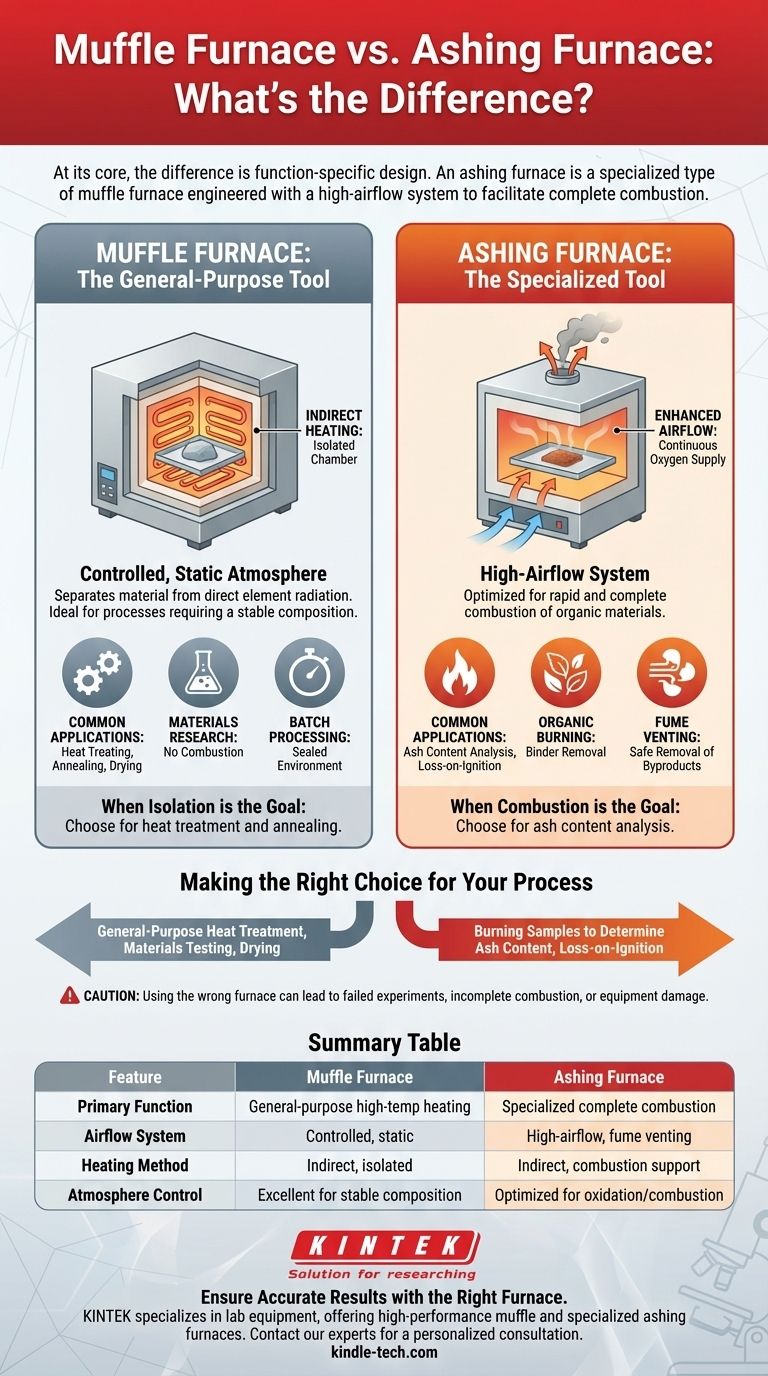
At its core, the difference is function-specific design. An ashing furnace is a specialized type of muffle furnace engineered with a high-airflow system to facilitate complete combustion. In contrast, a standard muffle furnace provides high-temperature heating in a controlled chamber isolated from the heating elements, but without the enhanced airflow required for burning materials.
While all ashing furnaces are a type of muffle furnace, not all muffle furnaces are suitable for ashing. The critical distinction lies in the furnace's ability to actively manage airflow to support combustion and vent fumes.

What is a Muffle Furnace? The General-Purpose Tool
A muffle furnace is a fundamental piece of laboratory equipment, essentially a high-temperature oven. Its defining characteristic is not its shape but its method of heating.
The Core Principle: Indirect Heating
The term "muffle" refers to the practice of separating the material being heated from the direct radiation of the heating elements.
This is achieved by placing the sample inside a chamber, which is then heated from the outside. This design prevents contamination from the fuel or heating elements, which is critical for many scientific applications.
Common Form Factor: The Box Furnace
Most laboratory muffle furnaces are "box" or "chamber" furnaces. This simply means they provide a sealed, box-shaped space for heating materials in batches.
These are the workhorses for a wide range of thermal processing applications where a controlled, static environment is needed.
Typical Applications
Standard muffle furnaces are used for processes like heat-treating metals, annealing, drying materials, and conducting materials research where the goal is to heat a sample without altering it through combustion.
What is an Ashing Furnace? The Specialized Tool
An ashing furnace is built on the same muffle furnace foundation but adds a crucial feature set designed for one specific purpose: burning samples completely.
The Defining Feature: Enhanced Airflow
The primary difference is an integrated system for managing air. Ashing furnaces introduce a continuous flow of fresh, often preheated, air into the chamber.
This constant supply of oxygen is essential for ensuring the complete and rapid combustion of organic materials in the sample.
Purpose-Built for Combustion
This design simultaneously removes the smoke and fumes generated during combustion, venting them safely away.
The entire process is optimized to burn off all combustible material, leaving only the non-combustible inorganic content, or ash, behind for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-off: Airflow vs. Atmosphere Control
Choosing between these two furnaces comes down to understanding the needs of your specific process. Using the wrong furnace can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, or safety hazards.
When Combustion is the Goal
If your process involves loss-on-ignition, ash content analysis, or burning off organic binders, you must use an ashing furnace.
Attempting this in a standard muffle furnace will result in incomplete combustion due to oxygen starvation. It can also fill your lab with hazardous smoke and allow corrosive byproducts to damage the furnace's heating elements and insulation.
When Isolation is the Goal
If you are performing heat treatment, annealing, or any process where the sample's chemical composition must remain stable (aside from the effects of heat), a standard muffle furnace is the correct choice.
Using an ashing furnace for these tasks would introduce a constant flow of oxygen, causing unwanted oxidation on the surface of your materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application dictates the necessary tool. To make a definitive choice, evaluate your primary thermal processing need.
- If your primary focus is burning samples to determine ash content: You must use an ashing furnace for complete, safe, and efficient combustion.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment, materials testing, or drying: A standard muffle furnace provides the necessary heat and controlled environment without unwanted airflow.
- If your process involves heating in an inert atmosphere: Neither of these is correct; you would require a specialized furnace with gas inlet ports to create a controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is the first step toward reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Ashing Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | General-purpose high-temperature heating | Specialized for complete sample combustion |
| Airflow System | Controlled, static atmosphere | High-airflow for oxygen supply & fume venting |
| Heating Method | Indirect heating, isolated chamber | Indirect heating with enhanced combustion support |
| Key Applications | Heat treatment, annealing, materials research | Ash content analysis, loss-on-ignition, organic burning |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent for processes requiring stable composition | Optimized for oxidation and combustion processes |
Ensure Accurate Results with the Right Furnace
Choosing between a muffle furnace and an ashing furnace is critical for your lab's success. Using the wrong equipment can lead to incomplete combustion, sample contamination, or damaged instruments.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts understand the precise requirements of thermal processing applications. We provide:
- High-performance muffle furnaces for controlled heat treatment and materials testing
- Specialized ashing furnaces with optimized airflow for complete combustion
- Technical guidance to match the right equipment to your specific application
Let us help you achieve reliable and repeatable results. Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how our furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heat treatment process for steel? A Guide to Controlling Hardness, Toughness, and Performance
- What is the role of a laboratory oven in Carbon Paper catalyst preparation? Stabilize Nickel Precursors Effectively
- Why is pre-calcination of CaO necessary for CCMS? Ensure High-Purity Calcium Oxide in Your Molten Salt Process
- What Role Do High-Temperature Furnaces Play in 304L Sensitization? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Material Research
- What are the primary functions of a high-temperature muffle furnace in the preparation of co-combustion ash samples?
- Why is a high-temperature furnace essential for catalyst preparation? Unlock peak catalytic activity and stability.
- What is the temperature of calcining? Unlock the Key to Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the function of muffle or tube furnaces in FeCrAl alloy oxidation research? Optimize Your Alumina Film Growth



















