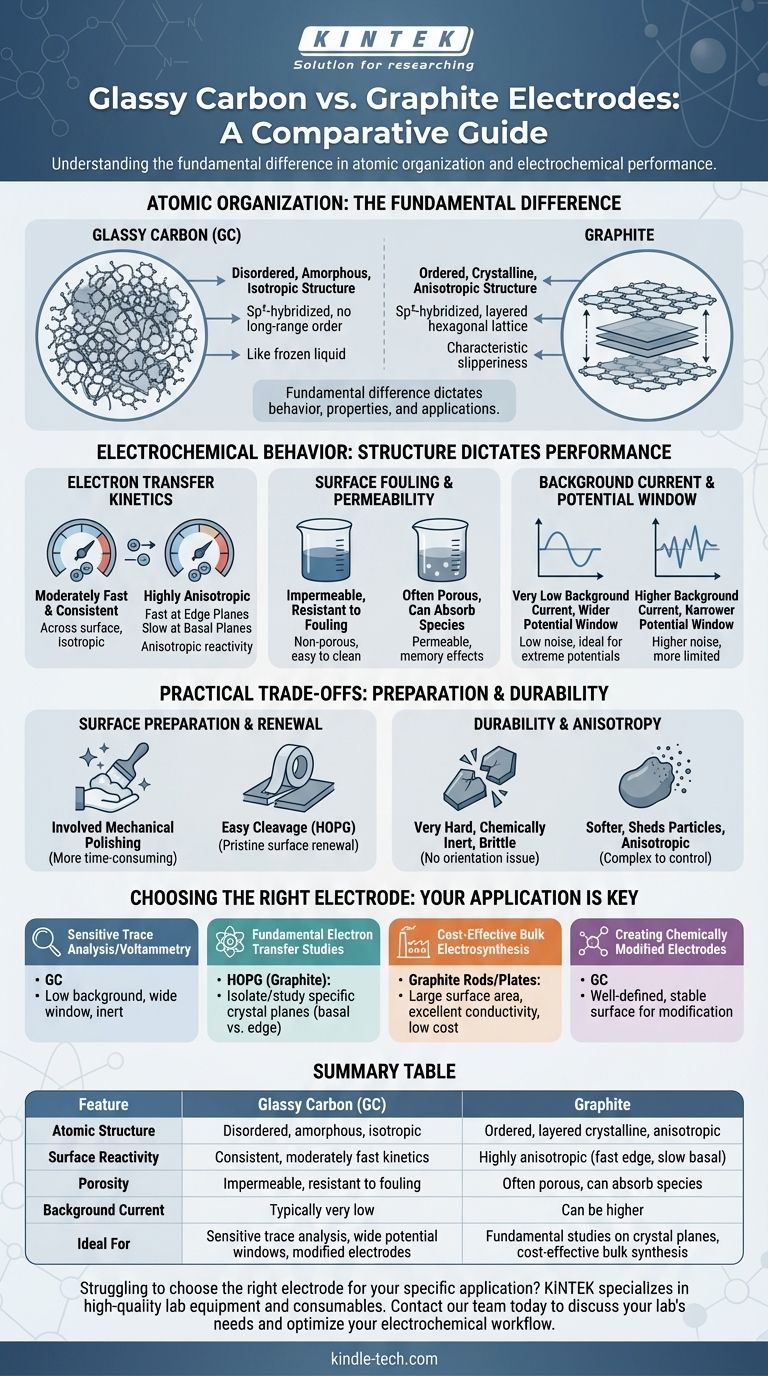
At their core, the difference between a glassy carbon (GC) and a graphite electrode is a matter of atomic organization. While both are made of sp²-hybridized carbon, glassy carbon has a disordered, tangled structure like a frozen liquid, whereas graphite has a highly ordered, layered crystalline structure. This fundamental structural difference dictates their electrochemical behavior, surface properties, and ideal applications.
The choice between glassy carbon and graphite is a foundational decision in electrochemistry. It is a trade-off between the disordered, inert, and impermeable surface of GC and the ordered, anisotropic, and renewable surface of crystalline graphite.
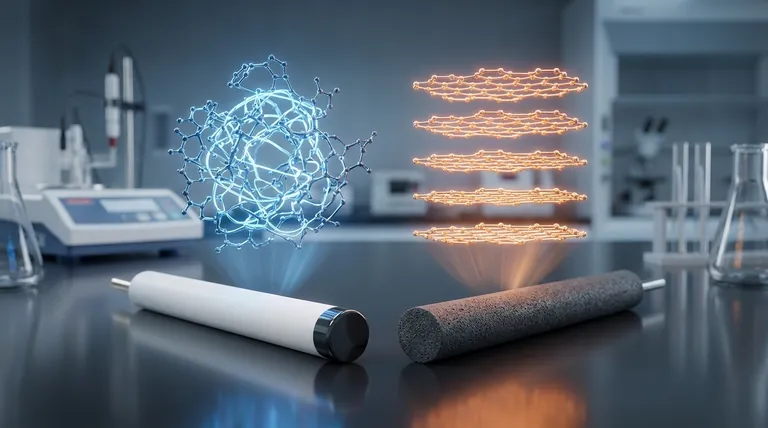
The Fundamental Difference: Atomic Structure
The properties of these two materials diverge at the nanoscale. Understanding this is key to predicting their performance in an electrochemical cell.
Graphite's Crystalline Order
Graphite consists of stacked sheets of graphene. Within each sheet, carbon atoms are strongly bonded in a hexagonal lattice.
These sheets are held together by weak van der Waals forces, allowing them to easily slide past one another, which gives graphite its characteristic slipperiness.
This layered structure creates two distinct surface types: the basal plane (the flat face of a sheet) and the edge plane (the side of a sheet), which have vastly different chemical and electronic properties.
Glassy Carbon's Disordered State
Glassy carbon, also known as vitreous carbon, is a non-graphitizing carbon. It is formed by the controlled heating of polymer precursors.
Instead of forming neat layers, its sp²-carbon structure is a tangled, chaotic network of graphene-like fragments. It possesses short-range order but lacks the long-range crystalline order of graphite.
This amorphous structure makes it isotropic, meaning its properties are the same in all directions. It is also extremely hard, brittle, and impermeable to gases and liquids, much like glass.
How Structure Dictates Electrochemical Behavior
The atomic arrangement directly translates into performance differences that are critical for experimental success.
Electron Transfer Kinetics
Graphite's reactivity is highly anisotropic. Electron transfer is extremely fast at the edge plane sites but very slow on the basal plane. The overall performance of a graphite electrode depends on the ratio of edge-to-basal sites exposed to the solution.
Glassy carbon, with its random mix of edge- and basal-like character, exhibits moderately fast electron transfer rates. Its key advantage is consistency; the kinetics are uniform across its entire surface.
Surface Fouling and Permeability
GC's glass-like, non-porous structure makes it highly resistant to fouling from species penetrating the electrode bulk. Solvents and analytes cannot soak into it, which simplifies cleaning and leads to more reproducible results.
Many forms of graphite, by contrast, are porous. They can absorb solvent or analyte species, which can either be a benefit (for preconcentration) or a drawback (causing memory effects and contamination).
Background Current and Potential Window
Due to its high purity and low surface area, a properly polished glassy carbon electrode typically provides a very low background current.
This low noise floor, combined with its chemical inertness, often results in a wider usable potential window compared to many standard grades of graphite, making GC ideal for studying processes at extreme potentials.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Choosing an electrode is also a practical decision involving preparation, durability, and experimental goals.
Surface Preparation and Renewal
Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), a research-grade form of graphite, can be easily cleaved with adhesive tape. This action peels off the top layers to expose a pristine, atomically flat basal plane surface for each experiment.
Glassy carbon cannot be cleaved. It requires a more involved mechanical polishing procedure using fine alumina or diamond slurries, followed by electrochemical cleaning, to produce a smooth, reproducible surface. This process is effective but more time-consuming.
Durability and Anisotropy
GC is very hard and chemically inert but can be brittle and may shatter if dropped. Its key mechanical advantage is being isotropic, which simplifies analysis as there is no orientation to consider.
Graphite is softer and can shed particles into the solution, but it is generally robust. Its anisotropy is its most complex feature; results can vary dramatically depending on how the electrode is oriented and prepared, a factor that must be controlled in fundamental studies.
Choosing the Right Electrode for Your Application
Your experimental goal should be the final determinant in your choice of electrode.
- If your primary focus is sensitive trace analysis or voltammetry: Glassy carbon is often the superior choice due to its low background current, wide potential window, and inert surface.
- If your primary focus is studying fundamental electron transfer: Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) is the ideal tool, as it allows you to isolate and study reactions on specific crystal planes (basal vs. edge).
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk electrosynthesis: Standard graphite rods or plates offer a large surface area and excellent conductivity at a low cost.
- If your primary focus is creating chemically modified electrodes: Glassy carbon's well-defined and stable surface provides a reliable and reproducible foundation for surface modification.
Understanding this structural distinction empowers you to move beyond simply choosing an electrode and begin designing your experiment with intention.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Glassy Carbon (GC) | Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Structure | Disordered, amorphous, isotropic | Ordered, layered crystalline, anisotropic |
| Surface Reactivity | Consistent, moderately fast kinetics | Highly anisotropic (fast at edge planes, slow at basal planes) |
| Porosity | Impermeable, resistant to fouling | Often porous, can absorb solvents/analytes |
| Background Current | Typically very low | Can be higher |
| Ideal For | Sensitive trace analysis, wide potential windows, modified electrodes | Fundamental studies on crystal planes, cost-effective bulk synthesis |
Struggling to choose the right electrode for your specific application? The performance of your electrochemical experiments depends on using the correct tools. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of electrodes tailored for research and analysis. Our experts can help you select the ideal electrode material to ensure accurate, reproducible results. Contact our team today to discuss your lab's needs and optimize your electrochemical workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties and applications of glassy carbon electrodes? | Your Guide to Superior Electrochemical Analysis
- How should an electrode be positioned for modification via drop-coating? Master the Upside-Down Technique
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- How should metal electrode holders be stored to ensure their longevity? Prevent Rust and Ensure Peak Performance
- What are the advantages of using a platinized titanium mesh? Boost Catalytic Efficiency and Durability
- How should a graphite electrode be cleaned and stored after an experiment? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What role does a non-consumable tungsten electrode play in arc furnaces? Master High-Purity Alloy Melting
- Why are multiple Ag/AgCl reference electrodes placed at different heights in bedBES? Mapping Potential Heterogeneity



















