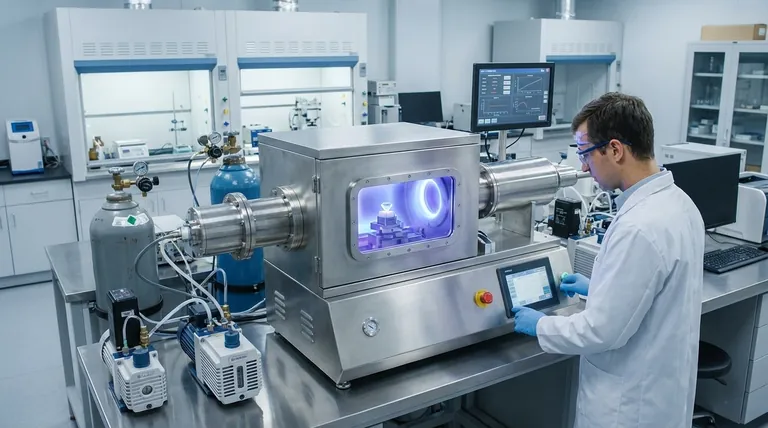
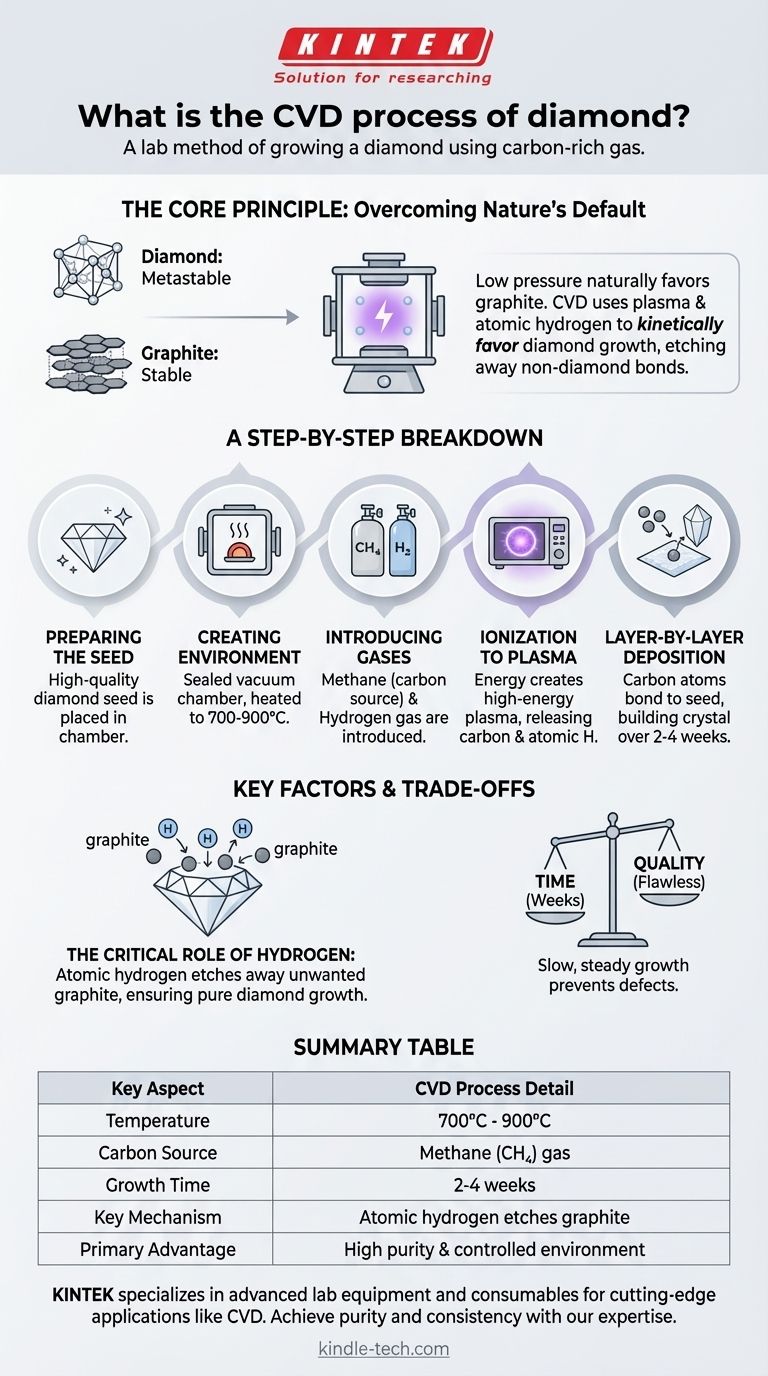
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a method of growing a diamond in a lab using a carbon-rich gas. A small, pre-existing diamond slice, known as a seed, is placed in a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is heated to around 800°C and filled with gases like methane, which are then energized into a plasma, causing them to decompose. This releases pure carbon atoms that systematically attach to the seed, building a new, larger diamond crystal layer by layer over several weeks.
The fundamental challenge in creating a diamond at low pressure is preventing carbon from forming its more stable state, graphite. The CVD process masterfully solves this by using a high-energy plasma and atomic hydrogen to selectively remove any non-diamond bonds, ensuring only the desired diamond crystal structure can grow.

The Core Principle: Overcoming Nature's Default
To truly understand the CVD process, we must first understand the core challenge it solves. At the low pressures used in a lab, carbon's natural inclination is to form graphite (like pencil lead), not diamond.
The Stability Problem: Diamond vs. Graphite
Diamond is a metastable form of carbon under surface-level atmospheric pressure. This means it's not the most stable arrangement of carbon atoms; graphite is. Geologic diamonds form under immense heat and pressure deep within the Earth, conditions that force carbon into the diamond structure.
The CVD Solution: Controlled Chemistry
The CVD process bypasses the need for immense pressure by using precise chemical control. It creates an artificial environment where diamond growth is kinetically favored over graphite growth, even though graphite remains the more stable material. The key is the presence of atomic hydrogen.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the CVD Process
The entire process is a carefully orchestrated sequence designed to build a flawless crystal lattice one atom at a time.
Step 1: Preparing the Seed
The process begins with a thin, high-quality slice of a diamond, which can be either a natural or a previously grown lab diamond. This diamond seed acts as the template or foundation upon which the new diamond will grow. It is meticulously cleaned to remove any impurities.
Step 2: Creating the Growth Environment
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed, low-pressure vacuum chamber. The chamber is heated to a precise temperature, typically between 700°C and 900°C.
Step 3: Introducing the Precursor Gases
A carefully measured mixture of gases is introduced into the chamber. The primary ingredient is a carbon-containing gas, such as methane (CH4), which serves as the source for the new diamond's carbon atoms. This is mixed with a much larger volume of hydrogen gas.
Step 4: Ionization into Plasma
Energy, often in the form of microwaves, is used to ionize the gases, stripping electrons from their atoms and creating a glowing ball of plasma. This high-energy state breaks down the methane molecules, releasing pure carbon atoms. It also splits the hydrogen molecules (H2) into highly reactive single hydrogen atoms (H).
Step 5: Layer-by-Layer Deposition
The freed carbon atoms are drawn down to the cooler diamond seed. They bond with the seed's existing crystal structure, perfectly replicating its atomic arrangement. This process continues slowly and methodically, building the diamond one atomic layer at a time. The entire growth cycle for a gem-quality diamond typically takes two to four weeks.
Understanding the Key Factors and Trade-offs
The success of the CVD process hinges on maintaining a delicate balance of conditions.
The Critical Role of Hydrogen
The atomic hydrogen created in the plasma is the unsung hero of the process. It serves as a "quality control" agent. It bonds far more readily to any non-diamond (graphitic) carbon that tries to form on the surface, essentially etching away the unwanted graphite and leaving only the pure diamond crystal to grow.
Purity and Control
Because the entire process occurs in a sealed, controlled vacuum with highly purified gases, the resulting diamonds can achieve exceptional chemical purity. This level of control over the inputs is a significant advantage of the method.
Time vs. Quality
The rate of diamond growth must be carefully managed. Attempting to grow the diamond too quickly can introduce structural defects and inclusions, compromising the final quality of the gem. The slow, steady deposition over weeks is essential for creating a flawless crystal.
How to Apply This to Your Understanding
Grasping the CVD process allows for a more informed perspective on lab-grown diamonds and materials science.
- If your primary focus is Purity and Traceability: The CVD process offers high control over the growth environment, resulting in chemically pure diamonds with a clear, documented origin.
- If your primary focus is the Technology: Recognize that CVD is a sophisticated materials science technique that bypasses geological conditions by using plasma chemistry to achieve a metastable growth state.
- If your primary focus is Distinguishing from Natural Diamonds: A CVD diamond is physically and chemically diamond, but its distinct, layered growth patterns can be identified by gemological laboratories.
Understanding the CVD process reveals it as a triumph of precise chemical engineering, not a mere imitation of a natural process.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | CVD Process Detail |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 700°C - 900°C |
| Carbon Source | Methane (CH₄) gas |
| Growth Time | 2-4 weeks |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic hydrogen etches graphite, allowing diamond growth |
| Primary Advantage | High purity and controlled growth environment |
Need precise control over material synthesis for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge applications like CVD. Our expertise can help you achieve the purity and consistency your work demands. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of physical vapor deposition? Achieve High-Purity, Durable Thin-Film Coatings
- What are the advantages of thin film resistors? Precision, Stability & Low Noise for Sensitive Circuits
- Why is high-purity nitrogen used as a carrier gas in the AACVD process? Achieve Precision Film Growth and Safety
- What critical fundamental components are made using CVD? The Atomic-Scale Process Powering Modern Tech
- How to do physical vapor deposition? A Guide to PVD Coating Techniques and Processes
- What are the steps in chemical vapour deposition method? A Guide to Thin Film Growth
- What is the size of a CVD diamond? From Micron-Thin Coatings to Multi-Carat Gems
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















