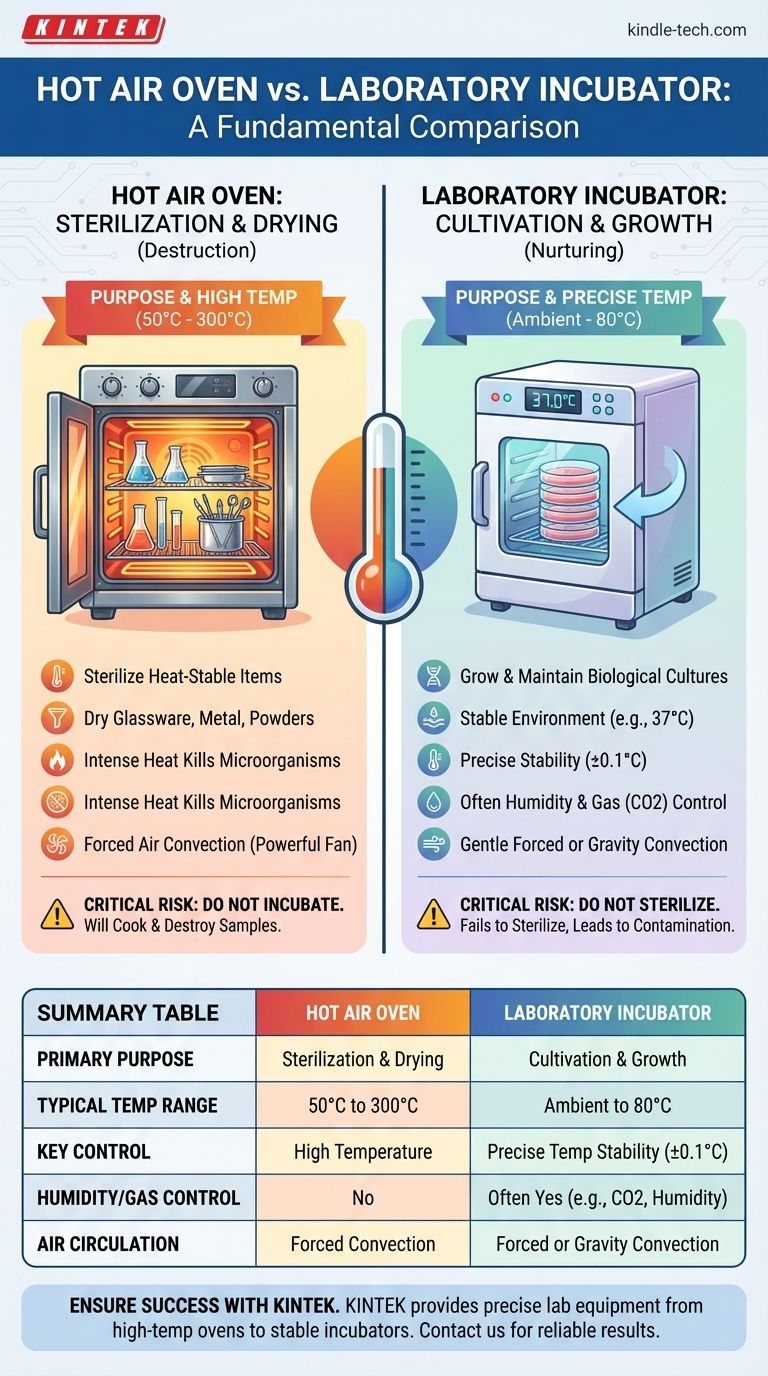
At a fundamental level, the difference between a hot air oven and a laboratory incubator is their intended purpose, which dictates their operating temperature range. A hot air oven uses very high temperatures (typically 50°C to 300°C) for sterilization and drying. In contrast, a laboratory incubator uses a much lower, precisely controlled temperature range (often near ambient to 80°C) to grow and maintain biological cultures.
Choosing between them isn't about which is "better," but about their opposing functions. Ovens use high heat to destroy microorganisms and remove moisture, while incubators use gentle, stable heat to nurture and cultivate life.

The Core Functional Difference: Purpose and Temperature
While both instruments are insulated boxes that generate heat, their applications are mutually exclusive. Using one for the other's task will lead to complete failure of the procedure.
Hot Air Ovens: The Power of High Temperatures
A hot air oven is designed for sterilization and drying. It uses forced air circulation to distribute high-temperature dry heat uniformly.
The primary applications include sterilizing heat-stable items like glassware, metal instruments, and powders. The intense heat (e.g., 160°C for 2 hours) denatures proteins and effectively kills all forms of life, including resilient bacterial spores.
Laboratory Incubators: The Art of Stable Cultivation
A laboratory incubator is designed to provide a controlled, stable environment for cultivation. Its goal is to mimic the conditions necessary for organisms or cells to grow.
For most biological applications, this means maintaining a constant temperature, often around human body temperature (37°C). Incubators are used for growing bacterial cultures, cell and tissue cultures, and for biochemical or enzymatic studies that require a specific, stable thermal environment over long periods.
Key Differences in Design and Control
The opposing functions of destroying versus nurturing lead to significant differences in how these instruments are designed and what parameters they control.
Temperature Range and Precision
The most obvious difference is the temperature range. A hot air oven must achieve very high temperatures, while an incubator operates in a much lower range.
More importantly, an incubator's value lies in its thermal stability. It must maintain a set point with extreme precision (e.g., ±0.1°C), as even small fluctuations can stress or kill sensitive cell cultures. An oven's precision is less critical than its ability to reach and sustain a high sterilizing temperature.
Humidity and Gas Control
Many advanced incubators, particularly CO2 incubators, also control humidity and atmospheric gas composition. They maintain high humidity to prevent samples from drying out and regulate CO2 levels to maintain the pH of the cell culture media.
Hot air ovens do not have these features. In fact, their function is often to drive moisture out of objects.
Air Circulation
Hot air ovens typically use powerful fans for forced air convection to ensure even heat distribution and rapid heating.
Incubators may use either forced (fan-assisted) convection for uniformity or gentler gravity convection, where air circulates naturally as it's heated. Gravity convection is often preferred for applications where the airflow from a fan could dry out samples or disturb cell cultures.
Understanding the Critical Risks: Why You Can't Swap Them
Confusing these two instruments is one of the most common and costly mistakes in a lab setting. The consequences are absolute and predictable.
Using an Oven for Incubation
Attempting to grow cell cultures in a hot air oven, even at its lowest setting, will fail. The temperature control is not precise enough, the environment is too dry, and the forced airflow is too harsh. You will invariably cook and destroy your samples.
Using an Incubator for Sterilization
Attempting to sterilize glassware or instruments in an incubator is equally futile and dangerous. The maximum temperature of an incubator is far too low to achieve sterilization. This will result in contaminated equipment, leading to failed experiments and the potential spread of microorganisms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is a simple decision once you define your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is sterilization, drying glassware, or heat-testing materials: You must use a hot air oven for its high-temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is growing and maintaining cell cultures, bacteria, or tissue: You must use a laboratory incubator for its precise, stable, and life-sustaining environment.
- If your procedure requires humidity or CO2 control: A specialized incubator is your only option.
Choosing the correct thermal instrument is the foundational step toward achieving reliable and repeatable scientific results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Laboratory Incubator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Sterilization & Drying | Cultivation & Growth |
| Typical Temp Range | 50°C to 300°C | Ambient to 80°C |
| Key Control | High Temperature | Precise Temperature Stability (±0.1°C) |
| Humidity/Gas Control | No | Often Yes (e.g., CO2, Humidity) |
| Air Circulation | Forced Convection (Powerful Fan) | Forced or Gravity Convection (Gentle) |
Ensure Your Lab's Success with the Right Equipment
Choosing between a hot air oven and an incubator is critical for your experiments' success. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need, from high-temperature ovens for sterilization to stable incubators for sensitive cell cultures.
Let our experts help you select the perfect instrument for your application. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure reliable, repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory autoclave necessary for Postgate Medium B (PMB)? Ensure Pure SRB Cultures & Accurate MIC Research
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the primary function of a laboratory Autoclave in seaweed hydrolysates? Sterilize and Optimize Fermentation
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam



















