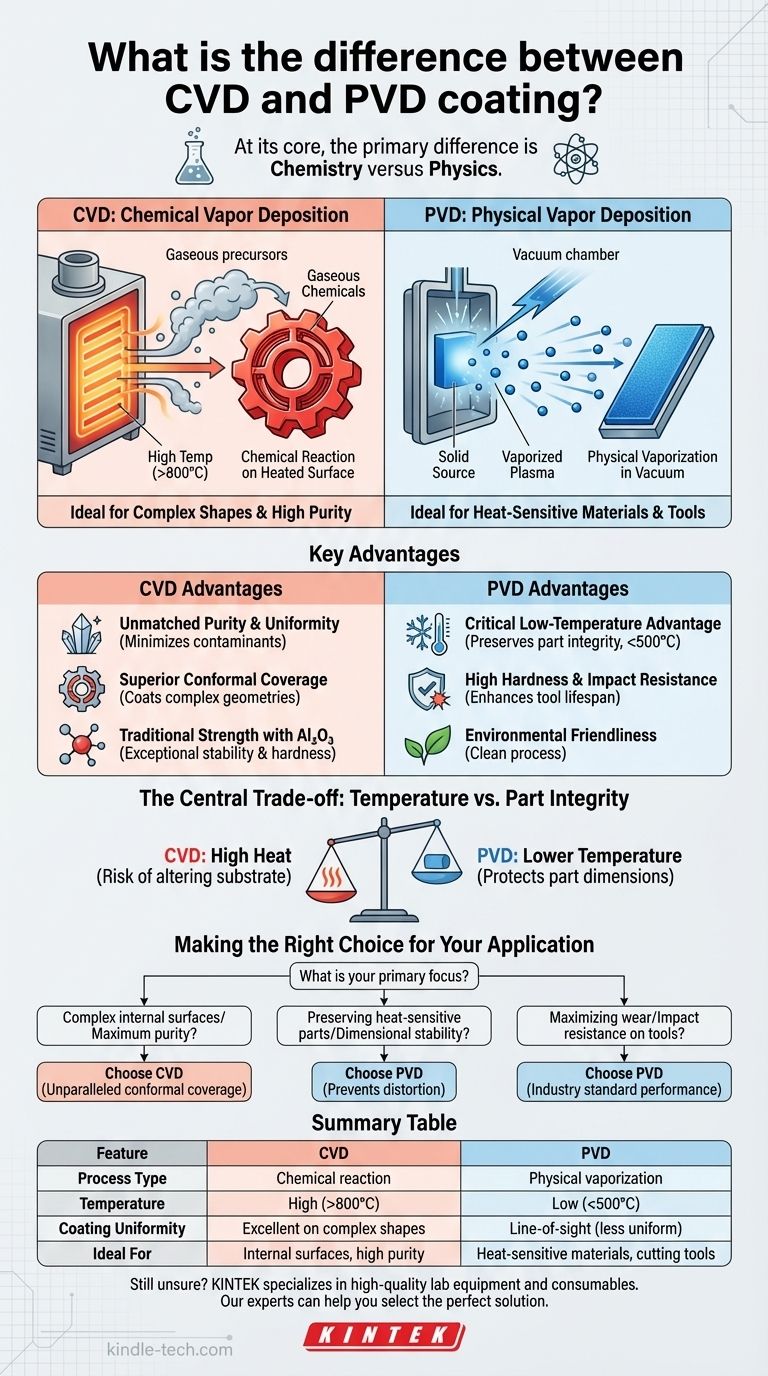
At its core, the primary difference is chemistry versus physics. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses a chemical reaction between gaseous precursors on a heated surface to create a solid film. In contrast, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) involves physically vaporizing a solid material in a vacuum and allowing its atoms to deposit onto a substrate, a process more akin to atomic spray painting.
The choice between CVD and PVD is fundamentally a trade-off between process temperature and desired outcome. CVD's high heat enables highly uniform coatings on complex shapes but risks damaging the part, while PVD's lower temperature preserves the part's integrity, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials.

How the Processes Fundamentally Differ
To select the right coating, you must first understand how each method works. Their names—Chemical versus Physical—point directly to their core distinction.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Chemical Reaction
In the CVD process, the part to be coated is placed in a chamber and heated to a very high temperature.
Gaseous chemical compounds are then introduced into the chamber. These gases react with the hot surface of the part, decomposing and forming a new, solid, and highly adherent coating layer.
This method ensures the coating material can penetrate and uniformly cover even the most complex shapes and internal surfaces.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The Physical Transfer
The PVD process also takes place in a high-vacuum chamber, but it operates at significantly lower temperatures.
A solid source material (like titanium or chromium) is bombarded with energy, causing it to vaporize into a plasma of atoms or molecules.
An electrical field then guides these vaporized particles, which travel in a line-of-sight path and deposit onto the cooler surface of the part, forming a dense and hard coating.
Key Advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is often chosen when the geometry of the part or the required purity of the coating is the primary concern.
Unmatched Purity and Uniformity
Because CVD uses gaseous coating materials, it's possible to achieve extremely high levels of purity, minimizing contaminants in the final film.
The gas-phase nature of the process allows the coating to form uniformly across the entire exposed surface.
Superior Conformal Coverage
CVD excels at coating complex shapes and internal channels. The reactant gases can flow into and around intricate features, ensuring a consistent coating thickness everywhere.
This ability to create precise, conformal layers is difficult to replicate with line-of-sight PVD methods.
Traditional Strength with Al₂O₃
Historically, CVD has been the superior method for depositing materials like Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), which offers exceptional chemical stability, hardness, and wear resistance at a low cost.
Key Advantages of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD has gained widespread adoption by solving the single biggest drawback of CVD: heat. This has made it the default choice for a vast range of modern applications.
The Critical Low-Temperature Advantage
This is the most significant advantage of PVD. Its lower process temperatures prevent the substrate material from being altered, distorted, or softened.
For example, coating a High-Speed Steel (HSS) end mill with high-temperature CVD would ruin its carefully engineered hardness and straightness. PVD is the ideal choice here.
High Hardness and Impact Resistance
PVD coatings are known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and impact resistance.
These properties make PVD the go-to solution for enhancing the performance and lifespan of cutting tools, molds, and other components subject to intense friction and abrasion.
Environmental Friendliness
The PVD process is clean and does not produce hazardous byproducts, making it a more environmentally friendly coating technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally "better." The optimal choice depends entirely on the material of your part and your performance goals.
Temperature vs. Part Integrity
This is the central trade-off. CVD's intense heat (often >800°C) can deliver excellent conformal coatings but will damage any heat-treated or dimensionally sensitive substrate. PVD's lower temperatures (typically <500°C) protect the part's integrity.
Coating Geometry vs. Process
CVD is the master of complexity, effortlessly coating internal bores and intricate designs. PVD is largely a line-of-sight process, which can make achieving uniform thickness on complex geometries more challenging.
Material Options and Cost
While CVD holds an advantage with certain materials like Al₂O₃, modern PVD technology has expanded its range of available coatings, gradually outperforming CVD in many areas. PVD often incurs higher equipment costs, but this is frequently justified by the value of preserving the underlying part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your component and its intended use.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal surfaces or achieving maximum purity: CVD's gas-based, high-temperature process provides unparalleled conformal coverage.
- If your primary focus is preserving the dimensional stability and hardness of a heat-sensitive part: PVD's low-temperature process is the only viable choice to prevent distortion and damage.
- If your primary focus is maximizing wear and impact resistance on cutting tools: PVD offers superior performance and is the industry standard for applications like HSS end mills.
Ultimately, selecting the right coating is less about the coating itself and more about respecting the limitations of the material you are trying to protect.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction | Physical vaporization |
| Temperature | High (>800°C) | Low (<500°C) |
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent on complex shapes | Line-of-sight (can be less uniform) |
| Ideal For | Internal surfaces, high purity | Heat-sensitive materials, cutting tools |
Still unsure whether CVD or PVD is right for your laboratory equipment? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific coating needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance durability, performance, and efficiency in your lab. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can benefit your research and development processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
- What are the advantages of PECVD over CVD? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method



















