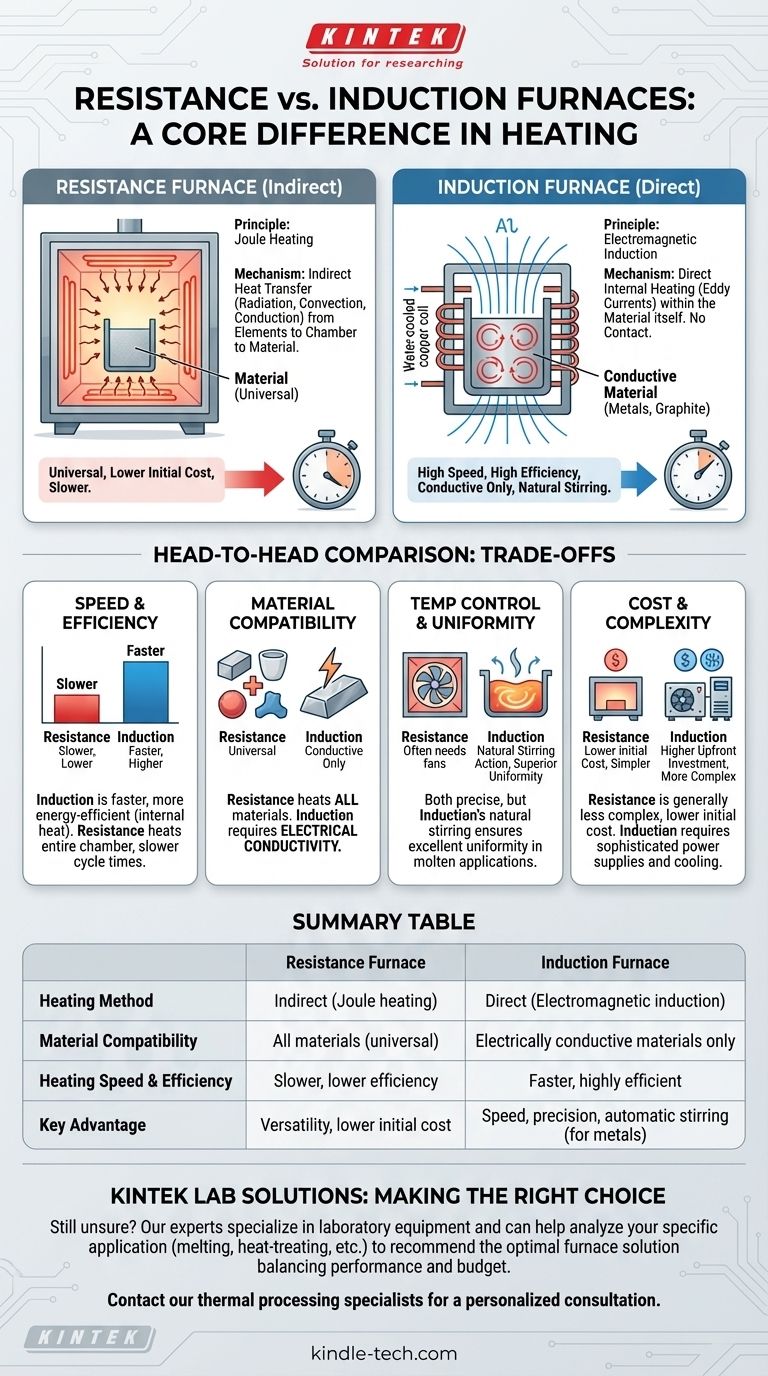
The fundamental difference between a resistance furnace and an induction furnace lies in their heating method. A resistance furnace uses heating elements that get hot and transfer heat to the material indirectly, much like a conventional oven. An induction furnace, in contrast, uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly inside the conductive material itself, with no physical contact.
The core decision between these two technologies comes down to a trade-off between versatility and efficiency. Resistance furnaces are the universal tool for heating any material, while induction furnaces are the high-speed, high-efficiency specialists for conductive materials like metal.

How a Resistance Furnace Works
A resistance furnace is the most common and straightforward type of electric furnace, operating on a principle familiar to anyone who has used a toaster or an electric stove.
The Principle: Joule Heating
The mechanism is based on electrical resistance. A high electric current is passed through a specially designed heating element made of a high-resistance material.
This resistance to the flow of electricity causes the element to become extremely hot, an effect known as Joule heating.
The Mechanism: Indirect Heat Transfer
The intense heat from these elements is then transferred to the material inside the furnace. This happens through a combination of radiation, convection, and conduction.
Essentially, the furnace heats the chamber's atmosphere and walls, which in turn heats the target material. It is an indirect heating process.
Key Characteristics
Resistance furnaces are known for their versatility, as they can heat any type of material, whether it's conductive or not. They are generally simpler in design and less expensive upfront.
How an Induction Furnace Works
Induction heating is a more advanced, targeted, and efficient method that fundamentally changes how thermal energy is delivered to a material.
The Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a powerful coil to generate a rapidly alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material (like steel or graphite) is placed within this field, the field induces electrical currents within the material itself.
These small, circular currents are known as eddy currents.
The Mechanism: Direct Internal Heating
The material's natural resistance to these eddy currents generates precise and rapid heat from the inside out. No external heating elements are needed.
The heat is generated directly within the workpiece, making the process extremely fast and efficient, as very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding space.
Key Characteristics
A unique benefit of induction heating for molten metals is the natural stirring action caused by the magnetic fields. This ensures excellent temperature uniformity and alloy mixing without mechanical stirrers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding the distinct advantages and limitations inherent to each heating method.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Induction furnaces are significantly faster and more energy-efficient. Because heat is generated internally, the target temperature is reached in a fraction of the time, and less energy is lost to the environment.
Resistance furnaces must first heat the elements and the entire furnace chamber, resulting in slower cycle times and lower overall efficiency.
Material Compatibility
Resistance furnaces are universal. They can heat metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites without issue, as their operation does not depend on the material's electrical properties.
Induction furnaces are specialists. They are highly effective but can only heat materials that are electrically conductive.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Both types can achieve high levels of temperature control. However, the natural stirring effect in an induction furnace provides superior thermal uniformity in molten metal applications.
In resistance furnaces, achieving high uniformity often requires fans to circulate the atmosphere, which adds complexity.
Cost and Complexity
Resistance furnaces are generally less complex and have a lower initial cost. Their maintenance is often simpler and less expensive over their lifetime.
Induction furnaces are more complex systems, requiring sophisticated power supplies and cooling systems, which results in a higher upfront investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by your specific material, process requirements, and budget.
- If your primary focus is versatility and lower initial cost: A resistance furnace is the superior choice, serving as a reliable workhorse for a wide variety of materials and applications.
- If your primary focus is speed, energy efficiency, and processing conductive metals: An induction furnace offers unmatched performance, especially for melting, brazing, or high-speed heat treating.
- If you are working with non-conductive materials like ceramics: A resistance furnace is your only viable option.
- If you require automatic stirring of a molten metal bath: The inherent electromagnetic stirring of an induction furnace is a major operational advantage.
Understanding this fundamental difference in heating mechanism is the key to selecting the most effective tool for your specific thermal processing task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Resistance Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (Joule heating) | Direct (Electromagnetic induction) |
| Material Compatibility | All materials (universal) | Electrically conductive materials only |
| Heating Speed & Efficiency | Slower, lower efficiency | Faster, highly efficient |
| Key Advantage | Versatility, lower initial cost | Speed, precision, automatic stirring (for metals) |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your lab's specific materials and processes?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you analyze your application requirements—whether you're melting metals, heat-treating alloys, or processing ceramics—to recommend the optimal furnace solution that balances performance, efficiency, and budget.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right furnace can enhance your lab's productivity and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















