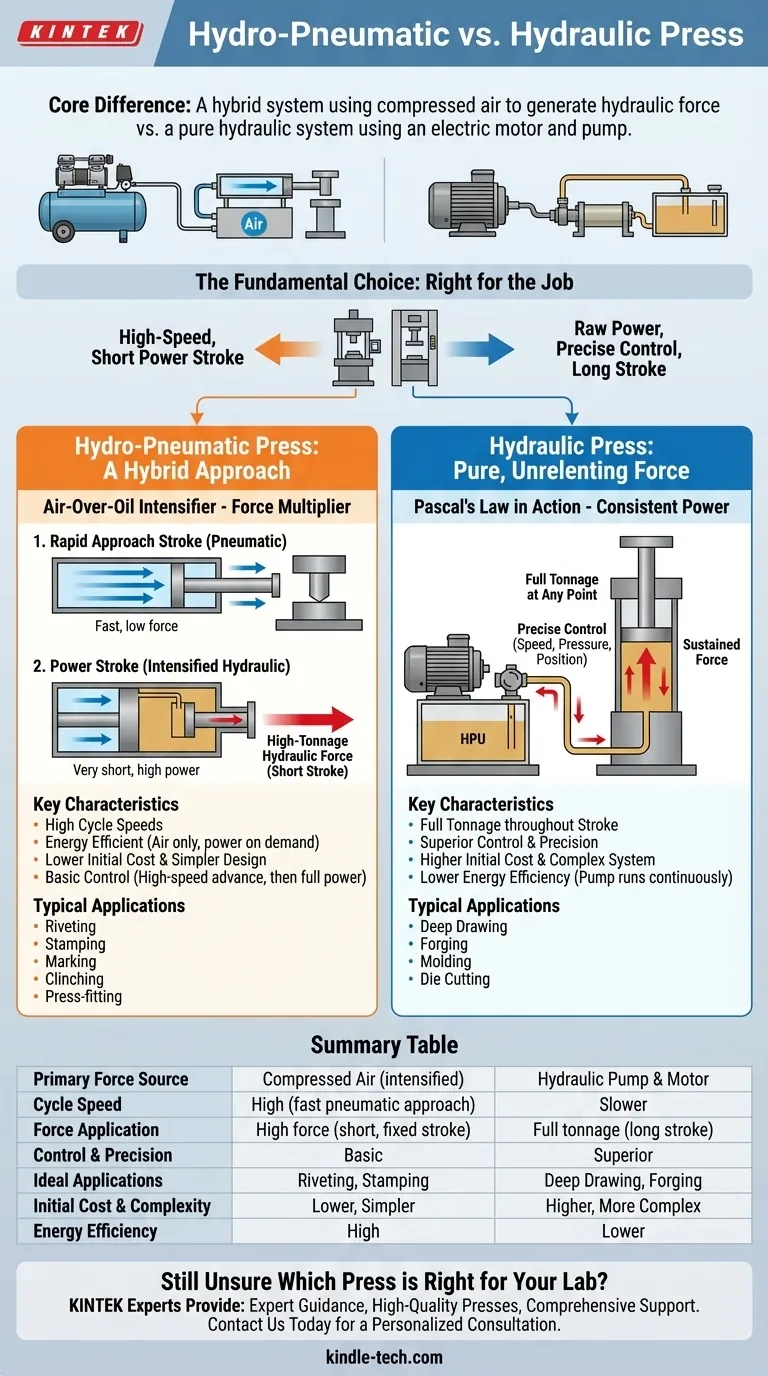
At its core, a hydro-pneumatic press is a hybrid system that uses compressed air to generate hydraulic force, while a traditional hydraulic press uses an electric motor and pump to pressurize hydraulic fluid directly. The hydro-pneumatic design combines the speed of pneumatics for the approach stroke with the power of hydraulics for the work stroke, whereas a hydraulic press provides high force throughout its entire movement.
The fundamental choice is not about which press is "better," but which is right for the job. Hydro-pneumatic presses excel at high-speed applications with a short power stroke, while hydraulic presses are the standard for raw power and precise control over long distances.

The Hydraulic Press: Pure, Unrelenting Force
A traditional hydraulic press is the benchmark for applications requiring massive, sustained force. Its operation is a direct application of fundamental fluid dynamics.
How It Works: Pascal's Law in Action
A hydraulic press consists of a hydraulic power unit (HPU)—which includes a motor, a pump, and a fluid reservoir—and a cylinder. The motor drives the pump, which pressurizes an incompressible fluid (typically oil).
This pressurized oil is directed into the cylinder, acting on a piston to generate a powerful, linear force. The force remains consistent and controllable throughout the entire extension and retraction of the ram.
Key Characteristics
The defining feature of a hydraulic press is its ability to deliver full tonnage at any point in the stroke. Speed, pressure, and position can be precisely controlled with proportional valves and feedback sensors, allowing for complex forming processes.
Typical Applications
These presses are the workhorses for heavy-duty tasks such as deep drawing, forging, molding, and die cutting. Any process that requires sustained, high force over a significant distance is a prime candidate for a hydraulic press.
The Hydro-Pneumatic Press: A Hybrid Approach
A hydro-pneumatic press, often called an air-over-oil intensifier, offers a clever solution that blends the advantages of two different power sources. It is not simply an air press; it is a true force multiplier.
How It Works: The Two-Stage Process
The cycle occurs in two distinct phases:
- Rapid Approach Stroke: Standard shop air rapidly extends the press ram with low force, quickly closing the distance to the workpiece. This movement is purely pneumatic and therefore very fast.
- Power Stroke: Once the ram meets resistance, an internal circuit automatically activates the hydraulic intensification. The air pressure acts on a large piston, which in turn pushes a smaller piston into a sealed oil chamber. This multiplies the initial air pressure into high-tonnage hydraulic force.
This power stroke is extremely powerful but is also very short—typically ranging from a few millimeters to a few centimeters.
Key Characteristics
The primary advantages are high cycle speeds and energy efficiency. The press only consumes compressed air, and the high-power stage only engages when needed, saving significant energy compared to a continuously running hydraulic pump.
Typical Applications
These presses are ideal for operations that need a quick action followed by a short burst of high force. Common uses include riveting, stamping, marking, clinching, and press-fitting small components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two systems requires a clear understanding of their inherent limitations and benefits.
Force and Stroke Length
A hydraulic press delivers high, constant force over a long stroke. A hydro-pneumatic press can only deliver its maximum force during its short, pre-defined power stroke. If your application requires pressing an object for several inches, a hydro-pneumatic press is not a viable option.
Speed and Cycle Time
For applications with significant "air time" (the distance the ram travels before contacting the part), the hydro-pneumatic press is significantly faster. Its pneumatic approach and retract strokes are much quicker than what a comparably priced hydraulic pump can deliver.
Energy and Cost
Hydro-pneumatic systems are generally more energy-efficient and have a lower initial purchase price. They are mechanically simpler, lacking a motor, pump, and complex hydraulic manifold, which also simplifies maintenance and reduces potential leak points.
Control and Precision
Hydraulic presses offer superior control. Operators can precisely manage speed, force, and position throughout the stroke. Control in a hydro-pneumatic press is more basic; it is essentially a high-speed advance followed by a binary "on/off" application of full power.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by the specific demands of your manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive tasks with a short work stroke (e.g., riveting, stamping): The speed and efficiency of a hydro-pneumatic press make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum tonnage, deep forming, or processes requiring precise control over a long stroke: A hydraulic press is the only technology that meets these requirements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment and operational complexity for lighter-duty assembly: The simplicity and lower cost of a hydro-pneumatic press make it a very strong contender.
Understanding this fundamental difference in operation allows you to select not just a machine, but the optimal process for your production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hydro-Pneumatic Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Force Source | Compressed Air (intensified to hydraulic) | Hydraulic Pump & Motor |
| Cycle Speed | High (fast pneumatic approach) | Slower |
| Force Application | High force only during short, fixed power stroke | Full tonnage at any point in a long stroke |
| Control & Precision | Basic (high-speed advance, then full power) | Superior (precise control of speed, force, position) |
| Ideal Applications | Riveting, Stamping, Marking, Press-fitting | Deep Drawing, Forging, Molding, Die Cutting |
| Initial Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, more complex system |
| Energy Efficiency | High (power only when needed) | Lower (pump runs continuously) |
Still Unsure Which Press is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct press is critical for your process efficiency and product quality. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and can help you analyze your specific application—whether it's high-speed assembly or heavy-duty forming—to recommend the perfect solution.
We provide:
- Expert guidance to match the press technology to your exact needs.
- High-quality, reliable hydro-pneumatic and hydraulic presses for laboratory and production environments.
- Comprehensive support to ensure your equipment delivers optimal performance.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK empower your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















