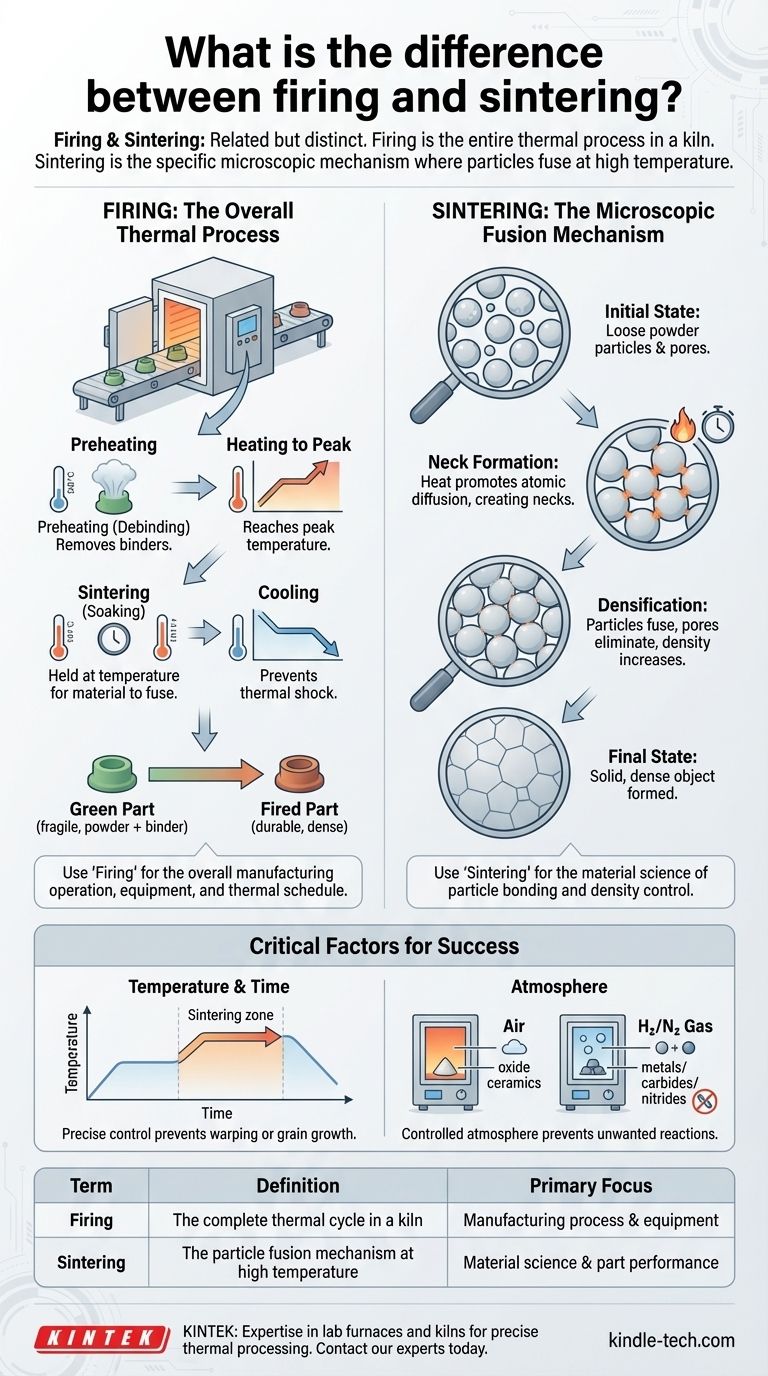
In practice, the terms "firing" and "sintering" are often used interchangeably, but they describe different aspects of the same goal. Firing refers to the entire thermal process of heating a "green" part in a kiln to make it hard and durable. Sintering is the specific, microscopic mechanism that occurs at high temperatures during the firing cycle, where individual material particles fuse together to create a solid mass.
While a part is fired in a kiln, it is the process of sintering that actually transforms the loose powder into a dense, strong final product. Understanding this distinction is key to controlling the outcome.
The Transformation: From Powder to Solid State
To truly grasp the difference, you must understand the journey a component takes from a fragile, powder-based form to a robust, finished part. This is a multi-stage thermal process.
The 'Green' Part
Before any heating occurs, the material (like ceramic or metal powder) is mixed with a binder and pressed into the desired shape. This initial object is called a "green" part, which is fragile and chalky.
The Firing Cycle: A Controlled Thermal Journey
Firing is the complete, carefully controlled heating and cooling cycle that the green part undergoes in a kiln. This cycle has distinct phases, often managed by moving the part through different temperature zones.
A typical firing process includes:
- Preheating (Debinding): The part is heated slowly to burn away the organic binders that held the powder together in its green state.
- Heating to Peak Temperature: The temperature is raised to the point where the primary transformation will occur.
- Sintering (Soaking): The part is held at this peak temperature for a set time. This is where the real magic happens as the material particles bond together.
- Cooling: The part is cooled down in a controlled manner to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
Sintering: The Microscopic Fusion
Sintering is the specific scientific phenomenon that provides the strength. It is not the entire heating process, but the crucial event that happens at the highest temperature.
During sintering, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the individual powder particles. This atomic movement first creates small "necks" between particles, then gradually eliminates the pores and gaps between them, fusing the powder into a dense, solid object.
Clarifying the Terminology: Firing vs. Sintering
While technically distinct, context determines which term is more appropriate. The overlap in usage stems from the fact that you cannot have sintering without a firing process.
Use 'Firing' for the Overall Operation
"Firing" is the best term when discussing the entire manufacturing process, the equipment (kilns), and the overall thermal schedule. It is the verb of the operation.
For example, an operator "fires" a batch of parts according to a specific time and temperature profile.
Use 'Sintering' for the Scientific Mechanism
"Sintering" is a more precise, technical term used to describe the actual material science of particle bonding through atomic diffusion.
Engineers and scientists talk about optimizing "sintering" by adjusting particle size, temperature, or atmospheric conditions to achieve maximum density.
Common Industry Usage
In traditional ceramics like pottery and bricks, the term firing is almost exclusively used.
In technical fields like powder metallurgy (for metals) and advanced ceramics (for engineered components), sintering is used more frequently because the focus is on precise control of the material's final microstructure and density.
Understanding the Critical Factors
Achieving a successful outcome depends on carefully controlling the conditions during the firing cycle to promote optimal sintering.
The Role of Temperature and Time
Sintering is driven by temperature. Higher temperatures increase the rate of atomic diffusion, but if the temperature is too high or held for too long, the part can warp or its grain structure can grow too large, weakening it.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Many materials cannot be fired in open air. Metals, carbides, and nitrides require specific gas atmospheres (like hydrogen or nitrogen) during sintering.
This controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that would otherwise ruin the material's properties. Oxide ceramics, on the other hand, can typically be fired in air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your focus will determine which term and concept is more relevant to your work.
- If your primary focus is on manufacturing operations: Think in terms of the entire firing cycle, optimizing kiln throughput and ensuring consistent heating and cooling profiles.
- If your primary focus is on material science and part performance: Concentrate on the sintering mechanism itself, manipulating variables like material composition and atmosphere to achieve target density and strength.
- If your primary focus is clear communication: Use "firing" to describe the general process of heating in a kiln and "sintering" to explain the specific stage where the part gains its strength.
By understanding both the macro process of firing and the micro mechanism of sintering, you gain full control over turning simple powder into a high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Term | Definition | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Firing | The complete thermal cycle in a kiln | Manufacturing process & equipment |
| Sintering | The particle fusion mechanism at high temperature | Material science & part performance |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? Whether you're optimizing a firing cycle or achieving perfect sintering density, KINTEK's expertise in lab furnaces and kilns is your solution. We provide the equipment and consumables to transform powders into high-performance components. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















