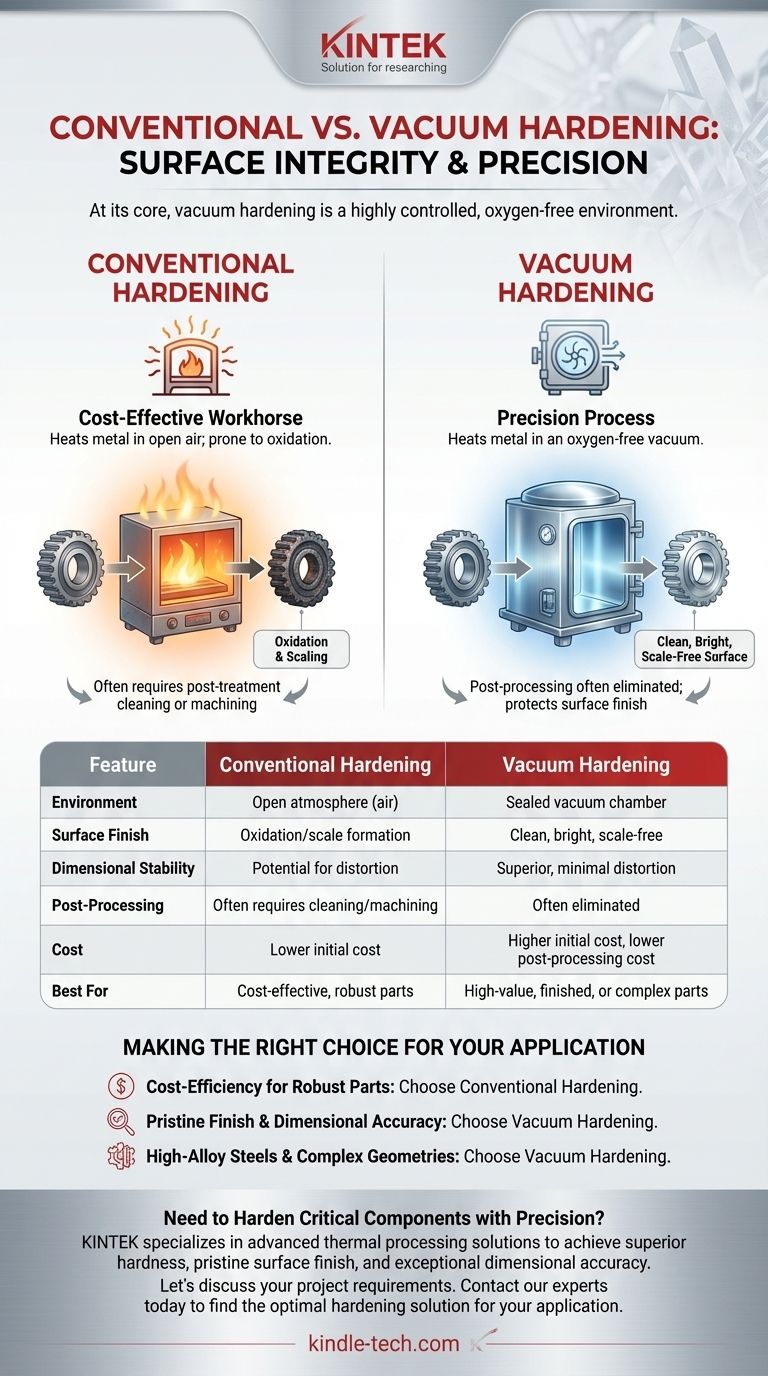
At its core, vacuum hardening is not a different process from hardening, but rather a highly controlled environment in which hardening takes place. While conventional hardening exposes metal to the open atmosphere during heating, vacuum hardening performs the same heating and cooling cycle inside a vacuum chamber. This single change—the removal of air—prevents surface reactions, resulting in a cleaner, more dimensionally accurate final product.
The fundamental choice between conventional and vacuum hardening is a choice about surface integrity. Conventional hardening is a cost-effective workhorse, while vacuum hardening is a precision process that protects the part's surface, eliminating the need for costly post-treatment cleaning or machining.

What is Hardening? A Foundational Overview
The Core Principle: Heat and Quench
All steel hardening operates on a simple principle: heat the metal to a specific critical temperature to change its internal crystal structure, then cool it rapidly (a process called quenching).
This rapid cooling traps the altered structure, dramatically increasing the metal's hardness and wear resistance. The specific temperatures, heating times, and quenching methods vary based on the type of steel and the desired properties.
The Problem with Air
In conventional hardening, this heating process happens in a furnace filled with air. The oxygen in the atmosphere reacts with the hot surface of the metal, causing oxidation (scaling) and potentially altering the carbon content on the surface (decarburization), which can soften the part.
How Vacuum Hardening Redefines the Process
Vacuum hardening follows the same heat-and-quench principle but performs it inside a sealed, computer-controlled chamber from which nearly all air has been removed.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Environment
By creating a vacuum, the process removes the reactive elements—primarily oxygen—that cause surface defects.
This oxygen-free environment completely prevents oxidation. As a result, parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright, and scale-free metallic surface.
The Impact on Surface Integrity and Finish
The most significant advantage of vacuum hardening is the pristine surface finish. Since there is no scale to remove, secondary operations like sandblasting, grinding, or machining are often eliminated.
This is especially critical for finished parts with tight tolerances or complex geometries where post-hardening cleaning could damage the component or alter its dimensions.
Unmatched Precision and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces offer exceptional computer-controlled temperature regulation. This ensures the entire part, regardless of its complexity, heats and cools at a uniform rate.
This uniformity minimizes internal stresses and distortion, resulting in superior dimensional stability. Furthermore, the digital control ensures that every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, is treated with identical parameters, guaranteeing high repeatability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right hardening method is a technical and financial decision. Neither process is universally superior; they are tools for different jobs.
The Case for Conventional Hardening
For many general-purpose components where surface finish is not a primary concern or where subsequent machining is already planned, conventional hardening is the most cost-effective solution.
It provides the necessary increase in hardness and durability for a vast range of applications at a lower price point. It is the reliable workhorse of the heat-treating industry.
The Investment in Vacuum Hardening
Vacuum hardening is a more expensive process due to the sophisticated equipment involved. However, this initial cost is often offset by the elimination of post-processing steps.
When you factor in the saved labor and time from not having to clean, grind, or machine away a scaled surface, vacuum hardening can become the more economical choice for high-value or finished parts.
Material and Geometric Considerations
Certain materials, particularly high-alloy tool steels, are highly sensitive to surface decarburization. For these metals, vacuum hardening is not just an option but a necessity to preserve their intended performance characteristics.
Complex parts with intricate details or thin sections also benefit immensely from the uniform heating of a vacuum furnace, which prevents warping and distortion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate process, you must align the method with your project's most critical outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for robust parts: Conventional hardening provides the required mechanical properties without the premium cost.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and dimensional accuracy: Vacuum hardening is the definitive choice to avoid post-treatment and preserve tolerances.
- If your primary focus is processing high-alloy steels or complex geometries: Vacuum hardening offers the necessary control to prevent material degradation and distortion.
Ultimately, choosing the right hardening process is about matching the tool to the specific demands of the component and its application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Hardening | Vacuum Hardening |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Open atmosphere (air) | Sealed vacuum chamber |
| Surface Finish | Oxidation/scale formation | Clean, bright, scale-free |
| Dimensional Stability | Potential for distortion | Superior, minimal distortion |
| Post-Processing | Often requires cleaning/machining | Often eliminated |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, lower post-processing cost |
| Best For | Cost-effective, robust parts | High-value, finished, or complex parts |
Need to Harden Critical Components with Precision?
Choosing the right hardening process is essential for the performance and longevity of your parts. KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum hardening, to meet the demanding needs of laboratories and manufacturers.
Our expertise ensures your high-alloy steels and complex geometries achieve superior hardness, a pristine surface finish, and exceptional dimensional accuracy—all while potentially reducing your total cost by eliminating costly post-processing.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the optimal hardening solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How hot can an industrial furnace get? Find the Right Temperature for Your Process
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- What are the applications of induction hardening? Boost Component Durability for Automotive & Industrial Parts
- How does the discharge effect of a DC pulse power supply affect SPS nickel-based alloys? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What is the step by step process of case hardening? A Guide to Creating Durable, Wear-Resistant Parts
- How are vacuum furnaces categorized based on their degree of vacuum? Select the Right Level for Your Process
- What is plasma nitriding? Achieve Superior Wear Resistance and Component Durability
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc furnace with a tungsten electrode? Achieve High-Purity Alloy Melting



















