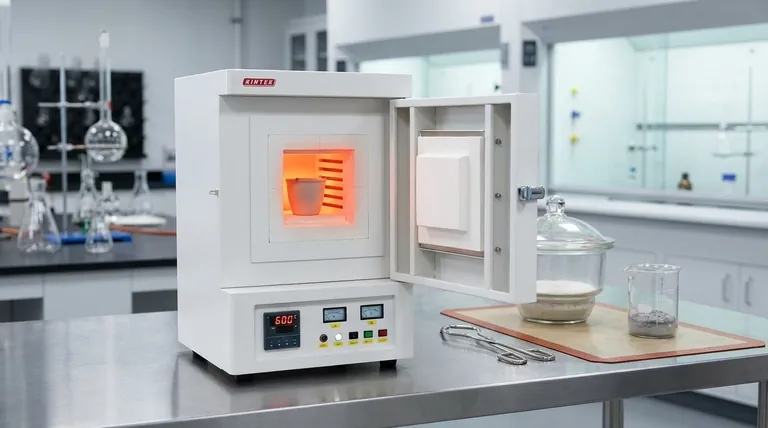
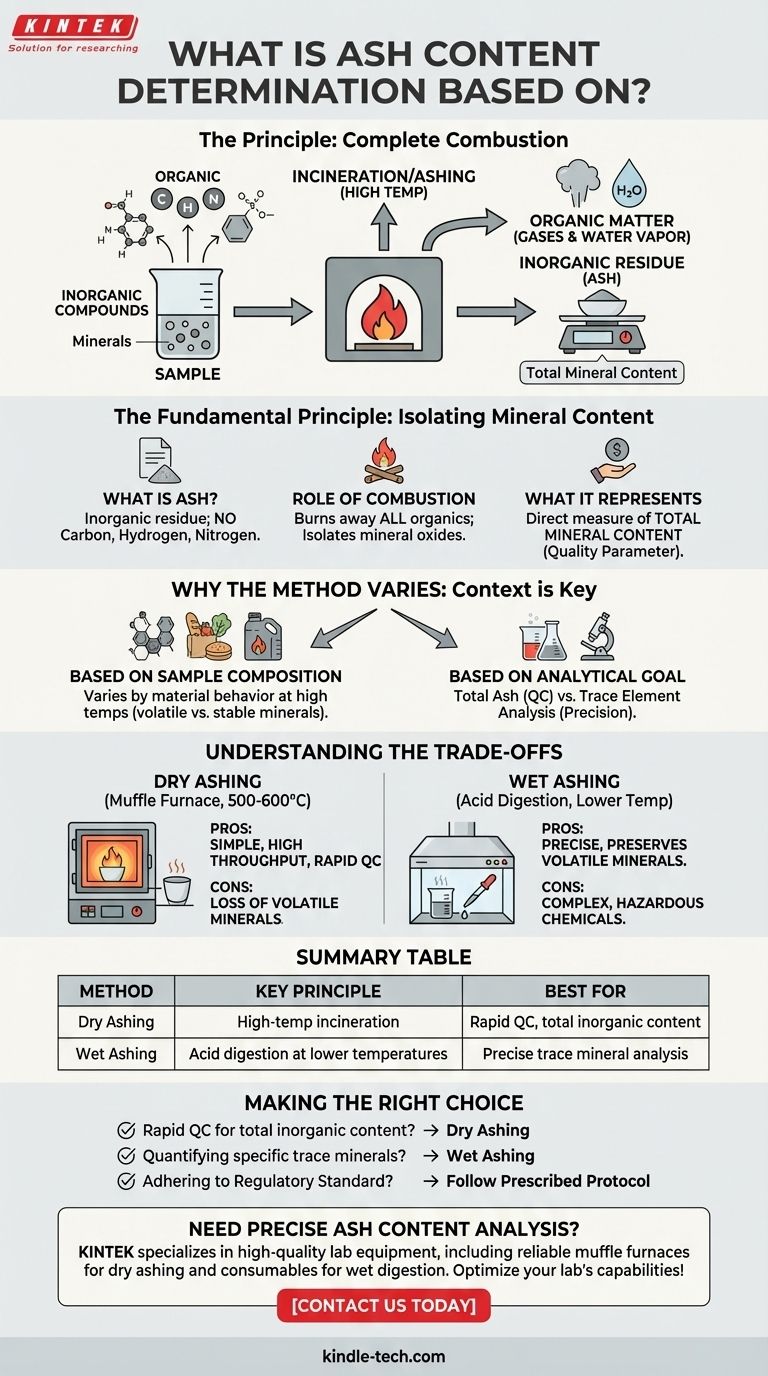
In short, ash content determination is based on the principle of complete combustion. The process involves burning a sample at high temperatures to eliminate all organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, noncombustible residue, which is then weighed. This residue, or ash, represents the total mineral content of the original material.
The core of ash analysis is separating the combustible organic components from the noncombustible inorganic minerals. The specific method used—how hot, for how long, and with what preparation—is chosen based on the sample type and the ultimate goal of the analysis.

The Fundamental Principle: Isolating Mineral Content
Ash determination is a foundational analytical technique used to quantify the total amount of inorganic material in a sample. The process hinges on a simple, yet powerful, separation method.
What is "Ash"?
The ash is the inorganic residue that remains after a sample has been completely incinerated. It does not contain the organic components like carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen, which are converted to gases and water vapor during burning.
The Role of Complete Combustion
To isolate the ash, a sample is heated in a high-temperature furnace. This process, known as incineration or ashing, burns away all the organic substances.
The remaining material is a mixture of oxides from the inorganic elements—the minerals—that were present in the original sample.
What the Result Represents
The weight of the ash is a direct measure of the total mineral content. This is a critical quality parameter in many industries, from food science (nutritional content) to polymers (filler content) and fuel analysis (impurities).
Why the Method Varies: Context is Key
There is no single, universal method for ash determination. The appropriate technique is selected based on the specific sample and the reason for conducting the test.
Based on Sample Composition
Different materials behave differently at high temperatures. The chosen method must ensure complete combustion of the organic matrix without accidentally losing any of the inorganic components you intend to measure.
For example, a sample high in volatile minerals (like lead or mercury) requires a different temperature protocol than one with stable minerals (like calcium or magnesium).
Based on the Analytical Goal
If the goal is simply to measure total ash as a quality metric, a straightforward dry ashing method is often sufficient.
However, if the ash is being prepared for further analysis of specific trace elements, a more controlled method like wet ashing might be required to ensure those elements are not lost during the process.
Key Method Parameters
The choice of method dictates several critical parameters:
- Furnace Temperature: Must be high enough to burn organics but low enough to prevent mineral volatilization.
- Residence Time: The duration in the furnace needed for complete combustion.
- Sample Preparation: Pre-drying or other steps needed to ensure consistent results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The two most common approaches, dry ashing and wet ashing, present a classic trade-off between simplicity and analytical precision.
Dry Ashing: Simplicity and Throughput
This is the most common method, involving heating the sample in a muffle furnace at temperatures typically between 500-600°C.
It is simple, safe, and allows for many samples to be processed at once. However, its high temperatures can cause the loss of volatile minerals, leading to inaccurate results if those elements are of interest.
Wet Ashing: Precision and Preservation
Wet ashing, or wet digestion, uses strong acids and oxidizing agents (like nitric or sulfuric acid) and lower heat to break down the organic matter.
This method is more complex and time-consuming, and it requires handling hazardous chemicals. Its primary advantage is the preservation of volatile minerals, making it the superior choice when the ash is a precursor to trace element analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on what you need to learn from the sample.
- If your primary focus is a rapid quality control check for total inorganic content: Dry ashing is typically the most efficient and practical method.
- If your primary focus is quantifying specific trace minerals, especially volatile ones: Wet ashing is necessary to prevent elemental loss and ensure accurate downstream analysis.
- If you are adhering to a regulatory or industry standard (e.g., AOAC, ASTM): The choice is made for you; you must follow the prescribed protocol exactly.
Ultimately, knowing what ash represents allows you to correctly interpret the data and make informed decisions.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | High-temperature incineration in a muffle furnace | Rapid quality control, total inorganic content |
| Wet Ashing | Acid digestion at lower temperatures | Precise trace mineral analysis, volatile elements |
Need to perform precise ash content analysis in your lab? The right equipment is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable muffle furnaces for dry ashing and consumables for wet digestion. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools to ensure your mineral analysis is both efficient and precise. Contact us today to optimize your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace required for the pre-treatment of catalyst supports? Engineering Performance
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in nitrogen-doped biochar prep? Key Benefits for Precise Atmosphere Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in Sm-doped SrTiO3 ceramics? Ensure Phase Purity and Precision Synthesis
- What is the ash content of a furnace? The Tool vs. The Measurement Explained
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the accurate ash content analysis of biochar samples? Expert Insights
- What is a microwave furnace? Unlock Faster, More Uniform Heating for Advanced Materials
- What role does a laboratory muffle furnace play in the secondary calcination process for chromium-based pigments?
- How does thermal uniformity of a muffle furnace affect SA508 alloy? Master Carbide Precipitation and Fatigue Resistance



















