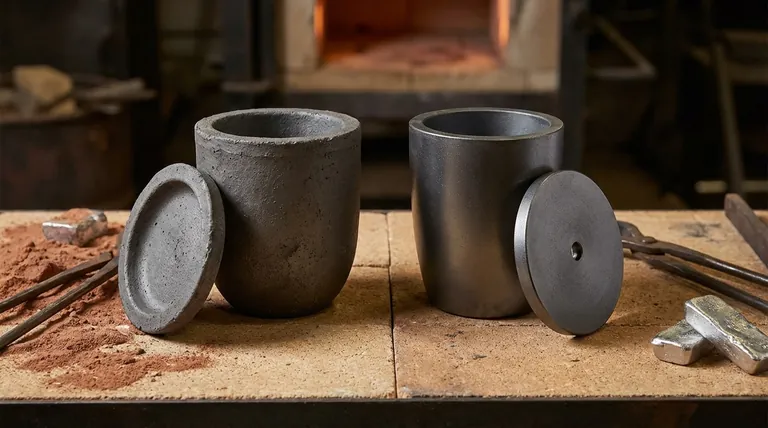
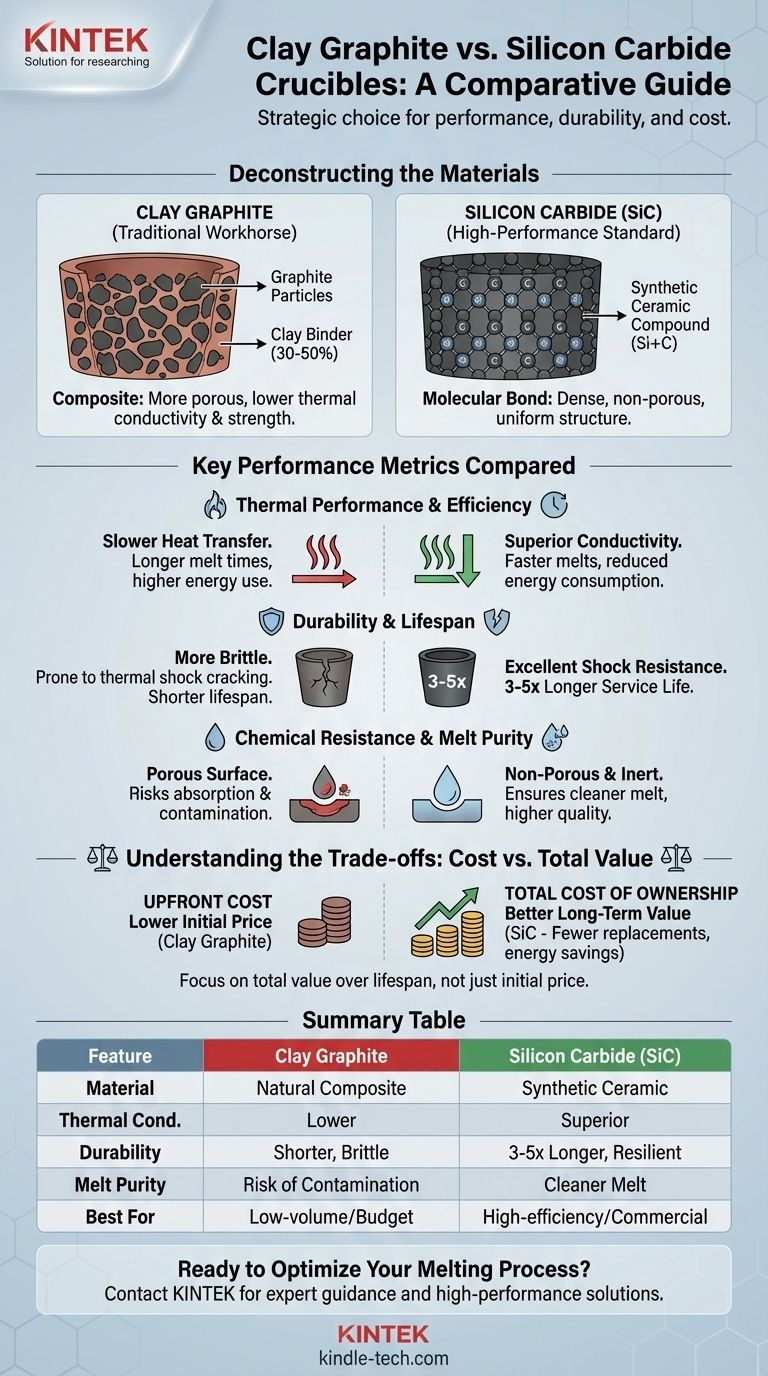
The fundamental difference between these crucibles lies in their material composition, which dictates their performance, durability, and cost. Silicon carbide (SiC) crucibles are a synthetic, high-performance ceramic offering superior strength, thermal conductivity, and a longer lifespan. In contrast, clay graphite crucibles are a mixture of natural clay and graphite, making them a more economical but less durable option with lower thermal performance.
Your choice between silicon carbide and clay graphite is not just a material preference; it's a strategic decision that balances upfront cost against long-term operational efficiency, melt quality, and total cost of ownership.

Deconstructing the Materials: Binder vs. Compound
Clay Graphite: The Traditional Workhorse
A clay graphite crucible is a composite material. It uses graphite particles for heat resistance and thermal properties, held together by a clay binder, typically comprising 30-50% of the mixture.
This clay binder makes the crucible more affordable but also introduces key limitations. It increases the material's porosity and reduces its overall thermal conductivity and strength compared to a more advanced material.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The High-Performance Standard
Silicon carbide is not a mixture; it is a synthetic ceramic compound of silicon and carbon bonded together at a molecular level. This creates a highly dense, uniform, and non-porous structure.
This structure is the source of its superior qualities. It possesses exceptional thermal conductivity for rapid heat transfer and outstanding high-temperature strength, allowing it to withstand intense thermal cycling.
Key Performance Metrics Compared
Thermal Performance and Efficiency
Silicon carbide's molecular structure allows it to transfer heat far more efficiently than clay graphite. This translates directly into faster melt times and reduced energy consumption, lowering your operational costs per cycle.
Clay graphite, with its less dense structure and insulating clay content, heats more slowly. This results in longer furnace times and higher fuel or electricity usage to achieve the same melt temperature.
Durability and Lifespan
The difference in longevity is significant. As noted, a silicon carbide crucible can have a service life 3 to 5 times longer than a clay graphite crucible.
This is due to SiC's superior resistance to thermal shock—the stress caused by rapid heating and cooling. Clay graphite is more brittle and prone to cracking under the same conditions, leading to more frequent and often unpredictable failures.
Chemical Resistance and Melt Purity
The non-porous surface of a silicon carbide crucible is highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and fluxes. This prevents the crucible from absorbing materials or leaching impurities, ensuring a cleaner melt and higher-quality final product.
The porous nature of clay graphite can be a liability. It can absorb moisture when not in use and may react with or absorb certain alloys and fluxes, potentially contaminating the melt and degrading the crucible itself over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Total Value
The Upfront Cost
There is no debate that clay graphite crucibles have a lower initial purchase price. For hobbyists, small-scale artisans, or operations with severe budget constraints, this can be the deciding factor.
However, focusing solely on this initial cost can be misleading and ultimately more expensive.
Calculating Total Cost of Ownership
True value is measured over the crucible's entire working life. Silicon carbide's higher initial cost is often quickly offset by its superior performance and longevity.
Consider these factors: a 3-5x longer lifespan means fewer replacements, faster melts mean lower energy bills and higher throughput, and cleaner melts mean fewer rejected castings. When combined, these advantages make SiC the more economical choice for most professional and commercial operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct crucible is a critical decision for your operational success. Use these guidelines to determine the best fit for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost for low-volume or infrequent use: Clay graphite is a viable starting point, but be prepared for its shorter lifespan and slower performance.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and long-term value: Silicon carbide is the clear choice for its faster melting, lower energy consumption, and significantly longer service life.
- If your primary focus is melt purity and casting quality: Silicon carbide's non-porous and chemically inert nature provides superior protection against contamination and ensures consistent results.
Ultimately, investing in the right crucible is an investment in the efficiency, quality, and safety of your entire melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Clay Graphite Crucible | Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay & graphite composite | Synthetic silicon carbide ceramic |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower | Superior (faster melting) |
| Durability & Lifespan | Shorter (more prone to cracking) | 3-5x longer (excellent thermal shock resistance) |
| Melt Purity | Porous (risk of contamination) | Non-porous (cleaner melt) |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best For | Low-volume use, budget-conscious operations | High-efficiency, high-purity commercial operations |
Ready to Optimize Your Melting Process?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the efficiency, quality, and safety of your operation. The expert team at KINTEK is here to help you navigate this important decision.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Get personalized recommendations based on your specific metals, volumes, and furnace type.
- High-Performance Equipment: Access top-quality crucibles designed for superior results.
- Long-Term Value: Invest in solutions that reduce your total cost of ownership through energy savings and extended lifespan.
Don't leave your melt quality to chance. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's crucible needs and find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What is a crucible furnace used for melting of? Melt Non-Ferrous Metals from Aluminum to Gold
- What are crucibles used for in lab? Ensuring Accurate, High-Temperature Sample Analysis
- Do you need a different crucible for different metals? Ensure Purity and Safety in Your Lab
- What temperature is a crucible? Choosing the Right Material for Your Heat Needs
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible required for pack cementation chromizing? Ensure Purity at 1050°C
- What is the role of a blast furnace or crucible melting furnace? Achieve Precise Aluminum Alloy Preparation
- Can you melt gold in a ceramic crucible? Discover the Right Crucible for Safe Melting



















