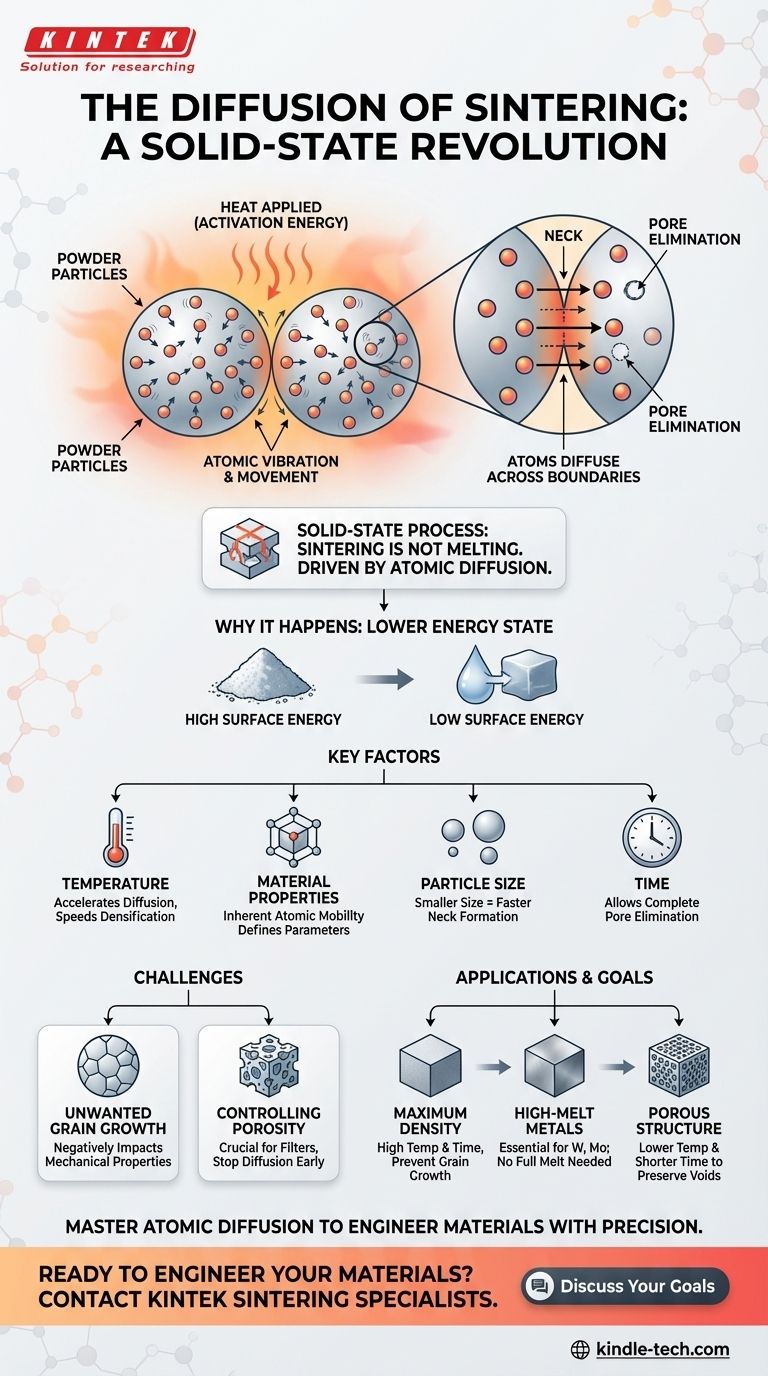
In short, diffusion is the fundamental mechanism that makes sintering possible. It is the process where atoms, energized by heat, move across the boundaries of individual material particles, causing them to fuse together and form a single, solid piece without ever melting.
The critical concept to understand is that sintering is not about melting particles together. It is a solid-state process driven entirely by atomic diffusion—the migration of atoms seeking to eliminate gaps and create a more stable, lower-energy structure.
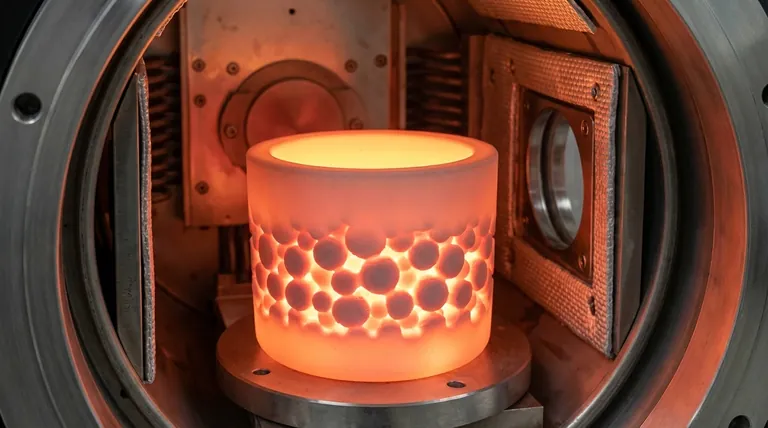

How Atomic Diffusion Drives Sintering
Sintering transforms a loose powder into a dense solid by harnessing the natural movement of atoms. This process is governed by temperature, time, and the inherent properties of the material.
The Role of Heat and Energy
Heat applied during sintering does not serve to melt the material. Instead, it provides the activation energy for the atoms.
As the material heats up, its atoms begin to vibrate intensely and randomly. This energy allows them to break free from their fixed positions and move through the material's crystal lattice.
Movement Across Particle Boundaries
The key action happens at the points where individual particles touch. Atoms diffuse across these boundaries, moving from one particle to another.
This migration of atoms effectively builds "necks" or bridges between the particles. As more atoms move, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together and systematically eliminating the empty spaces (pores) between them.
The Goal: A Lower Energy State
The underlying driving force for this entire process is the system's tendency to seek its lowest possible energy state.
A powder with countless individual particles has a massive amount of surface area, which corresponds to high surface energy. By fusing together and reducing this surface area, the material achieves a more stable, lower-energy configuration, much like how water droplets merge to form a larger drop.
Understanding the Key Factors
The efficiency and outcome of sintering depend on several variables that directly influence the rate of atomic diffusion.
Temperature
Temperature is the most critical factor. Higher temperatures provide more energy to the atoms, drastically increasing the rate of diffusion and speeding up the densification process.
Material Properties
Every material has a different inherent ability for its atoms to diffuse. This is why sintering parameters for a material like tungsten are vastly different from those for a ceramic.
Particle Size
Smaller initial particle sizes generally lead to faster sintering. This is because a greater surface area provides more contact points and pathways for diffusion to begin, accelerating the initial stages of neck formation.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, the sintering process requires careful control to achieve the desired outcome.
Sintering vs. Melting
The primary advantage of sintering is its ability to process materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. It allows for the creation of solid parts at temperatures well below their liquefaction point.
Controlling Porosity
The process of diffusion naturally reduces and eliminates porosity. If the goal is a fully dense part, the process must be allowed to complete. However, if some level of porosity is desired (for applications like filters), the process must be carefully controlled and stopped before full densification occurs.
Unwanted Grain Growth
A common side effect of the high temperatures and long times required for sintering is grain growth. The small crystal grains that make up the material can merge and grow larger, which can negatively impact the final mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding diffusion allows you to control the sintering process to achieve specific material outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximum density: You must optimize for a high rate of diffusion using sufficient temperature and time, carefully balancing it to prevent excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point metals: Sintering is the essential manufacturing method, as achieving a full melt is often technically or economically impractical.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous structure: You need to deliberately limit the extent of diffusion by using lower temperatures or shorter times to preserve the voids between particles.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of atomic diffusion is the key to controlling the sintering process and engineering materials with precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Sintering |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperatures accelerate atomic diffusion, speeding up densification. |
| Material Properties | Inherent atomic mobility dictates sintering parameters and time. |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles provide more surface area for faster diffusion and neck formation. |
| Time | Longer sintering times allow for more complete diffusion and pore elimination. |
Ready to Engineer Your Materials with Precision?
Understanding the science of diffusion is the first step; applying it is the next. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary to control the sintering process for optimal results—whether your goal is maximum density, controlled porosity, or processing high-melting-point metals.
Our expertise supports your R&D and production needs. Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss how we can help you achieve your material property goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts



















