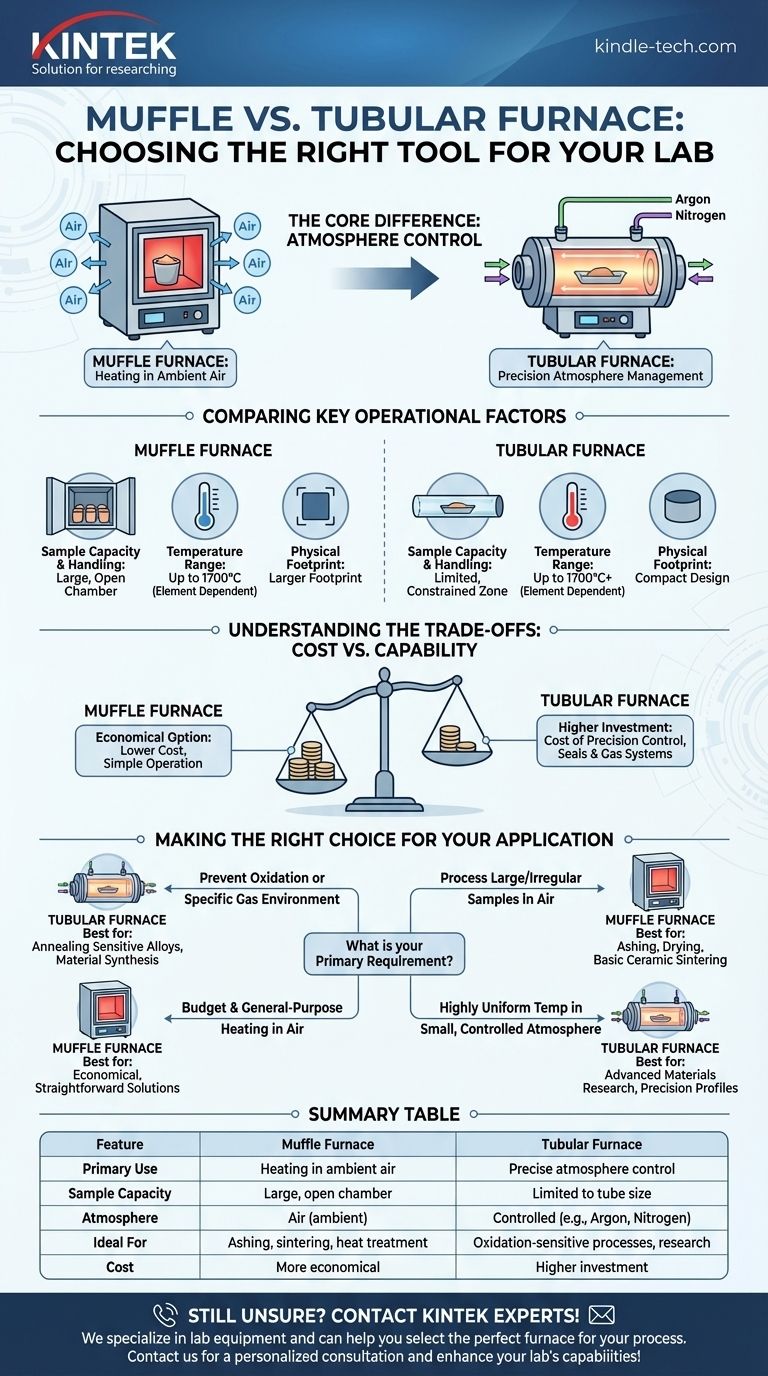
At its core, the choice between a muffle furnace and a tubular furnace comes down to one critical factor: atmosphere control. A muffle furnace is a box-style oven designed for heating samples in ambient air, while a tubular furnace uses a cylindrical chamber that allows you to precisely control the gaseous environment around your sample. This fundamental design difference dictates their respective applications, capabilities, and costs.
The decision is not about which furnace is superior, but which is correct for your specific process. You must choose a muffle furnace for simple heating in air and a tubular furnace when you absolutely need to control the atmospheric conditions.
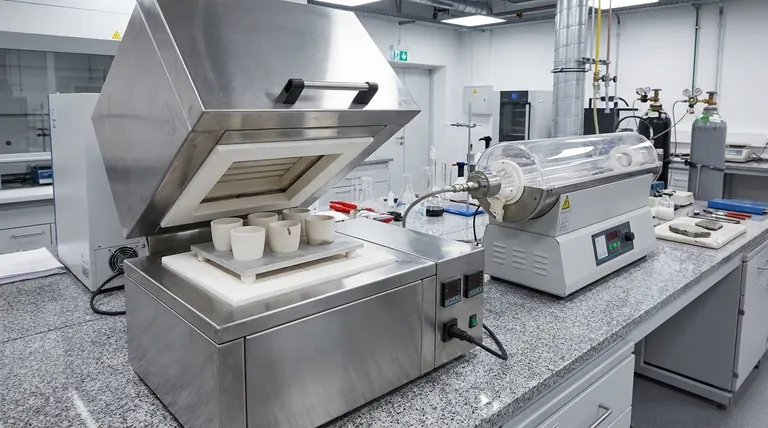

The Core Difference: Atmosphere Control
The primary distinction that drives all other differences between these two furnaces is how they handle the atmosphere surrounding the sample. This is the most important factor in your decision.
Muffle Furnace: The Workhorse for Heating in Air
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven with a chamber, or "muffle," typically made of insulating ceramic fiber.
Its key characteristic is that samples are heated directly in the ambient air inside the chamber. This makes it ideal for processes like ashing, gravimetric analysis, sintering, and general heat treating where an air atmosphere is acceptable or required.
Tubular Furnace: Precision Atmosphere Management
A tubular furnace heats samples inside a long, narrow tube, usually made of quartz, alumina, or ceramic.
The ends of the tube can be sealed, which allows you to purge the air and introduce a specific gas. This provides precise control over the environment, making it essential for preventing oxidation with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or for studying reactions with specific process gases.
Comparing Key Operational Factors
Beyond atmosphere control, several practical differences in design and function will impact your work.
Sample Capacity and Handling
The box-like chamber of a muffle furnace offers a large, open area. This makes it easy to load and unload multiple samples, irregularly shaped items, or crucibles.
In contrast, the tubular furnace has a much smaller, constrained heating zone within the tube. This limits the size and shape of your sample, often requiring specialized sample holders.
Temperature Range and Heating Elements
Both furnace types can achieve very high temperatures, but the maximum temperature is determined by the heating elements used, not the furnace style itself.
Common heating elements include:
- Heating Wires: Up to 1200°C
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: Up to 1400°C
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Rods: Up to 1700°C or higher
While both can use these elements, high-temperature tubular furnaces are common for specialized research requiring precise thermal profiles in a small, controlled zone.
Physical Footprint
Generally, tubular furnaces are more compact and take up less bench space due to their cylindrical design.
Muffle furnaces, being box-shaped and designed for larger capacity, typically have a larger physical footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Capability
Your choice will ultimately involve balancing your technical requirements against your budget.
The Cost of Control
A tubular furnace is significantly more expensive. This higher price pays for the critical capability of atmosphere control, including the cost of the tube, seals, and gas flow systems. The investment is justified only when your process cannot tolerate exposure to air.
The Value of Simplicity
A muffle furnace is the more economical option. Its simpler design makes it less expensive to purchase and easier to operate and maintain. For any application where heating in air is sufficient, the muffle furnace provides the best performance for the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct instrument, evaluate your primary process requirement.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or using a specific gas environment: The tubular furnace is your only viable option for applications like annealing sensitive alloys or certain types of material synthesis.
- If your primary focus is processing large batches or irregularly shaped samples in air: The muffle furnace offers superior capacity and ease of use for tasks like ashing, drying, or basic ceramic sintering.
- If your primary focus is budget and general-purpose heating in air: The muffle furnace provides the most straightforward and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving highly uniform temperature in a small, controlled atmosphere: The tubular furnace is engineered for this level of precision and is the standard for advanced materials research.
Ultimately, your choice is dictated by the scientific or industrial demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tubular Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Heating in ambient air | Precise atmosphere control (inert/reactive gases) |
| Sample Capacity | Large, open chamber for multiple/bulky items | Limited to size of the tube |
| Atmosphere | Air (ambient) | Controlled (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) |
| Ideal For | Ashing, sintering, general heat treatment | Oxidation-sensitive processes, materials research |
| Cost | More economical | Higher investment |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific process, whether you need the simplicity of a muffle furnace or the precision atmosphere control of a tubular furnace. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken while heating and cooling the crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Safety
- What are the five common heat treatments of metals? Master the Processes for Precise Material Properties
- How does quenching work chemistry? Mastering the Atomic Race for Harder Steel
- What is the power requirement for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is an example of quenching? Achieve Optimal Hardness with Precise Cooling



















