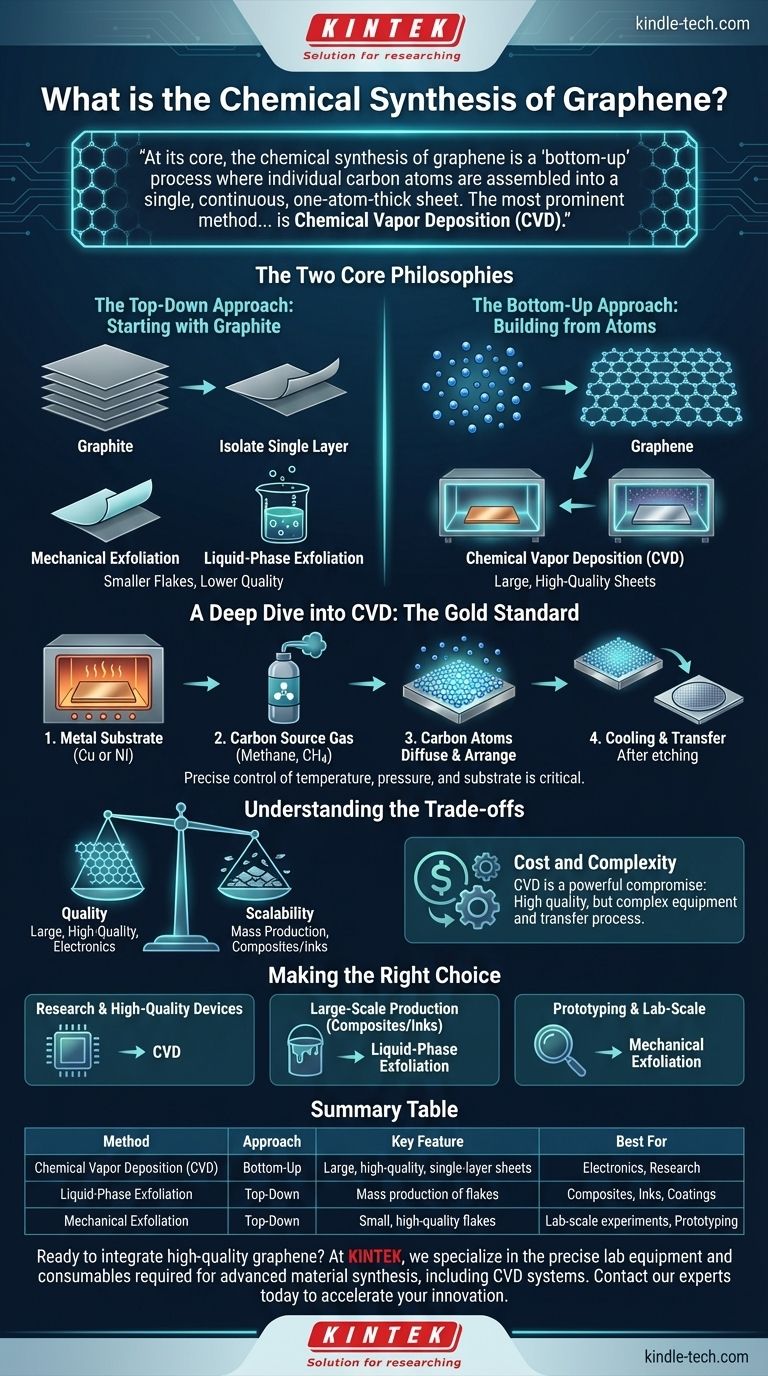
At its core, the chemical synthesis of graphene is a "bottom-up" process where individual carbon atoms are assembled into a single, continuous, one-atom-thick sheet. The most prominent and promising method for achieving this is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which involves growing a high-quality graphene film on a metallic substrate from a carbon-containing gas.
The critical distinction in graphene synthesis is not between dozens of complex methods, but between two core philosophies: breaking down graphite from the "top-down" versus meticulously building graphene from the "bottom-up." Chemical synthesis, specifically CVD, represents the latter and is the key to producing the large, high-quality sheets needed for advanced electronics.

The Two Core Philosophies of Graphene Production
To understand chemical synthesis, you must first understand its place in the broader landscape of graphene production. All methods fall into one of two categories.
The Top-Down Approach: Starting with Graphite
The top-down approach begins with bulk graphite, which is essentially a stack of countless graphene layers. The goal is to isolate a single layer from this stack.
Methods like mechanical exfoliation (using tape to peel off layers) or liquid-phase exfoliation (using solvents and energy to separate layers) fall into this category. While useful, they often produce smaller flakes or material with lower electrical quality.
The Bottom-Up Approach: Building from Atoms
This is the foundation of true chemical synthesis. Instead of starting with graphite, you begin with a source of individual carbon atoms and assemble them into a flawless graphene lattice.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the leading bottom-up technique. It offers unparalleled control over the quality and size of the graphene sheet, making it the most promising method for industrial-scale production.
A Deep Dive into Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD has become the gold standard for producing high-quality graphene because it allows for the growth of large, uniform, single-layer sheets. The process has a few critical components.
The Core Principle of CVD
The process involves heating a metal substrate, typically a thin foil of copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni), to a high temperature inside a vacuum chamber.
A carbon-containing gas, most commonly methane (CH4), is then introduced into the chamber. The high heat breaks down the methane molecules, releasing carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms diffuse and arrange themselves on the surface of the hot metal foil, forming a continuous, single layer of graphene. After the growth is complete, the system is cooled, and the graphene film is ready.
Key Components of the Process
The success of CVD depends on precise control over several variables. The substrate is critical; copper is widely used because carbon has low solubility in it, which helps restrict growth to a single layer.
The carbon source is typically a simple hydrocarbon gas like methane. The temperature and pressure inside the reaction chamber must be tightly controlled to manage the kinetics of the gas transport and surface reaction.
The Final Step: Transferring the Graphene
A crucial and often challenging step is that the graphene grown on the metal foil must be transferred to a different substrate (like silicon or plastic) for use in an actual device. This involves carefully etching away the metal foil while supporting the fragile graphene layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single synthesis method is perfect for every application. The choice always involves balancing competing priorities.
Quality vs. Scalability
CVD excels at producing large-area, high-quality graphene suitable for electronics. However, the process is complex.
Liquid-phase exfoliation, a top-down method, is much better for mass production of graphene flakes used in composites or inks, but the electrical quality of this material is significantly lower.
Cost and Complexity
High-end methods, like growing graphene on silicon carbide, can produce exceptional quality but are prohibitively expensive for most uses.
CVD represents a powerful compromise, but it is not simple. It requires specialized equipment and precise control over the growth process, and the subsequent transfer step adds another layer of complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best synthesis method is entirely dependent on the final application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or creating the highest-quality electronic device: CVD offers the best control for producing large, nearly flawless single-layer sheets.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production for composites, coatings, or inks: Liquid-phase exfoliation is often the more practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a prototype with minimal equipment: Mechanical exfoliation remains a viable option for obtaining small, high-quality flakes for lab-scale experiments.
Ultimately, understanding the principles behind each method empowers you to select the right tool for your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Method | Approach | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Bottom-Up | Large, high-quality, single-layer sheets | Electronics, Research |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Top-Down | Mass production of flakes | Composites, Inks, Coatings |
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Top-Down | Small, high-quality flakes | Lab-scale experiments, Prototyping |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene into your research or product development?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment and consumables required for advanced material synthesis, including Chemical Vapor Deposition systems. Our expertise can help you achieve the large-area, high-quality graphene sheets essential for your next breakthrough in electronics and materials science.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















