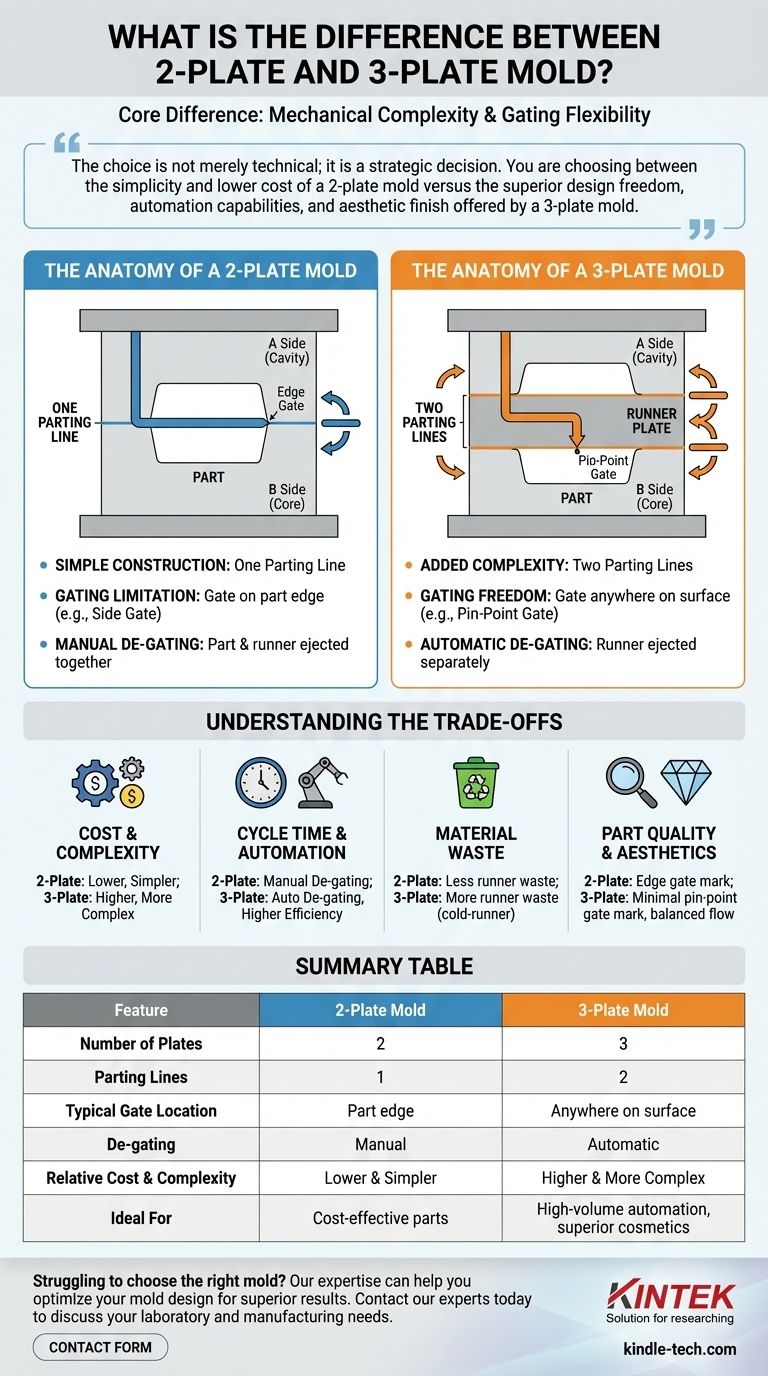
At its core, the difference between a 2-plate and a 3-plate injection mold is its mechanical complexity, which directly dictates where the molten plastic can be injected into the part—a concept known as "gating." A 2-plate mold is simpler and typically gates on the edge of the part, while a more complex 3-plate mold adds a third plate to create a separate path for the plastic, allowing it to be gated almost anywhere on the part's surface.
The choice is not merely technical; it is a strategic decision. You are choosing between the simplicity and lower cost of a 2-plate mold versus the superior design freedom, automation capabilities, and aesthetic finish offered by a 3-plate mold.

The Anatomy of a 2-Plate Mold
A 2-plate mold is the most common and straightforward type of injection mold construction. Its design is defined by its simplicity.
Simple Construction: One Parting Line
A 2-plate mold consists of two main sections, the "A" side (cavity) and the "B" side (core), which meet at a single plane. This meeting point is called the parting line.
When the mold opens, it separates only at this one parting line to eject the finished part, along with its attached runner system.
The Gating and Runner Limitation
In a 2-plate mold, the runner (the channel that transports plastic from the machine nozzle to the part) must exist on the same parting line as the part itself.
This structural constraint means the gate (the small opening where plastic enters the part cavity) must be located on the perimeter of the part. This leads to common gate types like edge gates or side gates.
Manual De-gating Requirement
Because the part and the runner are molded on the same plane and connected at the parting line, they are ejected as a single unit. This requires a secondary operation, often manual, to separate the runner from the finished part.
The Anatomy of a 3-Plate Mold
A 3-plate mold introduces a "runner plate" between the top clamping plate and the cavity plate, adding a layer of complexity for a significant advantage.
Added Complexity: Two Parting Lines
The defining feature of a 3-plate mold is its use of two parting lines. The mold opens in two separate stages.
First, an opening is created to release the runner system. Then, a second opening at the main parting line allows the finished part to be ejected.
Unlocking Gating Freedom
This dual-parting action is the key. The runner system lives on a separate plane from the part, connected by a "drop" that passes through the middle plate.
This allows the gate to be placed virtually anywhere on the part's surface, not just the edge. It enables the use of pin-point gates, which are ideal for balanced plastic flow and for cosmetic surfaces where a gate mark needs to be minimal or hidden.
Automatic De-gating by Design
As the 3-plate mold opens, the initial movement pulls the part away from the pin-point gate, automatically shearing the connection.
The runner system is ejected separately from the part, eliminating the need for a manual de-gating process. This is a critical advantage for high-volume, automated production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two mold types involves balancing cost, quality, and production efficiency.
Cost & Complexity
A 3-plate mold is more intricate to design, manufacture, and maintain. The additional plate, mechanisms, and precision required make it significantly more expensive upfront than a 2-plate mold.
Cycle Time & Automation
While a 3-plate mold has a more complex opening sequence that can slightly increase mechanical cycle time, its ability to automatically de-gate often results in a lower net production time and reduced labor costs per part.
Material Waste
In a cold-runner configuration, a 3-plate mold typically has a more extensive and complex runner system. This results in more plastic scrap per cycle, which can be a significant cost factor depending on the material price.
Part Quality & Aesthetics
For large, flat parts, a 3-plate mold allows for central gating, which promotes a more uniform and balanced flow of plastic. This drastically reduces the risk of defects like warpage. The small pin-point gates also leave a much less noticeable mark than the edge gates of a 2-plate mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Design
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your part and production goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simplicity: A 2-plate mold is the standard choice, especially if a gate mark on the part's edge is acceptable and production volumes don't demand full automation.
- If your primary focus is part quality for large components: A 3-plate mold is superior for large, flat parts that need central gating to ensure balanced flow and prevent warpage.
- If your primary focus is cosmetic appearance and automation: A 3-plate mold is the best option, as its pin-point gating leaves a minimal vestige and its self-shearing action is ideal for high-volume, "lights-out" manufacturing.
Understanding this fundamental tooling difference empowers you to make informed design and manufacturing decisions that align with your project's specific cost, quality, and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 2-Plate Mold | 3-Plate Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Plates | 2 | 3 |
| Parting Lines | 1 | 2 |
| Typical Gate Location | Part edge (e.g., side gate) | Anywhere on part surface (e.g., pin-point gate) |
| De-gating | Manual | Automatic |
| Relative Cost & Complexity | Lower & Simpler | Higher & More Complex |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective parts, simple designs | High-volume automation, superior cosmetics, large flat parts |
Struggling to choose the right mold for your plastic part? The decision between a 2-plate and 3-plate mold is critical for your project's cost, quality, and production speed. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables that support the entire injection molding process, from prototyping to high-volume production. Our expertise can help you optimize your mold design for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- High Performance Lab Homogenizer for Pharma Cosmetics and Food R&D
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- What functions do high-strength graphite molds serve? Key Roles in Yttrium Oxide Vacuum Hot-Press Sintering
- What role does laboratory mold pressing equipment play in Eu:Y2O3 ceramics? Optimize Green Body Formation Today
- What is the purpose of using a mold for pellet pressing when preparing catalyst test samples? Ensure Data Consistency
- What is the role of high-purity graphite molds in hot-pressing MAX phases? Achieve High-Density Material Synthesis
- What alternative material to KBr can be used for pellet-based infrared measurements in the low-wavenumber region? CsI Solutions
- What is a two plate Mould in injection molding? The Ultimate Guide to This Simple, Cost-Effective Tool
- What are the key functions of graphite molds in hot pressing sintering? Enhance High Entropy Alloy Coating Density
- How are samples typically prepared and measured using the diffuse reflection method? Optimize Your Lab's IR Spectroscopy








