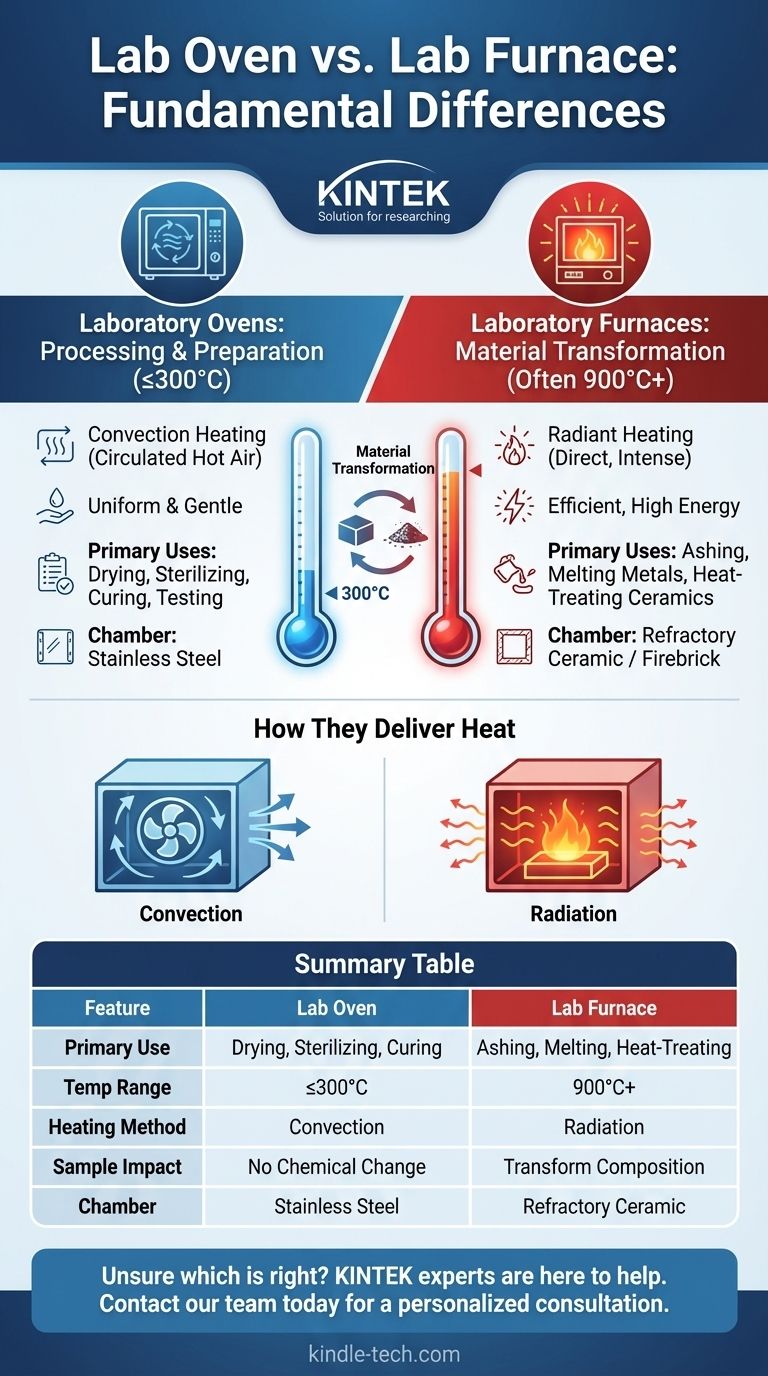
At its core, the difference between a laboratory oven and a laboratory furnace comes down to temperature range and heating method. An oven uses circulated hot air for lower-temperature applications like drying and sterilizing, typically below 300°C. A furnace, in contrast, uses direct, intense radiant heat to achieve extremely high temperatures, often starting at 900°C, for processes that fundamentally alter a material, such as ashing or melting metals.
Choosing the right heating instrument is critical for procedural success and safety. The decision hinges on a single question: are you trying to process a material with uniform warm air (oven), or are you trying to transform its fundamental composition with intense, direct heat (furnace)?

The Fundamental Divide: Temperature and Purpose
The most significant distinction between these two instruments is their operational temperature range, which directly dictates their primary use cases in the laboratory.
Laboratory Ovens: For Processing and Preparation (Up to ~300°C)
A lab oven is a workhorse for general heating, preparation, and testing. Its temperature is precisely controlled but remains in a range that processes materials without changing their chemical structure.
Common applications include drying glassware, sterilizing medical instruments, curing polymers and epoxies, and performing moisture content analysis.
Laboratory Furnaces: For Material Transformation (Often 900°C+)
A furnace is a specialized instrument designed for high-temperature applications that induce a physical or chemical change in a material. These are often called "muffle furnaces" because the heating elements are separated from the work chamber by a "muffle," or refractory ceramic liner.
Their purpose is transformative: ashing samples to determine inorganic content, melting or annealing metals, and heat-treating ceramics. They operate at temperatures that would destroy a conventional oven.
How They Deliver Heat: Convection vs. Radiation
The method of heat delivery is just as important as the temperature itself. This mechanical difference is key to understanding which tool is right for your sample.
Ovens: Circulated Hot Air (Convection)
In a laboratory oven, heating elements are located outside the main chamber. A fan then circulates the heated air throughout the interior.
This convection method ensures a highly uniform and gentle temperature distribution, preventing "hot spots" and protecting sensitive samples from direct exposure to a scorching heating element.
Furnaces: Direct, Intense Heat (Radiation)
In a furnace, the heating elements are typically inside the chamber, surrounding the sample. The sample is heated primarily through direct thermal radiation.
This method is far more efficient at transferring the massive amounts of energy required to reach temperatures of 1400°C or higher. It delivers intense, direct heat to the sample to initiate processes like combustion or melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While their functions are distinct, choosing between an oven and a furnace—or even different models of each—involves considering critical trade-offs.
Material and Chamber Construction
Ovens are most often built with stainless steel interiors. This makes them durable, corrosion-resistant, and relatively easy to clean between uses.
Furnaces must use refractory ceramic or firebrick insulation to withstand extreme heat. These materials can be porous, harder to clean, and may shed fine particles, which can be a source of contamination for high-purity analyses.
Airflow and Sample Integrity
An oven with a mechanical convection fan provides excellent temperature uniformity but can disturb delicate samples, such as fine powders or lightweight films.
While a furnace doesn't use a fan, the extreme heat can create its own convection currents. More importantly, the process of ashing is designed to burn off organic material, so it is inherently destructive to the original sample.
Energy and Safety Protocols
Furnaces consume significantly more energy than ovens to reach and maintain their extreme temperatures.
They also represent a much higher safety risk. Operating a furnace requires specialized personal protective equipment (PPE), careful material handling protocols, and an awareness of the severe burn hazards present even after the unit is turned off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is the first step toward a successful and repeatable thermal process. Your decision should be guided entirely by your intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing: An oven is the correct tool, providing gentle, uniform heat at precisely controlled low temperatures.
- If your primary focus is ashing, melting metals, or heat-treating ceramics: A furnace is required to reach the extreme temperatures needed for material transformation.
- If your primary focus is sample integrity at moderate temperatures: A gravity convection oven (without a fan) may be a better choice than a forced-air oven to avoid disturbing samples.
Understanding this fundamental difference ensures you select not just a heating device, but the precise instrument for your scientific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Oven | Laboratory Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Drying, Sterilizing, Curing | Ashing, Melting, Heat-Treating |
| Typical Temp Range | Up to ~300°C | 900°C and higher |
| Heating Method | Circulated Hot Air (Convection) | Direct Radiant Heat |
| Sample Impact | Processes without altering chemistry | Transforms material composition |
| Chamber Material | Stainless Steel | Refractory Ceramic / Firebrick |
Unsure which heating instrument is right for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your laboratory needs for success and safety.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation to select the perfect oven or furnace for your drying, sterilizing, ashing, or heat-treating processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- What is a disadvantage of dry ashing? Avoid Inaccurate Results with Better Alternatives
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What are the safety precautions for using a muffle furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation



















