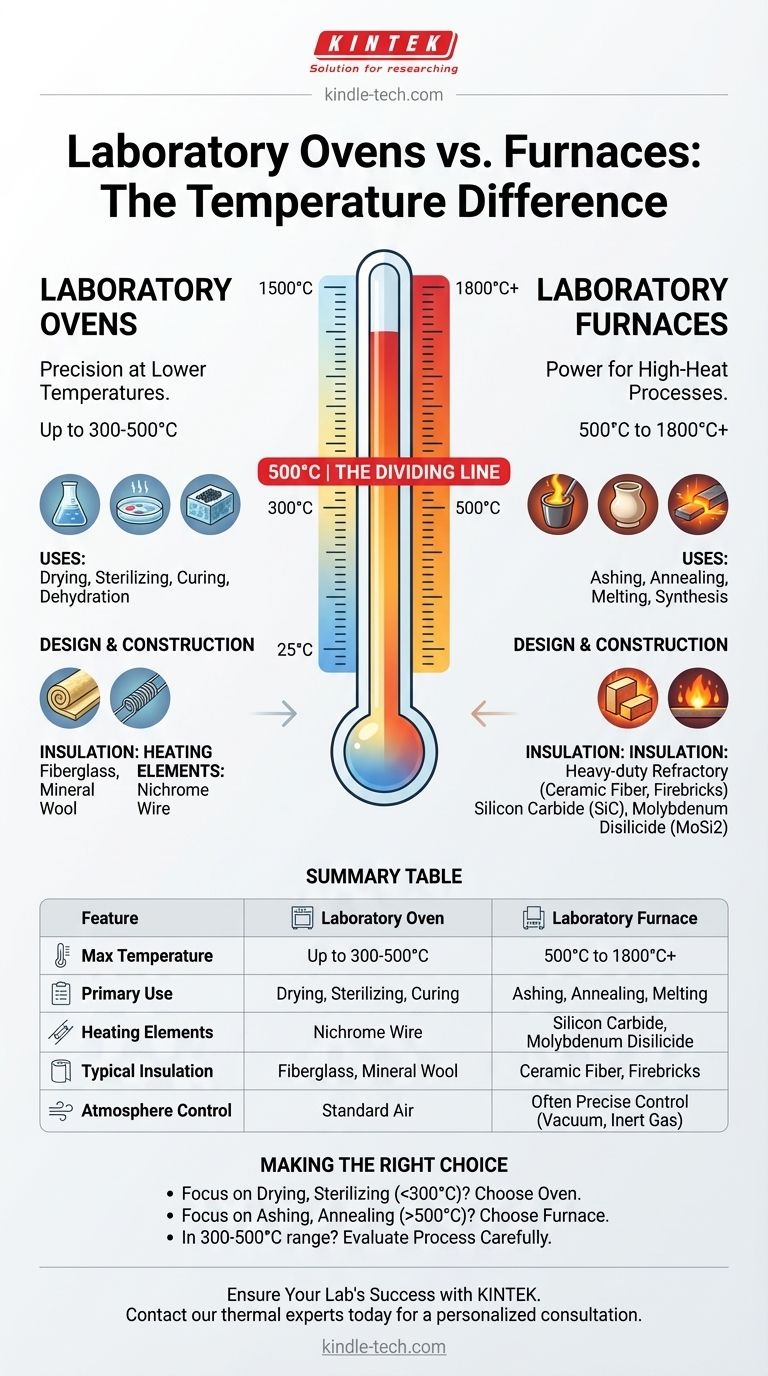
The primary difference between a laboratory oven and a furnace is temperature. While both are thermal processing chambers, ovens are designed for lower-temperature applications like drying and sterilizing, whereas furnaces are engineered for high-temperature processes such as ashing, melting, or heat-treating materials. The general dividing line is that furnaces operate at temperatures above 500°C, far exceeding the capabilities of a standard laboratory oven.
The choice between an oven and a furnace is determined entirely by your required temperature. Ovens handle processes up to roughly 300-500°C, while furnaces are built specifically for the extreme heat required for applications well above 500°C.

The Defining Factor: Operating Temperature
The function and design of each instrument are direct consequences of the temperature range they are built to achieve. This is the central distinction from which all other differences arise.
Laboratory Ovens: Precision at Lower Temperatures
A laboratory oven typically operates from just above ambient temperature to around 300°C. Some high-performance models can reach 500°C, but this is their upper limit.
Their primary role is to provide uniform, controlled heat for processes like drying glassware, sample dehydration, curing polymers, and sterilization. They are workhorses for general lab tasks that require gentle and precise heating.
Laboratory Furnaces: Power for High-Heat Processes
A laboratory furnace is designed for applications that begin where ovens leave off, typically starting at 500°C and often reaching 1200°C, 1800°C, or even higher.
Their applications are fundamentally different and include ashing samples, annealing metals, melting glass, and synthesizing ceramics. These processes require raw thermal power that would destroy a conventional oven.
How Temperature Dictates Design and Construction
The extreme heat inside a furnace necessitates a completely different approach to engineering and materials compared to an oven.
Insulation and Refractory Materials
Ovens use standard insulation like fiberglass or mineral wool, which is sufficient for containing heat up to a few hundred degrees Celsius.
Furnaces, by contrast, require heavy-duty refractory insulation, such as ceramic fiber blocks and firebricks, to safely contain extreme temperatures and protect the user and the surrounding lab environment.
Heating Elements
The heating elements in an oven are typically made of materials like nichrome wire.
Furnace heating elements must be made from specialized materials that can withstand repeated exposure to extreme heat without degrading. Common examples include silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
Chamber and Atmosphere Control
Ovens almost always heat standard air within their chamber.
Many furnaces, particularly tube furnaces, are designed to allow for precise control over the internal atmosphere. This enables processes to be run under a vacuum or in the presence of inert gases like argon or nitrogen, which is critical for many materials science applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument for your application leads to inefficient workflows, damaged equipment, or failed processes.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Due to their robust construction and massive power requirements, furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than ovens. The energy needed to reach and maintain 1100°C is substantially greater than that needed for 110°C.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Rates
The dense refractory insulation in a furnace means it has high thermal mass. As a result, furnaces heat up and cool down much more slowly than a laboratory oven. This must be factored into your process timing.
Precision vs. Power
While both instruments are precise, they are optimized for different goals. An oven is engineered for excellent temperature uniformity and stability in a lower range. A furnace is engineered for the raw power needed to reach extreme temperatures safely and reliably.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is simple when you focus on the primary variable: your maximum required temperature.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing below 300°C: A laboratory oven is the correct, energy-efficient, and cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is ashing, annealing, or materials testing above 500°C: You unequivocally need a laboratory furnace designed for these high-temperature applications.
- If your work spans the 300°C to 500°C range: Carefully evaluate your specific process, as some high-performance ovens and low-temperature furnaces may overlap in this zone.
Choosing the right equipment begins with a clear understanding of your required temperature range and process goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Oven | Laboratory Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 300-500°C | 500°C to 1800°C+ |
| Primary Use | Drying, Sterilizing, Curing | Ashing, Annealing, Melting |
| Heating Elements | Nichrome Wire | Silicon Carbide, Molybdenum Disilicide |
| Typical Insulation | Fiberglass, Mineral Wool | Ceramic Fiber, Firebricks |
Ensure Your Lab's Thermal Processing is a Success
Choosing between an oven and a furnace is critical for your research, quality control, and material synthesis. Using the wrong equipment can lead to inaccurate results, damaged samples, and costly downtime.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect thermal processing solution—whether it's a precise oven for gentle drying or a powerful furnace for high-temperature applications—ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Don't leave your process to chance. Contact our thermal experts today for a personalized consultation and get the right tool for your specific temperature requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the annealing temperature of quartz? Achieve Optimal Thermal Stability for Your Components
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of a laboratory furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of high temperature muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















