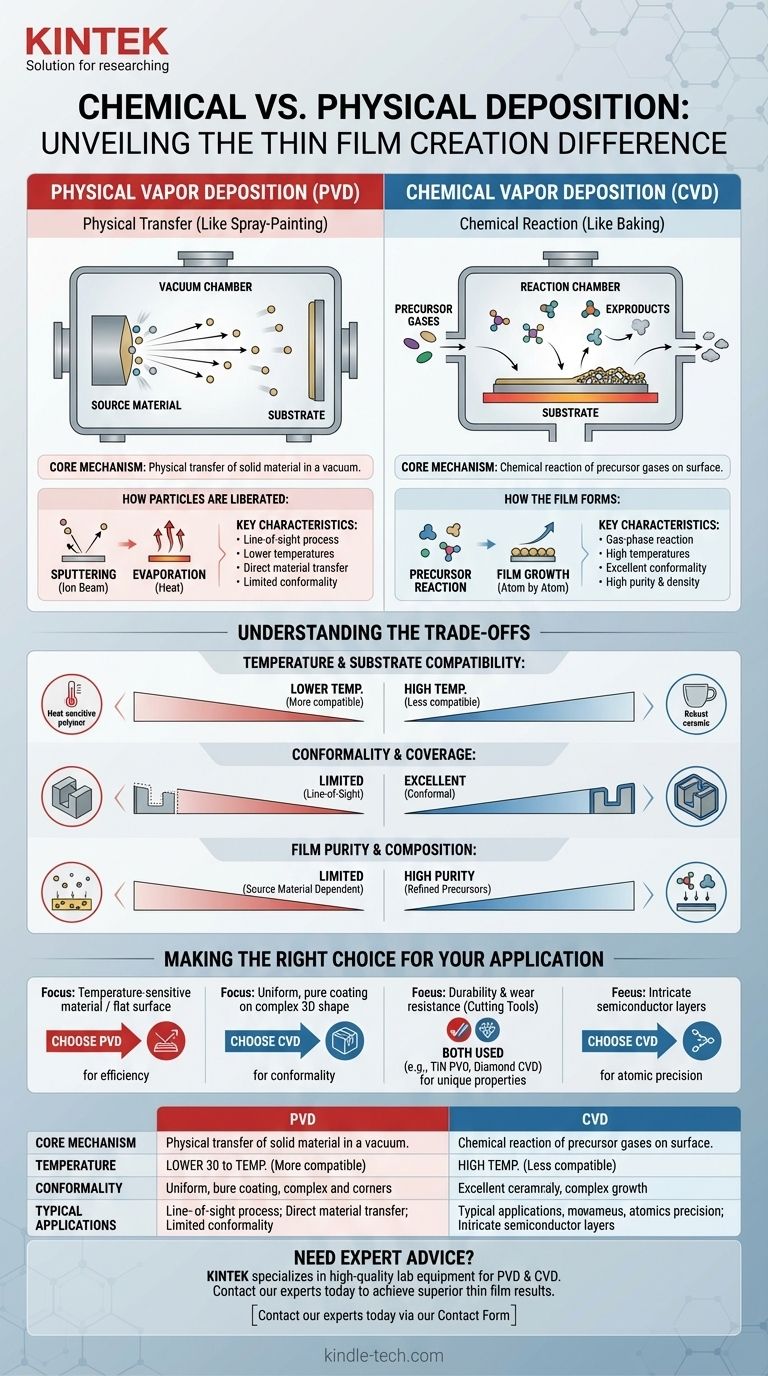
At its core, the difference between chemical and physical deposition lies in how a thin film is created on a surface. Physical deposition physically transfers a solid material from a source to the substrate, much like spray-painting. In contrast, chemical deposition uses precursor gases that undergo a chemical reaction at the substrate's surface to form an entirely new solid material, similar to baking a cake from ingredients.
The fundamental distinction is one of process: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a line-of-sight transfer of an existing material, while Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical creation of a new material that can conform to any shape.

Understanding Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
The Core Mechanism: Physical Transfer
PVD processes take place inside a vacuum chamber to allow particles to travel freely.
High energy is used to liberate atoms or molecules from a solid source material. These liberated particles then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler substrate, forming a solid thin film.
How Particles Are Liberated
The method of liberation defines the specific P_VD_ technique.
This is achieved through mechanical, electromechanical, or thermodynamic means. For example, sputtering uses an ion beam to bombard and eject particles from the source, while evaporation uses heat to turn the source material into a vapor.
Key Characteristics of PVD
Because PVD is a direct line-of-sight process, the coating is applied primarily to surfaces that are directly exposed to the source.
This method generally operates at lower temperatures than chemical deposition and can deposit a wide array of materials, including metals, alloys, and ceramics, without changing their fundamental composition.
Understanding Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The Core Mechanism: Chemical Reaction
CVD is fundamentally a process of synthesis.
It begins by introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. The substrate inside the chamber is heated to a specific temperature that initiates a chemical reaction.
How the Film Forms
The precursor gases react or decompose on the hot substrate surface.
This reaction forms a new, stable solid film, and the chemical byproducts are then removed from the chamber as exhaust gas. The film literally grows on the surface atom by atom.
Key Characteristics of CVD
Since the precursor gases can flow around complex objects, CVD provides excellent conformality. This means it can produce highly uniform coatings on intricate 3D shapes and internal surfaces.
The process often results in highly pure, dense, and durable films with excellent adhesion, making it critical for industries like semiconductor manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature and Substrate Compatibility
PVD is generally a lower-temperature process, making it suitable for coating materials that cannot withstand high heat, such as certain polymers or pre-processed components.
CVD typically requires very high temperatures to drive the necessary chemical reactions, which can limit the types of substrates that can be used without causing damage.
Conformality and Coverage
CVD excels at creating uniform coatings on complex, non-planar surfaces. The gas-phase nature of the process ensures all surfaces are coated evenly.
PVD is a line-of-sight technique. This makes it difficult to coat undercuts, sharp corners, or the inside of deep trenches, often resulting in a thinner coating on vertical walls than on horizontal surfaces.
Film Purity and Composition
CVD can produce films of exceptionally high purity. The precursor gases can be refined to part-per-billion levels, ensuring the resulting film is free of contaminants.
In PVD, the purity of the deposited film is directly limited by the purity of the source material being used. Any impurity in the source will be transferred to the film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between these methods requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The geometry of your part, the material required, and the desired film properties will dictate the best approach.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material or a flat surface with a specific metal or alloy: PVD is often the more direct, efficient, and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform, pure, and defect-free coating on a complex 3D shape: CVD is the superior method due to its exceptional conformality and control over film growth.
- If your primary focus is durability and wear resistance on a cutting tool: Both methods are used, but specific PVD coatings (like TiN) and CVD coatings (like diamond) are chosen for their unique properties.
- If your primary focus is building the intricate layers of a semiconductor chip: CVD provides the atomic-level precision necessary for growing the high-quality crystalline films required.
Understanding this fundamental difference—physical transfer versus chemical reaction—is the key to selecting the optimal deposition technology for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical transfer of material (line-of-sight) | Chemical reaction on the substrate surface |
| Temperature | Lower temperatures | High temperatures required |
| Conformality | Limited; coats exposed surfaces | Excellent; uniform coating on complex 3D shapes |
| Typical Applications | Coating flat surfaces, temperature-sensitive materials | Semiconductor manufacturing, intricate parts |
Need expert advice on selecting the right deposition method for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Whether you require the precise control of PVD systems or the conformal coatings of CVD reactors, our solutions are designed to enhance your research and production outcomes.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory challenges and help you achieve superior thin film results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures



















