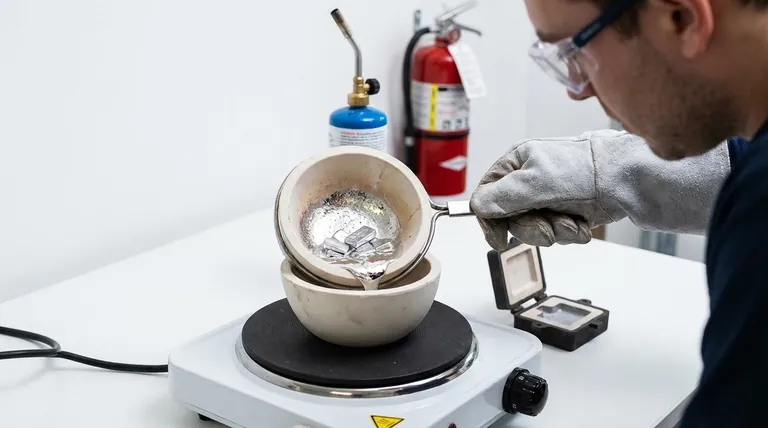
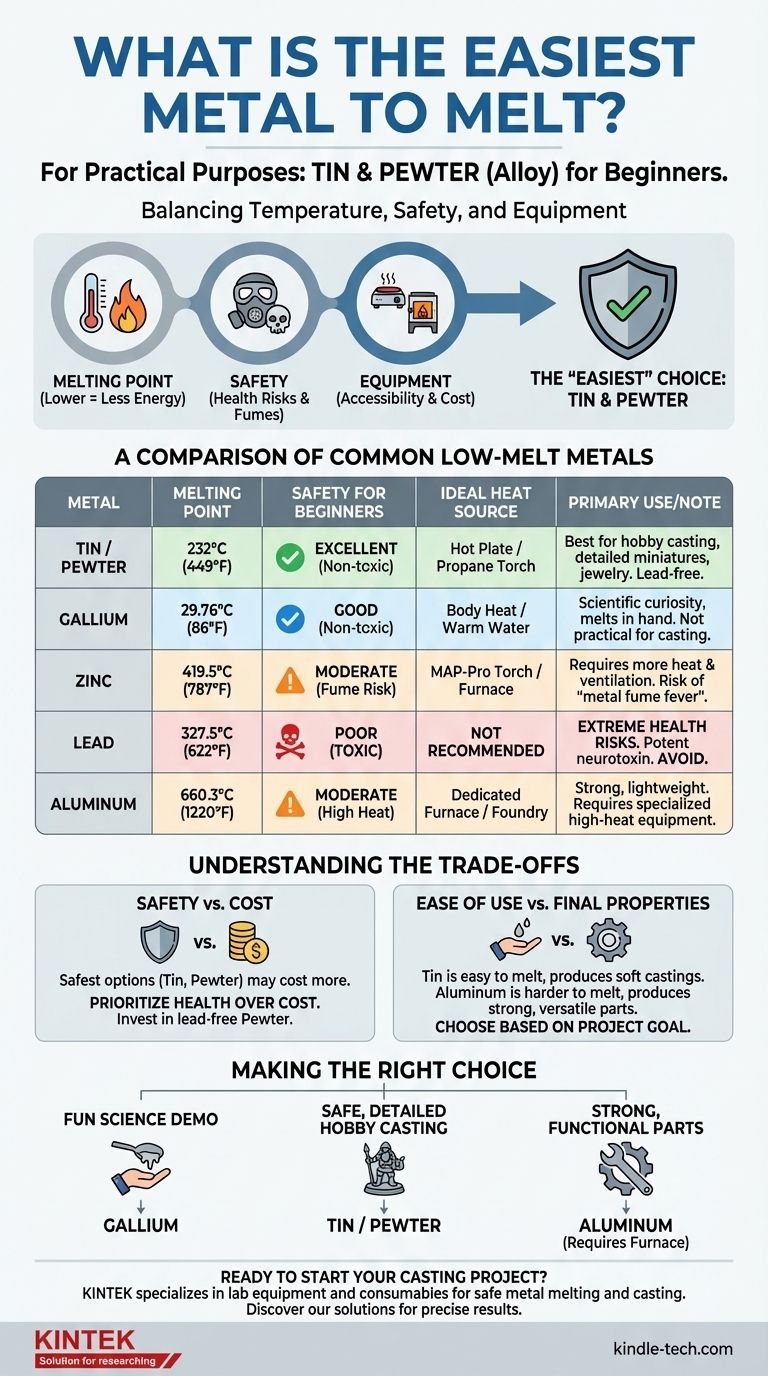
For practical purposes, the easiest and safest metals for a beginner to melt are Tin and its alloy, Pewter. While other metals like Gallium have lower melting points, Tin offers the best combination of low temperature (232°C / 449°F), safety, and availability for small-scale casting projects that can be done with simple equipment.
The question of the "easiest" metal to melt involves more than just temperature. For any practical application, the answer must balance melting point with safety, cost, and the type of equipment required.

Why "Easiest" Means More Than Just Temperature
When we look for an "easy" metal to melt, we are typically looking for the path of least resistance to creating a cast object. This involves several factors beyond the number on a thermometer.
The Obvious Factor: Melting Point
A lower melting point directly translates to less energy and simpler equipment. You can melt Tin on a stovetop hot plate, whereas Aluminum requires a dedicated furnace.
- Gallium: 29.76°C (85.58°F) - Melts from body heat.
- Tin: 232°C (449°F) - Easily melts with a propane torch or on a hot plate.
- Lead: 327.5°C (621.5°F) - Also a low temperature, but with major safety issues.
- Zinc: 419.5°C (787.1°F) - Requires more heat, often a propane torch is insufficient for volume.
- Aluminum: 660.3°C (1220.5°F) - Requires a purpose-built furnace or foundry.
The Critical Factor: Safety
Safety is the most important consideration. Many low-melting-point metals or their alloys are toxic, releasing dangerous fumes when heated.
Lead is the primary example. It is a potent neurotoxin, and inhaling its fumes during melting can cause severe, permanent health damage. Always use lead-free materials unless you are a trained professional with industrial-grade ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Zinc can also produce fumes that cause a flu-like condition known as "metal fume fever" or "the zinc shakes." This requires excellent ventilation.
The Practical Factor: Equipment and Availability
What you can melt is limited by the heat source you have.
- Hot Plate/Stovetop: Sufficient for Tin, Pewter, and some other low-melt alloys.
- Propane Torch: Ideal for small quantities of Tin and Pewter, but may struggle with Zinc.
- MAP-Pro Gas Torch: A step up from propane, capable of melting Zinc and very small amounts of Aluminum.
- Furnace/Foundry: Essential for melting Aluminum, Brass, or Bronze in any useful quantity.
A Comparison of Common Low-Melt Metals
Each accessible metal presents a different set of properties and challenges.
Tin & Pewter: The Hobbyist's Best Choice
Pewter is an alloy traditionally composed of Tin (85-99%) mixed with copper, antimony, or bismuth. Modern pewter is lead-free and is an outstanding choice for beginners.
It flows easily into molds, captures fine detail, and is non-toxic. You can buy it in bars online or even find it in thrift stores as old mugs, plates, or figurines.
Gallium: A Scientific Curiosity
Gallium is famous for melting in your hand. It's safe to handle and fascinating to demonstrate.
However, it is not a practical casting metal. It's expensive and has a unique property of making other metals, like aluminum, extremely brittle through a process called liquid metal embrittlement.
Lead: The Hazardous Option to Avoid
While historically used for casting soldiers and fishing weights due to its low melting point and high density, the extreme health risks of lead cannot be overstated.
For your safety and the safety of those around you, there is no compelling reason for a hobbyist to work with lead. Safer alternatives exist for every application.
Zinc: A Step Up in Challenge
Zinc is often found as a component in alloys like Zamak or is used as a protective coating on steel (galvanization).
While its melting point is still relatively low, it requires more heat than Tin and poses a fume hazard. The resulting castings are harder and more durable than Tin, but it's a step up in both difficulty and required safety precautions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a metal is a balance of priorities. There is no single "best" metal, only the best one for your specific goal and setup.
Safety vs. Cost
The safest options (Tin, Pewter) often cost more per pound than the more hazardous ones (Lead, Zinc). This is a trade-off you should not make. Prioritize your health and invest in a safe, non-toxic material like lead-free Pewter.
Ease of Use vs. Final Properties
Tin is easy to melt but produces soft, heavy castings. Aluminum is much more difficult to melt but produces lightweight, strong, and highly versatile parts. Your project's end-use should dictate your choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right metal, first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is a fun science demonstration: Gallium is the perfect choice for its unique, non-toxic properties.
- If your primary focus is safe, easy, detailed hobby casting (e.g., miniatures, jewelry): Start with lead-free Pewter or pure Tin.
- If your goal is to produce strong, functional parts: Plan to invest in the safety equipment and furnace required for working with Aluminum.
By understanding that "easiest" encompasses safety and accessibility, you can confidently select the right material for a successful and safe project.
Summary Table:
| Metal | Melting Point | Safety for Beginners | Ideal Heat Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tin / Pewter | 232°C (449°F) | Excellent (Non-toxic) | Hot plate or propane torch |
| Gallium | 29.76°C (86°F) | Good (Non-toxic) | Body heat |
| Zinc | 419.5°C (787°F) | Moderate (Fume risk) | MAP-Pro torch or furnace |
| Lead | 327.5°C (622°F) | Poor (Toxic) | Not recommended |
| Aluminum | 660.3°C (1220°F) | Moderate (High heat) | Dedicated furnace |
Ready to Start Your Casting Project?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable tools for safe metal melting and casting. Whether you're a hobbyist working with Tin or a professional handling advanced alloys, we provide the right equipment for your project.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our solutions can help you achieve precise, safe, and efficient results. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Where is a muffle furnace used? Essential for Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace? It's Not a Single Number—Find Your Perfect Range
- Which type of material is used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its High-Temperature Construction
- What are the characteristics of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What are the heating methods in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Safe & Precise Results



















