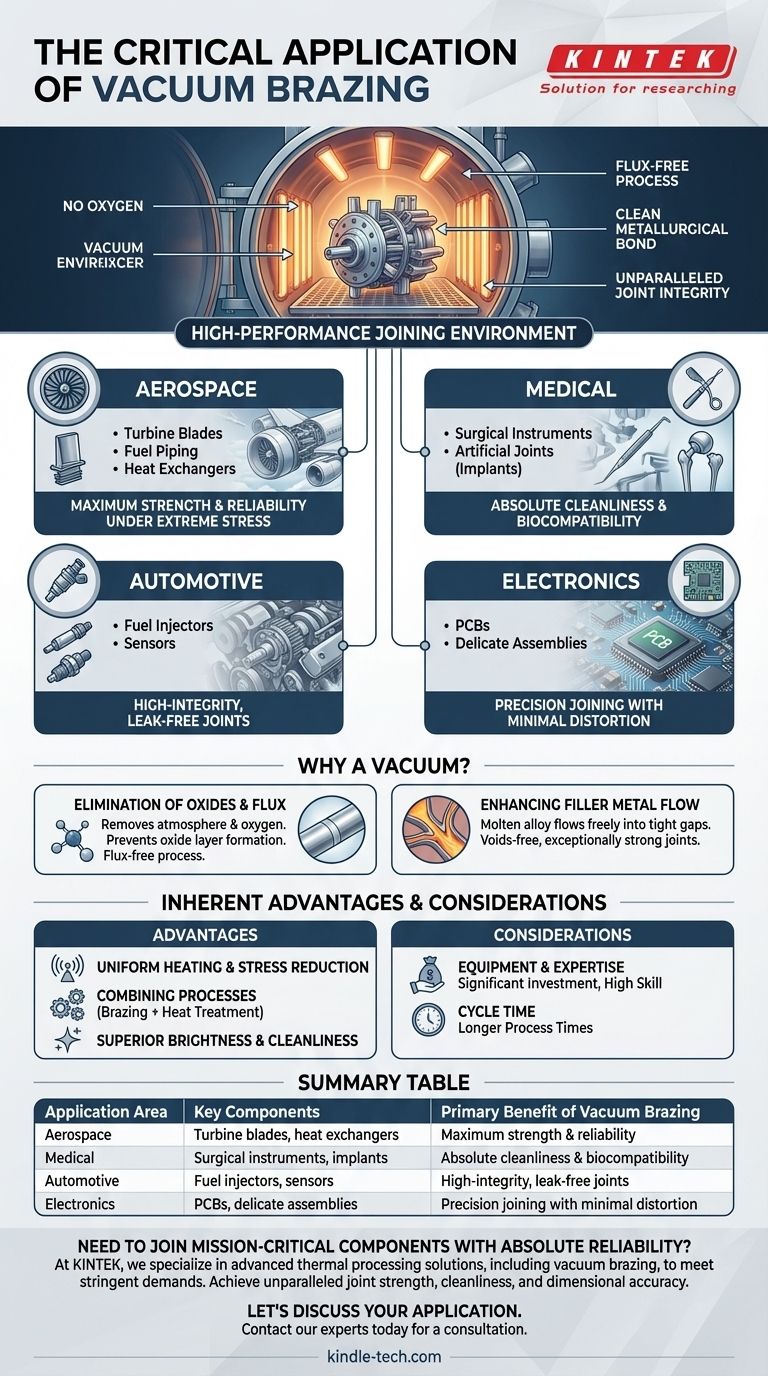
At its core, vacuum brazing is the go-to joining technology for manufacturing high-performance components where failure is not an option. It is used extensively in the aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics industries for parts like turbine blades, fuel injectors, surgical instruments, and complex heat exchangers. The process creates exceptionally strong, clean, and stress-free joints by performing the braze in a controlled, contaminant-free vacuum environment.
Vacuum brazing is selected for critical applications not because it is merely a method of joining parts, but because the vacuum environment itself solves the most common points of failure. It eliminates oxides and the need for corrosive flux, resulting in unparalleled joint integrity, cleanliness, and strength.

Why a Vacuum Creates the Perfect Joining Environment
The fundamental advantage of vacuum brazing comes from removing the atmosphere—and specifically oxygen—from the process. This has profound implications for the quality of the final joint.
The Elimination of Oxides and Flux
In a normal atmosphere, metals instantly form an oxide layer on their surface. This layer prevents the filler metal (the braze alloy) from properly wetting and bonding with the base materials.
Traditional brazing solves this by using a chemical agent called flux, which cleans away the oxides. However, flux itself can become trapped in the joint, leading to corrosion and potential weak points.
Vacuum brazing removes the oxygen, preventing oxides from forming in the first place. This allows for a flux-free process, resulting in a perfectly clean metallurgical bond with no risk of flux inclusion or future corrosion.
Enhancing Filler Metal Flow
With no oxides to impede its path, the molten braze alloy can flow freely into the tightest of gaps via capillary action. This ensures the joint is completely filled, free of voids, and exceptionally strong. This is critical for complex geometries and micro-channel assemblies.
Key Applications Where Failure is Not an Option
The superior integrity of vacuum-brazed joints makes the process essential for industries producing components that must perform flawlessly under extreme conditions.
Aerospace and Automotive Components
In aerospace, parts like turbine blades, fuel piping, and heat exchangers are subjected to immense thermal stress, vibration, and pressure. A joint failure here would be catastrophic.
Vacuum brazing is used because it produces joints that are as strong as the parent materials, are completely sealed, and have minimal residual stress, greatly improving fatigue life. The same principles apply to critical automotive parts like fuel injectors and sensors.
Medical Devices and Electronics
For medical applications such as surgical instruments and artificial joints (implants), cleanliness is paramount. Vacuum brazing produces an immaculately clean finish with no leftover flux that could cause biocompatibility issues.
In electronics, the ability to join intricate shapes without distortion is key for producing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other delicate components. The uniform heating of the vacuum furnace ensures precision.
Understanding the Inherent Advantages of the Process
Beyond the joint itself, the vacuum furnace process offers several production benefits that make it highly desirable for high-specification manufacturing.
Uniform Heating and Stress Reduction
Heating inside a vacuum furnace occurs primarily through radiation, ensuring slow, uniform temperature changes across the entire part.
This controlled heating and cooling cycle drastically reduces internal stresses and distortion. This is essential for maintaining the tight dimensional tolerances of complex, precision-machined components.
Combining Processes for Production Efficiency
A single cycle in a vacuum furnace can be used to perform multiple thermal processes. A part can be brazed, heat-treated, and age-hardened without ever leaving the furnace.
This consolidation streamlines production, reduces handling, and improves the overall yield and consistency of high-volume parts.
Superior Brightness and Cleanliness
Parts emerge from the vacuum furnace in a bright, clean state. The vacuum environment effectively removes surface oils and light oxides during the heating cycle, eliminating the need for post-process chemical cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specialized process with specific considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Equipment and Expertise
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The process also requires a high level of technical expertise to manage the variables of temperature, vacuum level, and material science to achieve optimal results.
Cycle Time
The slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles that reduce stress also result in longer process times compared to torch or induction brazing. While some advanced furnaces offer rapid cooling (quenching) options, the standard process is inherently more time-consuming.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing vacuum brazing depends entirely on the performance, quality, and complexity requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and strength: For mission-critical parts in aerospace or high-performance systems where joint failure is unacceptable, vacuum brazing is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or delicate geometries: For assemblies with intricate shapes, thin walls, or tight tolerances that cannot withstand distortion, this process provides unparalleled precision.
- If your primary focus is absolute cleanliness and biocompatibility: For medical and electronic applications, the flux-free, contaminant-free nature of vacuum brazing is a non-negotiable advantage.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency for high-spec parts: When you can combine joining with subsequent heat treatments in one cycle, vacuum brazing can deliver significant economic benefits.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is the solution for engineering challenges where the integrity of the joint is as important as the design of the part itself.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Components | Primary Benefit of Vacuum Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, heat exchangers | Maximum strength & reliability under extreme stress |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants | Absolute cleanliness & biocompatibility |
| Automotive | Fuel injectors, sensors | High-integrity, leak-free joints |
| Electronics | PCBs, delicate assemblies | Precision joining with minimal distortion |
Need to join mission-critical components with absolute reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing, to meet the stringent demands of laboratories and high-tech manufacturers. Our expertise ensures your components achieve unparalleled joint strength, cleanliness, and dimensional accuracy.
Let's discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can solve your most challenging joining applications.
Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer



















