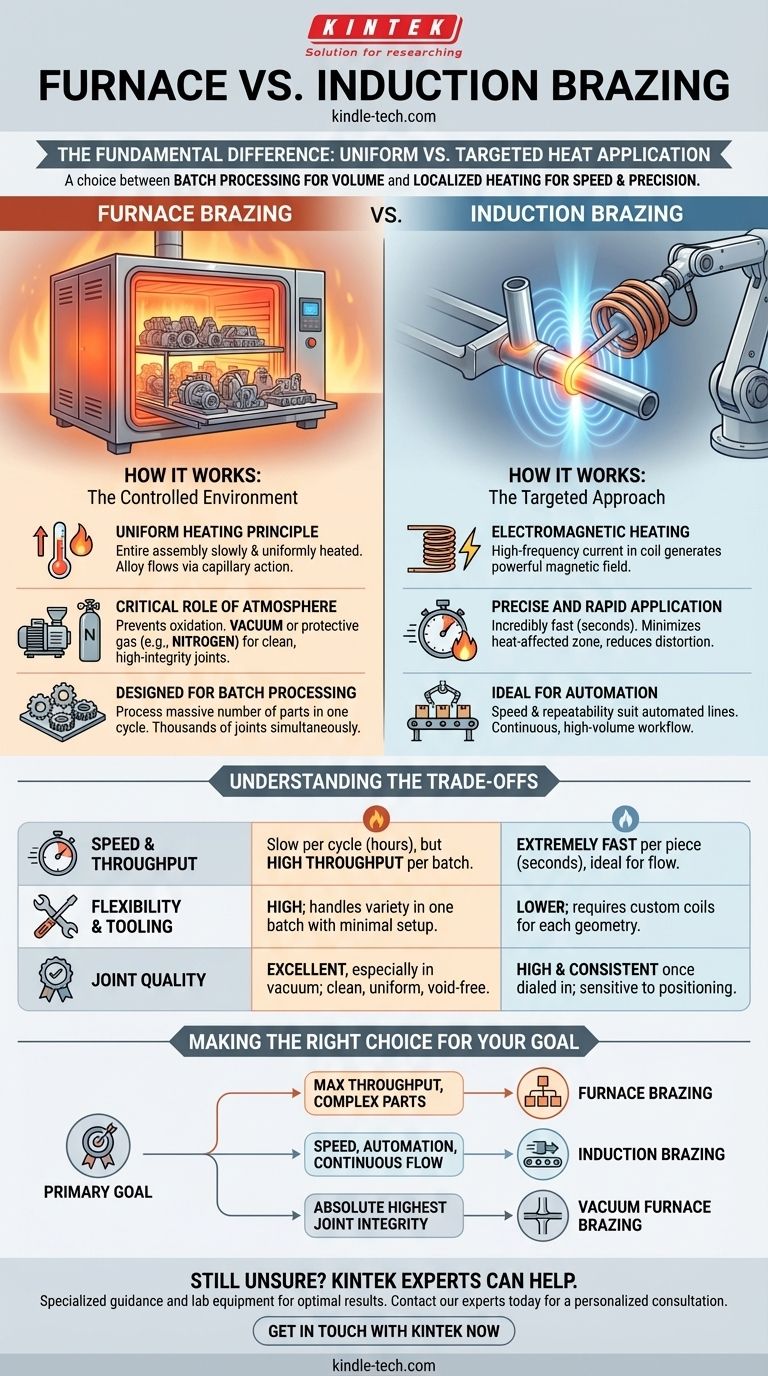
The fundamental difference between furnace brazing and induction brazing lies in the method of heat application. Furnace brazing heats an entire assembly uniformly within a controlled atmosphere, making it ideal for processing many parts at once. In contrast, induction brazing uses a targeted electromagnetic field to rapidly and selectively heat only the specific joint area, excelling in speed and automated production lines.
Your choice between these methods is a decision between batch processing for volume and localized heating for speed and precision. Furnace brazing is unmatched for complex assemblies or large quantities, while induction brazing is the superior choice for integrating into a high-speed, continuous-flow manufacturing process.

How Furnace Brazing Works: The Controlled Environment
Furnace brazing is a thermal process that relies on bringing entire assemblies up to brazing temperature within a carefully managed furnace. The success of the process depends heavily on controlling the environment.
The Uniform Heating Principle
The core concept is simple: the entire assembly, including the base metals and the pre-placed brazing filler alloy, is slowly and uniformly heated. Once it reaches a temperature above the filler metal's melting point, the alloy flows into the joints via capillary action.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
To prevent the parts from oxidizing at high temperatures, the process is performed in a controlled atmosphere. This is most often a vacuum or a protective gas like nitrogen.
Vacuum brazing, where air is pumped out of the furnace, is particularly effective. It eliminates oxygen and other contaminants, resulting in exceptionally clean, strong, and high-integrity joints for critical applications.
Designed for Batch Processing
A key advantage of furnace brazing is its ability to process a massive number of parts in a single cycle. Assemblies can be loaded onto trays and placed in the furnace, allowing for the creation of thousands of joints simultaneously.
How Induction Brazing Works: The Targeted Approach
Induction brazing operates on a completely different principle. Instead of heating the entire part, it focuses intense energy precisely where it is needed—at the joint itself.
Electromagnetic Heating
This method uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the joint area.
The magnetic field induces electrical "eddy" currents within the metal parts. The resistance of the metal to the flow of these currents generates intense, localized heat very quickly.
Precise and Rapid Application
The heating is incredibly fast, often taking only a few seconds. Because the heat is confined to the joint, it minimizes the heat-affected zone, reduces part distortion, and protects nearby sensitive components.
Ideal for Automation
The speed and repeatability of induction brazing make it exceptionally well-suited for automated and semi-automated production lines. It can be easily integrated into a manufacturing cell for a continuous, high-volume workflow.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the right choice depends entirely on your application's specific priorities. The key trade-offs involve balancing speed, volume, flexibility, and final joint quality.
Speed vs. Throughput
Induction is dramatically faster per piece, making it ideal for single-piece flow. Furnace brazing is slow per cycle (often hours), but its ability to process thousands of parts at once gives it an enormous throughput for large batches.
Flexibility and Tooling
Induction brazing requires a custom-designed coil for each specific joint geometry. This makes it less flexible for job shops with a high mix of different parts. Furnaces are highly flexible and can handle a wide variety of part shapes and sizes in a single batch with minimal setup changes.
Joint Quality and Consistency
Vacuum furnace brazing is often considered the gold standard for quality. It produces the cleanest, most uniform, and void-free joints because the entire part is heated evenly in a pure environment, preventing oxides from forming.
Induction brazing produces highly consistent joints once the process is dialed in, but it is more susceptible to variations in part positioning and coil alignment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires aligning the method's strengths with your primary manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput for large batches of complex parts: Furnace brazing is the clear choice for its ability to process thousands of assemblies simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is speed and integration into an automated assembly line: Induction brazing is superior for its rapid, repeatable heating of individual joints in a continuous flow.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest joint integrity for critical components: Vacuum furnace brazing provides the cleanest, strongest, and most reliable results by eliminating atmospheric contamination.
Understanding these core differences in heating method is the key to selecting the most effective and economical process for your specific manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Furnace Brazing | Induction Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Uniform heating of entire assembly in a controlled atmosphere | Targeted, localized heating of the joint via electromagnetic field |
| Best For | High-volume batches, complex assemblies, highest joint integrity | High-speed automation, single-piece flow, minimal heat distortion |
| Speed | Slow per cycle (hours), but high throughput per batch | Extremely fast per piece (seconds) |
| Flexibility | High; handles various parts in one batch | Lower; requires custom coils for each joint geometry |
| Joint Quality | Excellent, especially in a vacuum; clean and uniform | High and consistent, but sensitive to part positioning |
Still unsure which brazing method is right for your project?
The team at KINTEK specializes in providing expert guidance and the right lab equipment for your brazing applications. We understand that the choice between furnace and induction brazing impacts your production efficiency, cost, and final product quality.
Let us help you achieve optimal results. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the steps of the annealing process? Master the 3 Stages to Optimize Material Properties
- What are powder sintering methods? A Guide to Metal & Ceramic Part Manufacturing
- What is the role of a vacuum drying oven in PEO-based membrane treatment? Achieve Peak Solid-State Battery Purity
- What is a sinter furnace? Transform Powdered Materials into High-Performance Parts
- Why is vacuum heat treatment done? Achieve Superior Metal Properties with Pristine Surfaces
- What is plasma pyrolysis waste to energy? Harness Extreme Heat for Maximum Waste Conversion
- What role does ammonolysis reaction equipment play in Co3Mo3N synthesis? Master High-Performance Catalyst Production
- What are sintered products? Engineered Materials Built from Powder for Superior Performance



















