and greater energy efficiency compared to many traditional furnace types.
Limitation: Conductive Materials Only
The fundamental principle relies on inducing current in the charge. Therefore, induction furnaces can only be used to melt electrically conductive materials.
Limitation: Refractory Wear
The combination of extreme temperatures and the constant stirring action of the molten metal can cause significant wear and tear on the refractory lining of the crucible, which requires regular maintenance and replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, specialized steel alloys: The induction furnace offers unparalleled control over composition and eliminates contamination from fuel sources.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting cycles and operational flexibility: A coreless induction furnace is ideal for its quick startup and ability to efficiently handle diverse batch sizes.
- If your primary focus is maintaining large volumes of molten metal efficiently: A channel induction furnace is superior due to its high power efficiency, making it perfect for holding and casting operations.
Ultimately, the steel induction furnace is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy because it provides a clean, fast, and precise method for melting metal from the inside out.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal heating via induced eddy currents (Joule heating). |
| Key Advantage | High-purity melts, no combustion contamination. |
| Melting Speed | Rapid melting due to direct internal heat generation. |
| Material Limitation | Can only melt electrically conductive materials. |
| Common Types | Coreless (flexible batches) and Channel (efficient holding). |
Ready to enhance your metallurgy process with precise, high-purity melting?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction melting systems perfect for producing high-quality steel and specialty alloys. Our solutions deliver the speed, purity, and control your R&D or production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an induction furnace can optimize your operations and achieve your specific metallurgical goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















