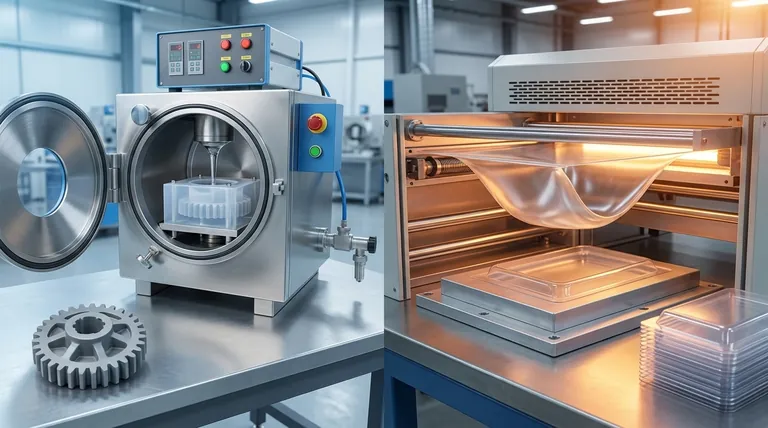
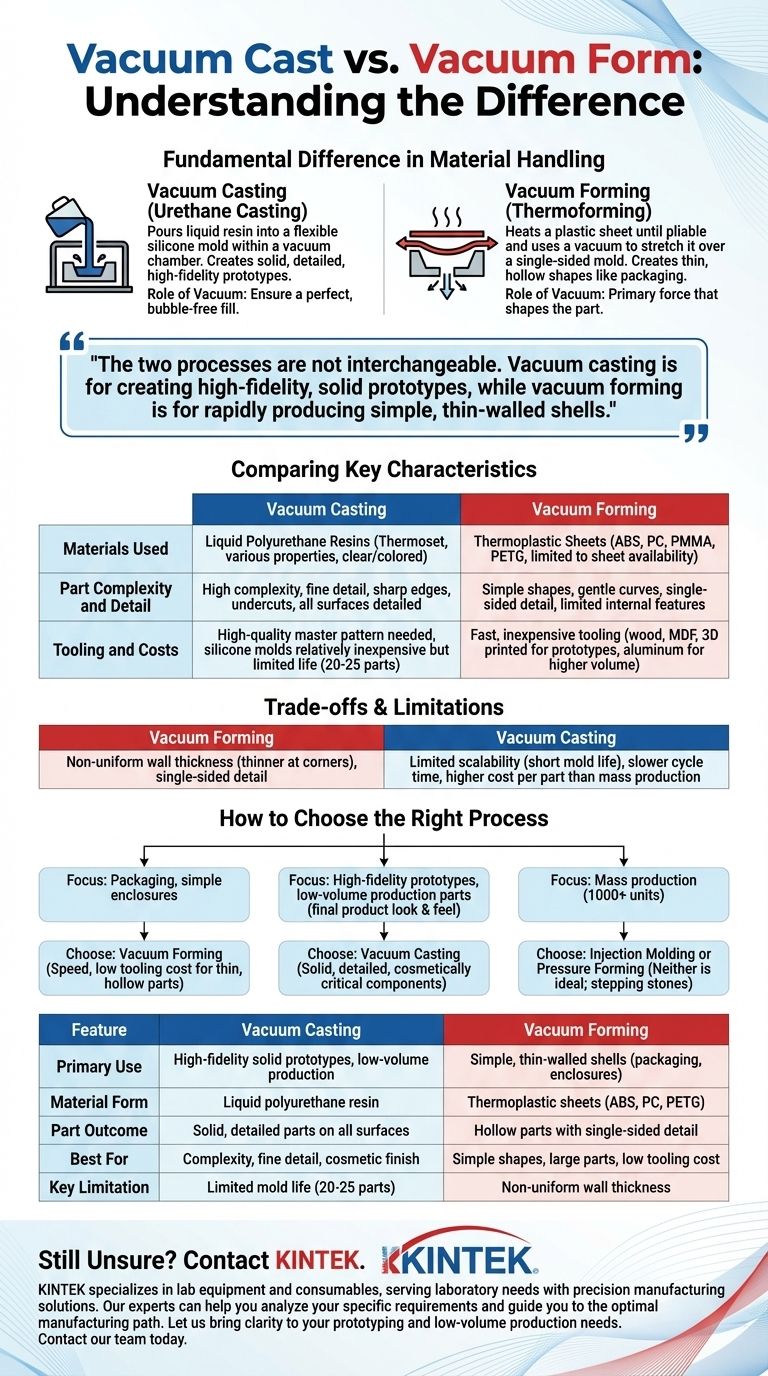
At a fundamental level, the difference is in how the material is handled. Vacuum casting involves pouring a liquid resin into a flexible mold within a vacuum chamber to create solid, detailed parts. In contrast, vacuum forming heats a sheet of plastic until it is pliable and uses a vacuum to stretch it over a single-sided mold, creating thin, hollow shapes.
The two processes are not interchangeable and serve entirely different purposes. Vacuum casting is for creating high-fidelity, solid prototypes that mimic injection-molded parts, while vacuum forming is for rapidly producing simple, thin-walled shells like packaging or enclosures.

The Process: How Each Method Works
To choose the right method, you must first understand the distinct workflow of each. Although both use the word "vacuum," its role is completely different in each process.
Vacuum Forming (Thermoforming)
In vacuum forming, the vacuum is the primary force that shapes the part.
The process involves clamping a sheet of thermoplastic material into a frame, heating it to a pliable temperature, and then draping it over a mold. A vacuum is then activated, pulling the air from between the sheet and the mold, forcing the plastic to conform tightly to the mold's surface.
Vacuum Casting (Urethane Casting)
In vacuum casting, the vacuum's role is to ensure a perfect, bubble-free fill.
This process begins with a high-quality master pattern, often 3D printed or CNC machined. A two-part silicone mold is created around this pattern. Once cured, the master is removed, leaving a detailed cavity. Two-part polyurethane resins are then mixed and poured into this silicone mold inside a vacuum chamber, which removes all air to prevent bubbles and ensure the resin fills every tiny detail.
Comparing Key Characteristics
The differences in process lead to vastly different outcomes in materials, complexity, and cost.
Materials Used
Vacuum forming exclusively uses thermoplastic sheets. Common materials include ABS, polycarbonate (PC), acrylic (PMMA), and PETG. The material choice is limited to what is available in sheet form.
Vacuum casting uses thermoset polyurethane resins. These are two-part liquid systems that can be formulated to have a huge range of properties, from rigid and strong to soft and rubber-like. They can be easily colored or produced in a clear, transparent finish.
Part Complexity and Detail
Vacuum forming is best for simple shapes with gentle curves. Detail is only captured on one side of the part, and sharp corners or deep sections can cause the material to thin out unevenly.
Vacuum casting excels at producing parts with high complexity and fine detail. It can easily replicate intricate textures, sharp edges, and even undercuts, thanks to the flexible silicone mold. The resulting parts are dimensionally accurate and highly detailed on all surfaces.
Tooling and Costs
Tooling for vacuum forming is relatively fast and inexpensive. Molds can be made from wood, MDF, or 3D-printed plastics for prototypes and low volumes. For higher volumes, aluminum is used.
Vacuum casting requires a high-quality master pattern, which adds to the initial cost. The silicone molds themselves are relatively inexpensive but have a limited lifespan, typically producing only 20-25 parts before degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. Understanding the inherent limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
The Downsides of Vacuum Forming
The primary limitation is non-uniform wall thickness. As the plastic sheet stretches over the mold, it becomes thinner, especially at corners and in deep-drawn areas. This process is also restricted to creating parts with single-sided detail and cannot produce complex internal features.
The Downsides of Vacuum Casting
The main trade-off is limited scalability. The short life of the silicone molds makes it unsuitable for high-volume production. While part quality is excellent, the cycle time is slower and the cost per part is significantly higher than mass-production methods like injection molding.
How to Choose the Right Process for Your Project
Your project's specific requirements will point you to the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is creating packaging, equipment covers, or simple enclosures: Vacuum forming is the clear choice for its speed and low tooling cost for thin, hollow parts.
- If your primary focus is producing high-fidelity prototypes or low-volume production parts that look and feel like a final product: Vacuum casting is the superior method for creating solid, detailed, and cosmetically critical components.
- If your primary focus is mass production (1000+ units): Neither of these is the ideal solution. They are stepping stones to methods like injection molding (for solid parts) or pressure forming (for higher-detail shells).
Understanding this core distinction between "forming a shell" and "casting a solid" is the key to selecting the right manufacturing path for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Casting | Vacuum Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-fidelity solid prototypes, low-volume production | Simple, thin-walled shells (packaging, enclosures) |
| Material Form | Liquid polyurethane resin | Thermoplastic sheets (ABS, PC, PETG) |
| Part Outcome | Solid, detailed parts on all surfaces | Hollow parts with single-sided detail |
| Best For | Complexity, fine detail, cosmetic finish | Simple shapes, large parts, low tooling cost |
| Key Limitation | Limited mold life (20-25 parts) | Non-uniform wall thickness |
Still Unsure Which Process is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between vacuum casting and vacuum forming is critical for achieving the right part quality, cost, and timeline. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision manufacturing solutions.
Our experts can help you analyze your specific requirements—whether you need a solid, injection-molded-like prototype or a durable, thin-walled enclosure—and guide you to the optimal manufacturing path.
Let us bring clarity to your prototyping and low-volume production needs. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's expertise can save you time and ensure a superior result.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in High-Performance Systems
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts



















