At its core, a protective coating is a thin film applied to a surface to shield it from damage and, in many cases, to alter its appearance or function. These films are engineered to protect against a wide range of threats, including mechanical wear, scratches, chemical corrosion, and even fingerprints. They are a critical component in manufacturing, especially for sensitive items like optical elements.
Protective coatings are more than just a shield; they are a strategic tool for fundamentally modifying a material's properties, enabling it to perform in demanding environments and meet specific aesthetic standards.

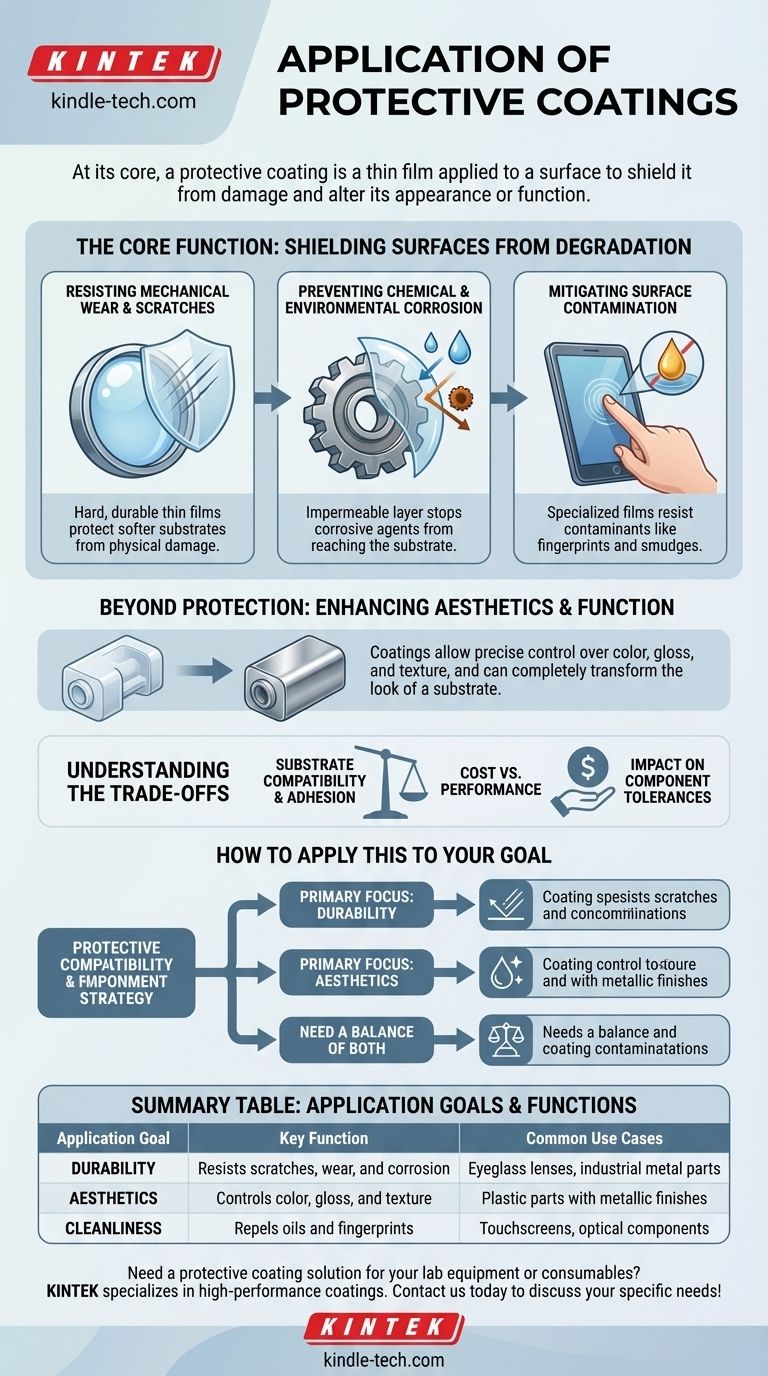
The Core Function: Shielding Surfaces from Degradation
The primary role of any protective coating is to form a barrier between the underlying material, known as the substrate, and the outside world. This barrier serves several critical defensive purposes.
Resisting Mechanical Wear and Scratches
Hard, durable thin films are often applied to softer substrates to protect them from physical damage. This is essential for products that experience frequent handling or contact.
For example, the lenses in eyeglasses or high-precision optical elements are coated to prevent scratches that would otherwise degrade their performance.
Preventing Chemical and Environmental Corrosion
Coatings create an impermeable layer that stops corrosive agents like moisture, salt, and oxygen from reaching the substrate. This function is vital for extending the life of metals in outdoor or industrial settings.
By blocking these environmental attacks, the coating prevents rust and other forms of chemical breakdown.
Mitigating Surface Contamination
Specialized coatings are designed to resist contaminants that can mar a surface's appearance or function. A common application is creating oleophobic (oil-repelling) coatings for touchscreens.
These films prevent fingerprints and smudges from adhering to the surface, keeping it clean and clear, which is particularly important for displays and optical components.
Beyond Protection: Enhancing Aesthetics and Function
While protection is the primary goal, coatings are also used to deliberately change how a product looks and feels. This dual function is key to modern product design.
Achieving a Desired Visual Effect
Coatings can be purely decorative, completely transforming the look of a substrate. They allow for precise control over a product's color, gloss level, and even its texture.
A classic example is the application of metallic coatings onto plastic parts using high-vacuum evaporation. This process gives an inexpensive plastic substrate the premium look and feel of real metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Applying a protective coating is an engineering decision that involves balancing benefits with potential constraints. Ignoring these trade-offs can lead to product failure or unnecessary costs.
Substrate Compatibility and Adhesion
A coating is only effective if it can properly bond to the substrate. Not all coatings adhere well to all materials, and a mismatch can lead to peeling, cracking, or flaking, rendering the protection useless.
Cost vs. Performance
Higher performance often comes at a higher cost. Advanced processes like high-vacuum evaporation, while excellent for creating durable and decorative films, are more complex and expensive than simpler methods like painting or dipping.
Impact on Component Tolerances
While the films are "thin," they still add a layer of material. For high-precision components where nanometer-level tolerances matter, the thickness of the coating must be factored into the design to ensure the final product functions correctly.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
When selecting a coating, your primary objective should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is durability: Prioritize a coating engineered specifically for hardness and chemical resistance to shield the substrate from mechanical wear and environmental corrosion.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: Select a decorative coating based on its ability to deliver the exact color, finish, and texture required for your product's design.
- If you need a balance of both: Seek a multifunctional film that provides a baseline of protection against common issues like scratches while also enhancing the product's visual appeal.
Ultimately, a well-chosen protective coating transforms a simple material into a high-performance, resilient, and visually appealing product.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Key Function | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Resists scratches, wear, and corrosion | Eyeglass lenses, industrial metal parts |
| Aesthetics | Controls color, gloss, and texture | Plastic parts with metallic finishes |
| Cleanliness | Repels oils and fingerprints | Touchscreens, optical components |
Need a protective coating solution for your lab equipment or consumables? KINTEK specializes in high-performance coatings that enhance durability and aesthetics for laboratory applications. Our expertise ensures your equipment withstands harsh conditions while maintaining precision. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength









