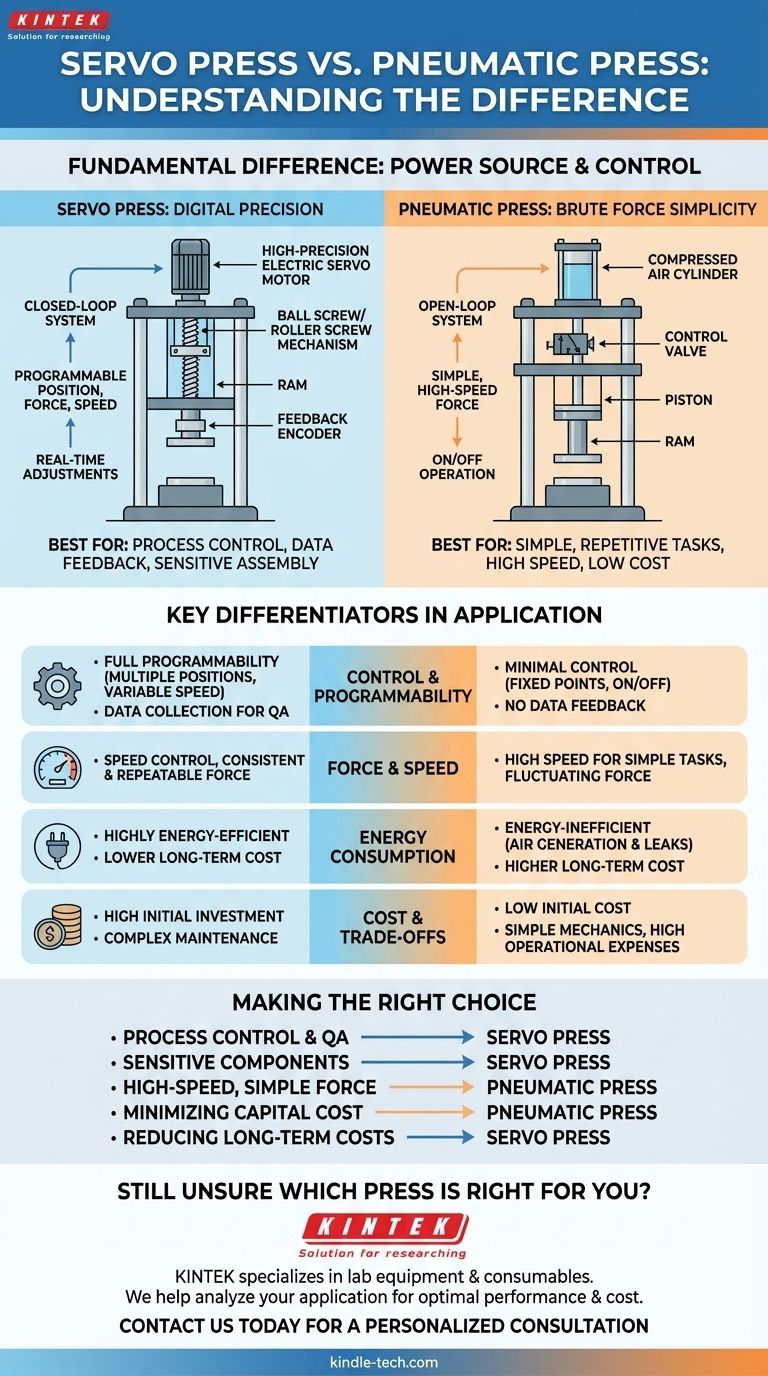
At a fundamental level, the difference between a servo press and a pneumatic press lies in their power source and control mechanism. A servo press uses a high-precision electric servo motor to drive the ram, offering exact, programmable control over position, force, and speed. In contrast, a pneumatic press uses compressed air to power a cylinder, providing a simpler, high-speed force that is powerful but far less precise.
The core choice is not about which press is "better," but about matching the technology to the task. Servo presses are designed for applications requiring process control and data feedback, while pneumatic presses excel at simple, repetitive tasks where low cost and high speed are the primary drivers.

The Core Mechanism: How They Work
Understanding how each press generates force reveals its inherent strengths and weaknesses. The underlying technology dictates the machine's capabilities.
The Servo Press: Digital Precision
A servo press is a closed-loop system built for precision. It consists of a servo motor, a feedback device (encoder), and a mechanical actuator, typically a ball screw or roller screw.
The controller sends a precise electrical signal to the motor to begin the stroke. The encoder constantly reports the exact position and speed of the motor back to the controller.
This closed-loop feedback allows the system to make real-time adjustments, guaranteeing that the commanded force, distance, and speed are achieved with extreme accuracy and repeatability.
The Pneumatic Press: Brute Force Simplicity
A pneumatic press is a far simpler, open-loop system. Its primary components are an air cylinder, a piston, and a control valve.
When the valve opens, compressed air rushes into the cylinder, forcing the piston and attached ram downward. The force is determined by the air pressure and the cylinder's surface area.
Speed can be moderately adjusted using flow control valves that restrict how quickly air enters or exits the cylinder. However, there is no inherent feedback on the actual force applied or the final position achieved.
Key Differentiators in Application
The differences in mechanism translate directly to how these presses perform in a production environment.
Control and Programmability
This is the most significant differentiator. A servo press offers full programmability of the entire press cycle. You can program multiple positions, specific forces, and variable ram speeds within a single stroke.
This allows for complex profiles, such as approaching the part quickly, pressing slowly with controlled force, and then verifying the final position. The press can also collect data on every cycle for quality assurance and process traceability.
Pneumatic presses generally operate between two fixed points: fully retracted and fully extended. They are essentially "on/off" devices, offering minimal control over the process itself.
Force and Speed
Pneumatic presses are known for their extremely high speeds in simple, short-stroke applications. They deliver their force with a rapid impact.
Servo presses can also be very fast, but their true strength is speed control. They can vary velocity throughout the cycle, which is critical for applications like seating bearings without causing damage.
While pneumatic force is dependent on fluctuating plant air pressure, a servo press delivers a highly consistent and repeatable force on every cycle.
Energy Consumption
Servo presses are significantly more energy-efficient. The motor only draws significant power during the actual press stroke.
Pneumatic systems are notoriously inefficient. Generating compressed air is energy-intensive, and leaks in air lines are common, leading to constant energy waste even when the press is idle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a press technology requires balancing initial costs against long-term capabilities and operational expenses.
The Cost of Precision (Servo Presses)
The primary drawback of a servo press is its high initial investment. The servo motor, drive, ball screw, and sophisticated control system are expensive components.
Maintenance can also be more complex, potentially requiring a technician with expertise in electronics and software, not just mechanics.
The Limits of Simplicity (Pneumatic Presses)
The main limitation of a pneumatic press is its lack of process control and verification. It is difficult to confirm that the correct force was applied or the part was seated to the proper depth.
They are also susceptible to performance variations caused by fluctuations in plant air pressure. Over the long term, their high energy consumption can lead to a higher total cost of ownership despite the low purchase price. They are also significantly noisier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your application's requirements for precision, data, and cost should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is process control and quality assurance: A servo press is the necessary choice for assembling sensitive components, collecting data, or when press profiles must be tightly managed.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, simple force operations: A pneumatic press offers an unbeatable combination of speed and low upfront cost for tasks like punching, stamping, or basic assembly.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront capital cost: A pneumatic press is the clear winner, requiring a much smaller initial investment.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operating costs: A servo press's superior energy efficiency will likely result in a lower total cost of ownership over the machine's lifetime.
By understanding this fundamental trade-off between sophisticated control and brute-force simplicity, you can confidently select the technology that aligns with your manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Servo Press | Pneumatic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric Servo Motor | Compressed Air |
| Control & Precision | High (Programmable position, force, speed) | Low (Simple on/off operation) |
| Best For | Process control, data collection, sensitive assembly | High-speed, repetitive, simple tasks |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Long-Term Cost | Lower (Energy Efficient) | Higher (Energy Inefficient) |
| Data Feedback | Yes (Quality Assurance & Traceability) | No |
Still Unsure Which Press is Right for Your Lab or Production Line?
Choosing between a servo press and a pneumatic press is critical for your process efficiency, quality control, and bottom line. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, and we can help you analyze your specific application—whether it's sensitive component assembly requiring data traceability or high-volume, simple pressing tasks.
We provide the right equipment to meet your laboratory needs, ensuring you invest in a solution that optimizes performance and cost.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let us help you make the perfect press selection for your success. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic floor press used for? A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Lab Applications
- How does a laboratory hot press improve the microscopic structure of polymer-ceramic composite cathodes? | KINTEK
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems



















