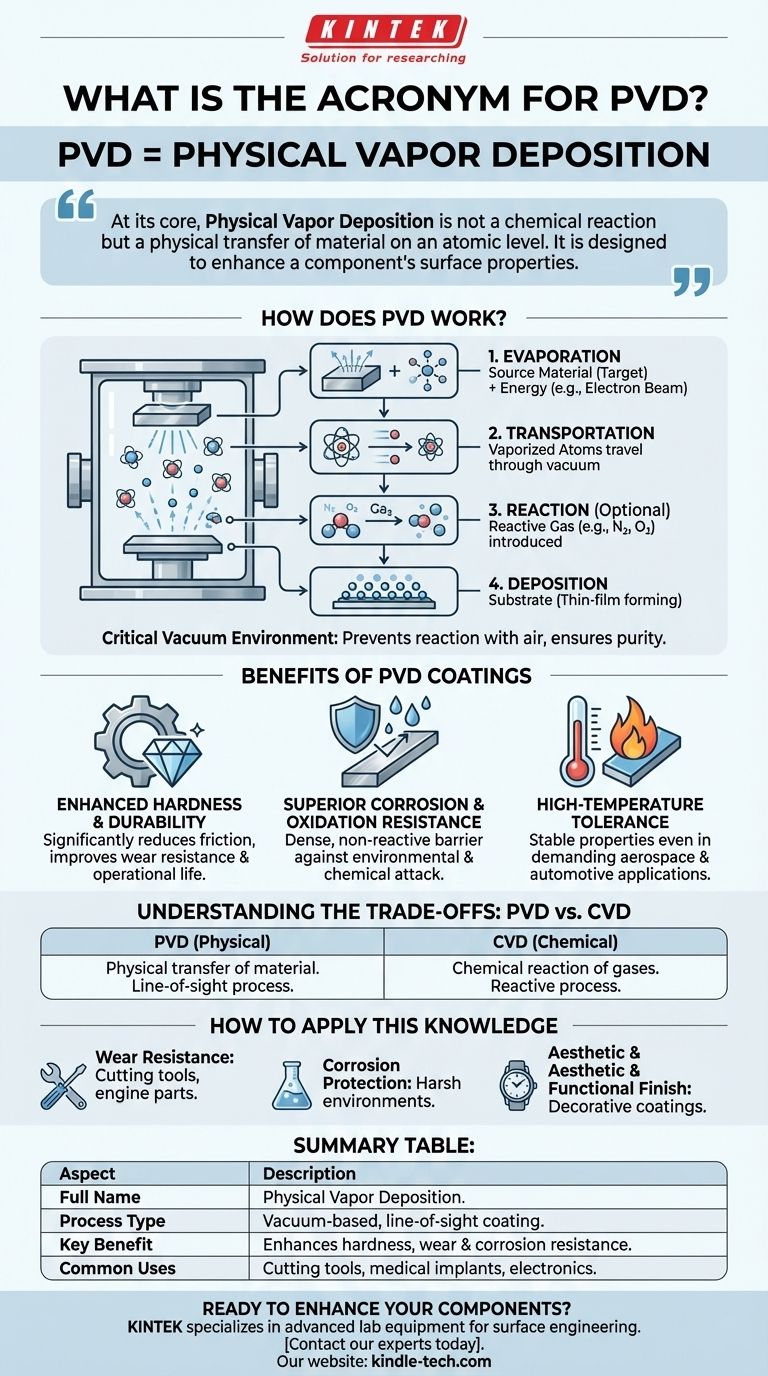
The acronym PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. It is a family of vacuum-based coating processes where a solid material is vaporized, transported through the vacuum, and then deposited onto a substrate as a high-performance, thin-film coating.
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition is not a chemical reaction but a physical transfer of material on an atomic level. It is designed to enhance a component's surface properties—like hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance—without altering the underlying material itself.
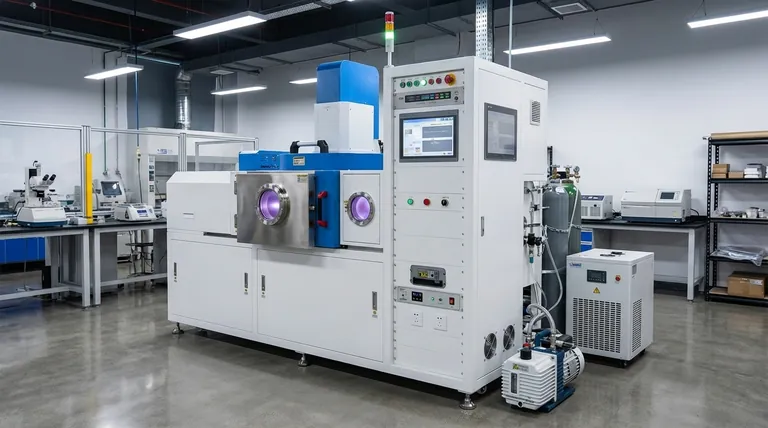

How Does Physical Vapor Deposition Work?
PVD is fundamentally a line-of-sight process that takes place within a controlled vacuum chamber. This environment is critical to ensuring the purity and quality of the final coating.
The Critical Vacuum Environment
The entire process is conducted under a vacuum to prevent the vaporized coating material from reacting with or being scattered by particles in the air, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This ensures the atoms travel unimpeded from the source to the target substrate.
The Source Material
The process begins with a solid precursor material, often called the "target." This is the material that will ultimately form the thin-film coating on the final component.
The Key Stages of Deposition
While there are many variations of PVD, the process generally follows four distinct stages:
- Evaporation: Energy is applied to the solid source material to vaporize it, releasing atoms from its surface. This can be achieved through methods like bombarding it with a beam of electrons or ions.
- Transportation: The vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum chamber from the source to the substrate.
- Reaction: In some cases, a reactive gas (like nitrogen or oxygen) is introduced into the chamber, allowing the traveling atoms to react and form specific compounds.
- Deposition: The atoms arrive at the substrate and condense, forming a thin, dense, and highly adherent film on the component's surface.
What Are the Benefits of PVD Coatings?
Engineers and designers specify PVD coatings to fundamentally improve the surface characteristics of a part. The resulting films offer significant performance advantages.
Enhanced Hardness and Durability
PVD coatings are extremely hard and can significantly reduce friction on moving parts. This directly translates to improved wear resistance and a longer operational life for the component.
Superior Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
The deposited film creates a dense, non-reactive barrier between the substrate and its environment. This shield protects the underlying material from corrosion, oxidation, and chemical attack.
High-Temperature Tolerance
Many PVD coatings are highly stable and can maintain their protective properties even when exposed to high temperatures, making them suitable for demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, and tooling industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its relationship to other processes, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), is key to appreciating its specific applications.
PVD vs. CVD: A Fundamental Difference
The primary distinction is in the name. Physical Vapor Deposition involves the physical transfer of a material. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves introducing precursor gases into a chamber that react with the substrate to form a new material on its surface.
The Evolution of PVD
The core concept of PVD has been known for over a century, but modern advancements have created many specialized sub-processes. Technologies like plasma-assisted PVD (PAPVD) use plasma to further enhance the coating process, leading to even better adhesion and film properties.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the purpose of PVD helps you identify when it is the appropriate surface engineering solution for a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and reduced friction: PVD is an excellent choice for hardening surfaces on cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection: PVD provides a robust, inert barrier ideal for protecting components in harsh environmental or chemical conditions.
- If your primary focus is a specific aesthetic and functional finish: PVD can create durable, decorative coatings in a variety of colors and finishes for consumer products like watches, faucets, and electronics.
Ultimately, Physical Vapor Deposition is a versatile technology that allows engineers to precisely tailor the surface of a material to meet the most demanding performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Process Type | Vacuum-based, line-of-sight coating |
| Key Benefit | Enhances hardness, wear & corrosion resistance |
| Common Uses | Cutting tools, medical implants, consumer electronics |
Ready to enhance your components with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise can help you select the right PVD solutions to improve durability, corrosion resistance, and performance for your laboratory or manufacturing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















