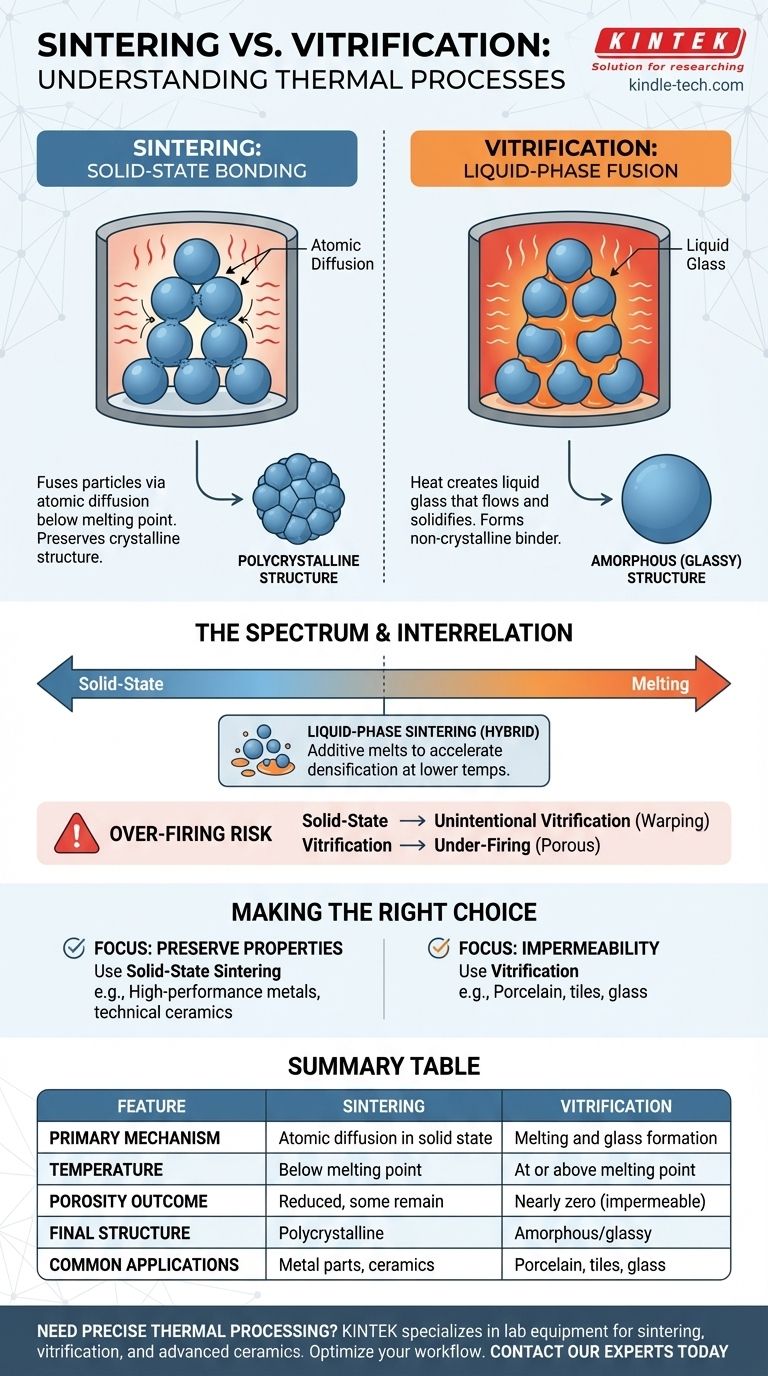
In materials science, sintering and vitrification are both thermal processes that use heat to bind particles together, but they achieve this through fundamentally different mechanisms. Sintering fuses particles by atomic diffusion in the solid state, well below the material's melting point. Vitrification, in contrast, involves heating a material until at least some of it melts into a liquid glass, which then cools to form a solid, non-crystalline binder.
The crucial distinction is the state of matter involved: Sintering bonds particles while they remain solid, while vitrification involves creating a liquid, glassy phase that solidifies to fuse the remaining components and eliminate porosity.

The Mechanics of Sintering: Building Strength Without Melting
The Core Principle: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering involves heating a compacted powder to a high temperature, but one that is still below its melting point.
At this elevated temperature, atoms at the contact points of the particles become mobile. They diffuse across the particle boundaries, causing the individual particles to fuse and form larger grains.
The Goal: Densification and Strength
The primary purpose of sintering is to reduce the empty space (porosity) between the particles.
As the particles bond and the pores shrink, the material becomes significantly denser, stronger, and more stable. This is the process used to turn metal powders into solid gears or ceramic powders into engine components.
The Outcome: A Polycrystalline Structure
Because extensive melting does not occur, sintering generally preserves the original crystalline structure of the material. The final part is a solid mass of interlocked crystals.
Materials like metals, carbides, and many high-performance technical ceramics are processed this way to maintain their desirable crystalline properties.
The Mechanics of Vitrification: The Role of a Liquid Phase
The Core Principle: Creating a Glassy Binder
Vitrification occurs when a material is heated to a temperature high enough to cause partial or complete melting.
This molten, viscous liquid flows into the pores between any remaining solid particles. Upon cooling, this liquid does not re-crystallize but instead hardens into an amorphous, glass-like state.
The Goal: Impermeability
The glass formed during vitrification effectively seals all open pores, making the final product impervious to water, air, and other fluids.
This is the key process for creating products like porcelain dinnerware, ceramic floor tiles, and glass itself, where preventing absorption is critical.
The Outcome: An Amorphous (Glassy) Structure
The defining characteristic of a vitrified product is the presence of a continuous, non-crystalline (amorphous) glass phase. This phase acts as a strong, impermeable matrix that holds the entire structure together.
Understanding the Interrelation and Trade-offs
A Spectrum of Processes
It is most useful to think of these not as two completely separate processes, but as outcomes on a spectrum of heat treatment. Many ceramic processes involve both.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
A common industrial process known as liquid-phase sintering is a perfect hybrid. A small amount of an additive with a lower melting point is mixed with the main powder.
When heated, this additive melts and vitrifies, creating a liquid that accelerates the densification and sintering of the primary solid particles. This allows for processing at lower temperatures or achieving higher densities.
The Risk of Over-Firing
The key trade-off is control. If a material intended only for solid-state sintering is overheated, it can begin to unintentionally vitrify.
This can lead to slumping, warping, and a loss of the precise dimensions and crystalline properties required for high-performance applications. Conversely, under-firing a ceramic meant to vitrify will result in a porous, weak, and non-waterproof product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal process depends entirely on the desired properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is preserving a material's high-temperature properties and crystalline structure: You are concerned with solid-state sintering, which is critical for high-performance metals and technical ceramics.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, non-porous, and water-tight body: You must achieve vitrification, which is the defining process for products like porcelain and glass.
- If your primary focus is accelerating densification at lower temperatures: You may use liquid-phase sintering, which leverages a controlled amount of vitrification to aid the bonding of solid particles.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction allows you to control a material's final density, porosity, and performance through the precise application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sintering | Vitrification |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion in solid state | Melting and glass formation |
| Temperature | Below melting point | At or above melting point |
| Porosity Outcome | Reduced porosity, but some may remain | Nearly zero porosity (impermeable) |
| Final Structure | Polycrystalline | Amorphous/glassy |
| Common Applications | Metal parts, technical ceramics | Porcelain, tiles, glass |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for sintering, vitrification, and advanced ceramic processes. Whether you're developing high-performance technical ceramics or impermeable glass products, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and consistent results. Contact our experts today to optimize your thermal processing workflow and achieve your desired material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you keep a sample in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Placement
- What causes increase in ash content? Uncover the hidden culprits that harm your equipment.
- What are the uses of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Essential for Drug Purity & Safety
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
- How long does heating take on a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key Factors for Your Lab's Efficiency



















