For many common thermal processes, the primary alternative to a tube furnace is a muffle furnace. While a tube furnace excels at heating samples within a precisely controlled atmosphere or vacuum, a muffle furnace is designed for heating samples in ambient air. The choice between them depends entirely on whether your process requires atmospheric control.
The decision is not about which furnace is superior, but which tool is correct for the job. Tube furnaces are for controlling the gaseous environment, while muffle furnaces are for straightforward heating in air.
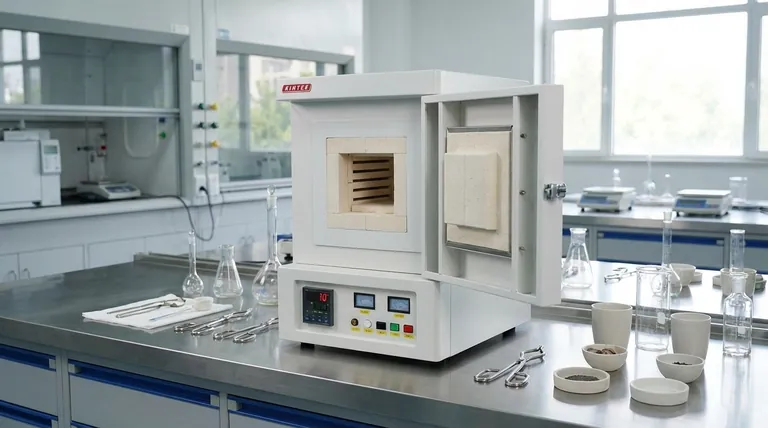

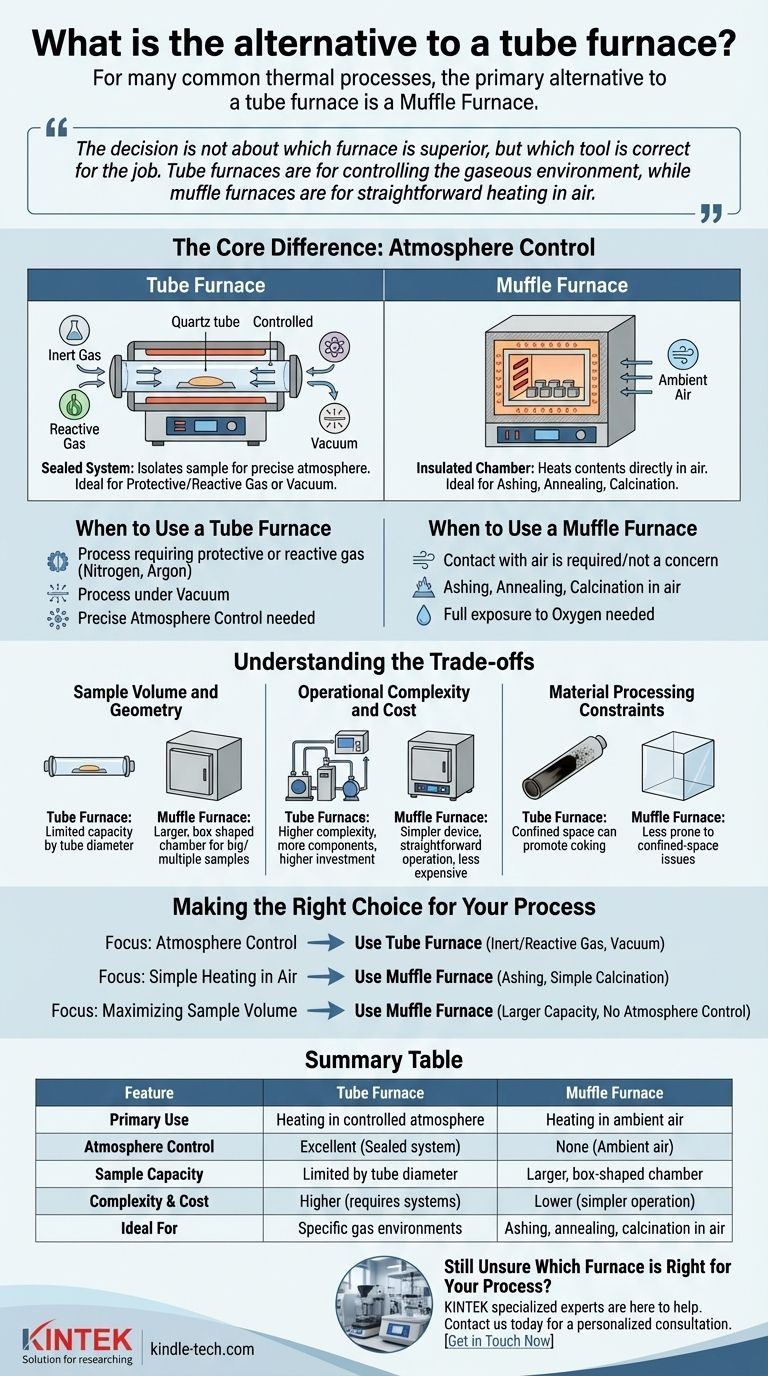
The Core Difference: Atmosphere Control
The fundamental distinction between these two types of furnaces is how they manage the environment surrounding the sample. This single factor dictates nearly every other aspect of their design and application.
When to Use a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is essentially a sealed system. Its core function is to isolate the sample from the outside air, allowing you to introduce a specific environment.
This design makes it the necessary choice for processes that require a protective or reactive gas, such as nitrogen or argon, or for those that must be conducted under a vacuum. The sealed tube (often made of quartz or alumina) and associated vacuum fittings are critical to maintaining this controlled environment.
When to Use a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace, in contrast, is an insulated chamber that heats its contents directly in the ambient air inside. It is the ideal tool for applications where contact with air is either required or not a concern.
Common uses include ashing, annealing, and calcination, where full exposure to oxygen is often necessary for the chemical reaction to complete successfully.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong furnace can lead to failed experiments, inefficient processing, and unnecessary costs. Understanding their inherent limitations is key to making the right decision.
Sample Volume and Geometry
A tube furnace's capacity is constrained by the diameter of its tube, which is often quite small. This limits the size and shape of the samples you can process.
Muffle furnaces typically offer a larger, box-shaped chamber, providing much more flexibility for processing bigger samples or handling multiple samples at once.
Operational Complexity and Cost
Tube furnaces are more complex systems. They require vacuum pumps, gas flow controllers, and careful sealing to function correctly, which increases both the initial investment and the potential for maintenance issues.
A muffle furnace is a far simpler device, often just a heated box with a controller, making it more straightforward to operate and generally less expensive.
Material Processing Constraints
The enclosed nature of a tube furnace can be a significant drawback for certain industrial processes.
For example, when cracking heavy raw materials, the confined space can promote coking (the formation of carbon residue), which can damage the furnace tube and reduce production efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct equipment, you must first define the non-negotiable requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere control: You must use a tube furnace, as it is the only way to reliably process samples in an inert gas, reactive gas, or vacuum.
- If your primary focus is simple heating in air: A muffle furnace is the more efficient, cost-effective, and straightforward solution for processes like ashing or simple calcination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample volume: A muffle furnace generally provides significantly more capacity for larger or numerous samples, provided no atmospheric control is needed.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of the specific environment your material requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Heating in a controlled atmosphere (vacuum, inert gas) | Heating in ambient air |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (Sealed system) | None (Ambient air) |
| Sample Capacity | Limited by tube diameter | Larger, box-shaped chamber |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher (requires gas/vacuum systems) | Lower (simpler operation) |
| Ideal For | Processes requiring specific gas environments | Ashing, annealing, calcination in air |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Process?
Choosing the correct thermal processing equipment is critical for your lab's efficiency and success. The expert team at KINTEK is here to help you make the right choice. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including both tube and muffle furnaces, tailored to your specific application needs.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation, and let our experts guide you to the perfect solution for your heating requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity and Quality
- What precautions you will take while handling the muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What energy transfer happens in a furnace? Master Convection, Conduction & Radiation for Your Process
- What are the different types of heat transfer in a furnace? Mastering Conduction, Convection & Radiation
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes



















