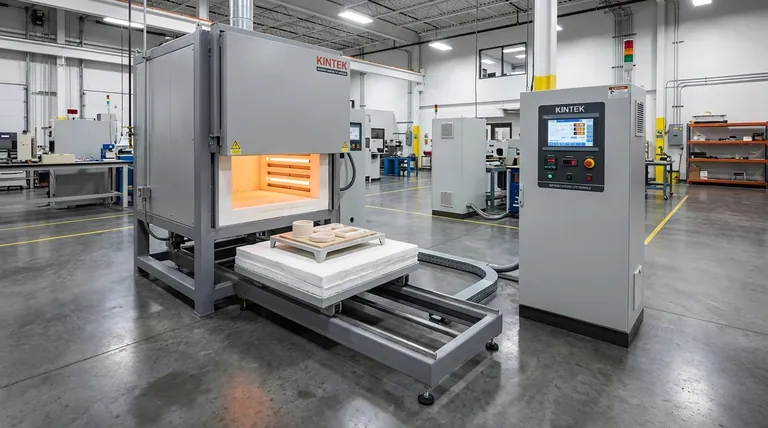
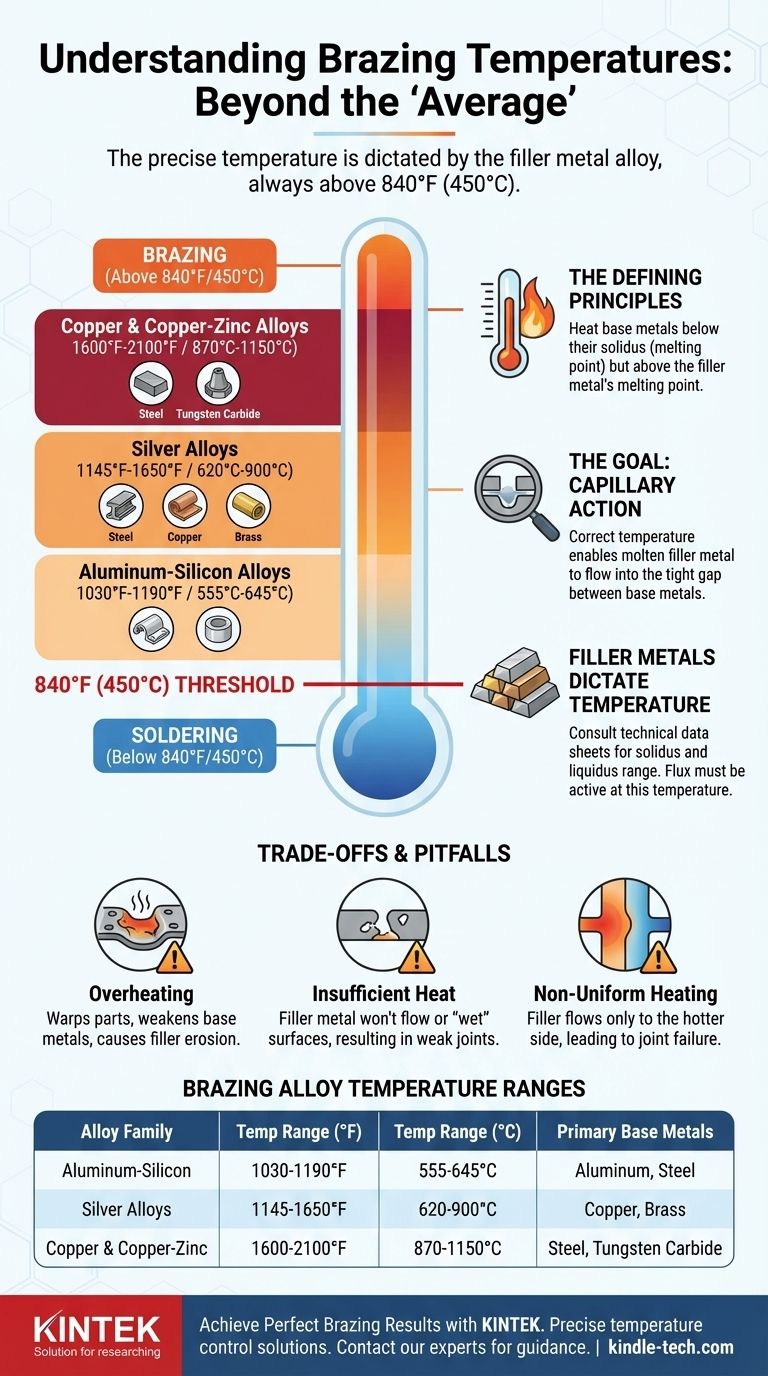
Brazing is fundamentally defined by temperature, but there is no single "average" value that applies to all situations. Instead, the process occurs over a broad range that always begins above 840°F (450°C). The precise temperature required is determined entirely by the filler metal alloy used to join your specific base metals.
The critical takeaway is not to seek an 'average' brazing temperature, but to understand that the correct temperature is dictated by the melting point of your chosen filler alloy. This temperature must be high enough to melt the filler but low enough to keep the base metals solid.

The Defining Principles of Brazing Temperature
Brazing occupies a specific thermal space between soldering and welding. This temperature window is what allows for strong, clean joints without melting the parts being joined.
The 840°F (450°C) Threshold
This temperature is the internationally recognized dividing line. Any joining process using a filler metal that melts below 840°F (450°C) is classified as soldering. Any process above this point is classified as brazing.
Staying Below the Base Metal's Solidus
The solidus is the temperature at which a metal or alloy begins to melt. The core principle of brazing is to heat the base metals to a temperature that is below their solidus but above the melting point of the filler metal.
The Goal: Enabling Capillary Action
Achieving the correct brazing temperature is what creates the conditions for capillary action. This is the physical force that draws the molten filler metal into the tight-fitting gap between the base metals, creating a complete and strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
How Filler Metals Dictate Brazing Temperature
The specific alloy you choose as a filler metal is the single most important factor in determining your target temperature. Different alloys are designed for different base metals and have vastly different melting ranges.
Common Temperature Ranges by Alloy Family
- Aluminum-Silicon Alloys: Used for brazing aluminum, these operate in a very narrow and relatively low-temperature window, typically around 1030°F - 1190°F (555°C - 645°C).
- Silver Alloys: These are some of the most common general-purpose brazing alloys for joining steel, copper, and brass. They have a wide operating range from 1145°F - 1650°F (620°C - 900°C).
- Copper & Copper-Zinc Alloys: Often used for brazing steel and tungsten carbide, these require higher temperatures, typically in the range of 1600°F - 2100°F (870°C - 1150°C).
Reading a Filler Metal's Specifications
Professionals never guess. Always consult the technical data sheet provided by the filler metal manufacturer. This sheet will list the alloy's solidus (when it starts to melt) and liquidus (when it is fully molten), giving you the precise working range.
The Role of Flux
Brazing flux, which cleans the joint and prevents oxidation, also has an active temperature range. You must select a flux that is fully active at the temperature required by your chosen filler metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Controlling heat is the most critical skill in brazing. Simply reaching a temperature is not enough; how you apply and maintain it determines the success or failure of the joint.
The Danger of Overheating
Exceeding the necessary temperature can warp the parts, weaken the base metals through annealing, or even melt them entirely. It can also cause the filler metal to erode the base metal, creating a weak point.
The Problem of Insufficient Heat
If the base metals are not hot enough, the filler metal will not flow or "wet" the surfaces correctly. This prevents capillary action, resulting in an incomplete, low-strength bond with voids and gaps.
The Need for Uniform Heating
Both parts being joined must reach the target temperature at the same time. If one part is hotter than the other, the filler will flow only to the hotter side, leading to a failed joint.
Selecting the Correct Temperature for Your Project
Your choice of base metal is the starting point for every brazing decision. From there, you can select the appropriate filler and determine the exact temperature required.
- If your primary focus is joining copper or steel: Start by looking at silver-based brazing alloys, which typically operate in the versatile 1145°F to 1650°F (620°C to 900°C) range.
- If your primary focus is working with aluminum: You must use a lower-temperature aluminum-silicon filler alloy specifically designed for its narrow working range, around 1100°F (600°C).
- If you are unsure of the materials: Always identify your base metals first, as this is the single most important factor in selecting the correct filler metal and, therefore, the correct brazing temperature.
Ultimately, the right brazing temperature is not an average, but a precise value dictated by the materials you intend to join.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Alloy Family | Common Temperature Range (°F) | Common Temperature Range (°C) | Primary Base Metals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-Silicon | 1030°F - 1190°F | 555°C - 645°C | Aluminum |
| Silver Alloys | 1145°F - 1650°F | 620°C - 900°C | Steel, Copper, Brass |
| Copper & Copper-Zinc | 1600°F - 2100°F | 870°C - 1150°C | Steel, Tungsten Carbide |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Results with KINTEK
Selecting the right brazing temperature is critical for creating strong, reliable joints. The precise heat required depends on your specific filler metal and base materials. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to ensure precise temperature control and successful brazing outcomes every time.
Our experts can help you:
- Identify the correct filler metal for your specific base metals.
- Select the right furnace or heating system to achieve and maintain the precise temperature your project demands.
- Source the necessary fluxes and consumables to ensure a clean, strong bond.
Don't let incorrect temperatures compromise your work. Contact our technical team today to discuss your brazing application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What are the factors affecting the rate of melting process? Master Heat Transfer for Faster Results
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science



















