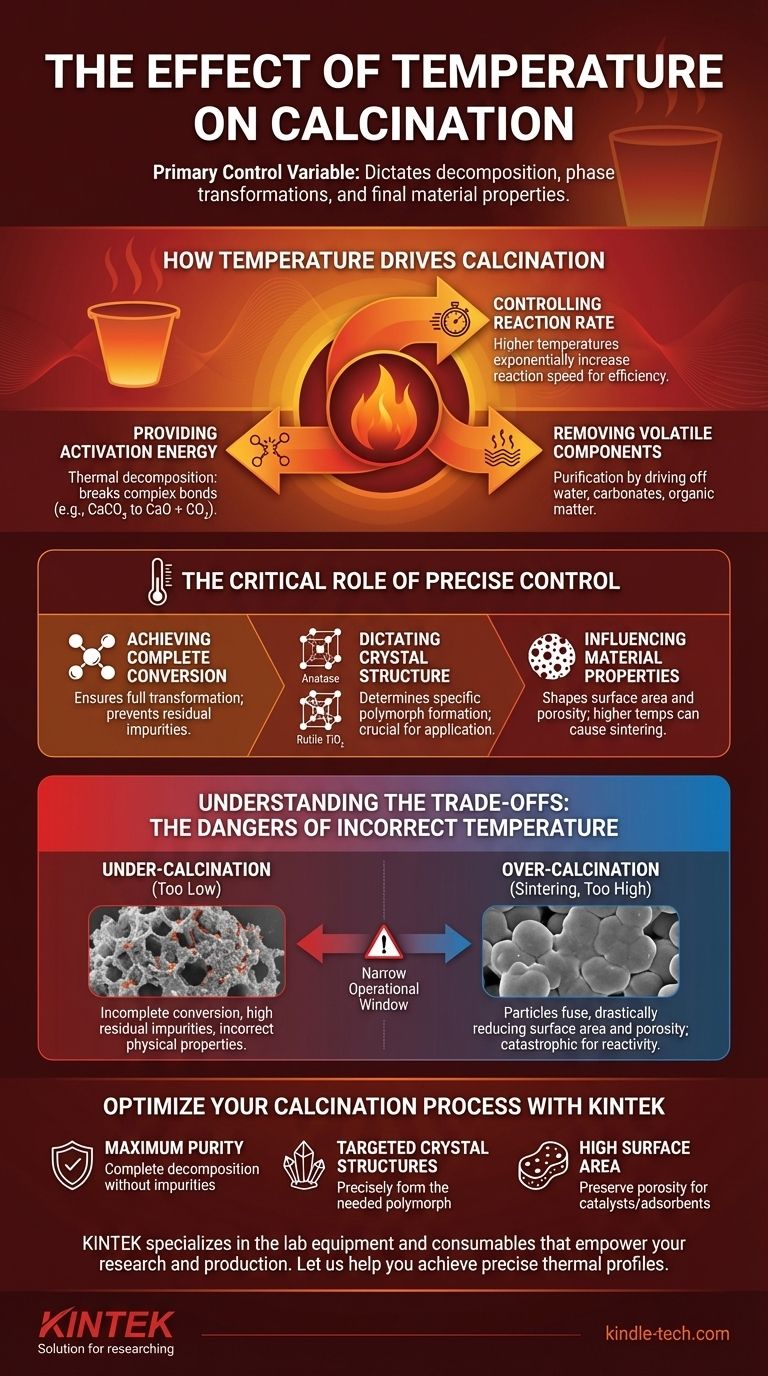
In calcination, temperature is the primary control variable. It is the energy input that dictates the rate and extent of chemical decomposition, drives phase transformations, and ultimately determines the final properties of the material, such as its purity, crystal structure, and surface area.
The core challenge of calcination is not simply reaching a high temperature, but achieving a precise thermal profile. The right temperature drives the desired reaction to completion, while the wrong temperature—too low, too high, or reached too quickly—results in an impure, inactive, or structurally compromised final product.

How Temperature Drives Calcination
Temperature is the fundamental force behind the changes that occur during calcination. It acts on the material in several distinct ways to achieve the desired transformation.
Providing Activation Energy
Most calcination processes involve thermal decomposition, where a compound breaks down into simpler substances. Temperature provides the necessary activation energy to break the chemical bonds holding the original compound together.
A classic example is the production of lime (CaO) from limestone (CaCO₃). Heat provides the energy to break the carbonate bonds, releasing carbon dioxide gas.
Controlling Reaction Rate
The rate of calcination is highly dependent on temperature. According to kinetic principles, higher temperatures exponentially increase the speed of chemical reactions.
This means that a process might take hours at a lower temperature but only minutes at a significantly higher one. This relationship is critical for industrial process efficiency.
Removing Volatile Components
A primary goal of calcination is often purification by removing unwanted volatile substances. Temperature is the mechanism that drives off these components.
This includes removing physically adsorbed water, chemically bound water (hydroxides), carbon dioxide (carbonates), or residual organic matter from a raw material.
The Critical Role of Precise Temperature Control
Simply applying heat is insufficient; controlling the exact temperature and duration is what defines the outcome. Different thermal setpoints produce vastly different materials from the same starting substance.
Achieving Complete Conversion
For any decomposition reaction, there is a minimum calcination temperature. Below this threshold, the reaction will not proceed at a practical rate, leading to an incomplete conversion.
The product will be a mixture of the original raw material and the desired final product, compromising its purity and performance.
Dictating Crystal Structure
Many materials can exist in different crystal structures, or polymorphs, with unique properties. Temperature is often the deciding factor in which polymorph is formed.
For instance, in producing titanium dioxide (TiO₂), lower calcination temperatures yield the anatase phase, while higher temperatures irreversibly convert it to the more stable rutile phase.
Influencing Material Properties
The final calcination temperature directly shapes the physical characteristics of the product. This is especially true for surface area and porosity.
As temperature increases, atoms become more mobile, which can lead to particle growth and the fusion of adjacent particles, a process known as sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Dangers of Incorrect Temperature
Optimizing a calcination process requires navigating a narrow window between two failure modes. The consequences of missing this window can be severe.
The Problem of Under-calcination
If the temperature is too low or the holding time is too short, the material will not be fully transformed.
This results in a final product with high levels of residual impurities, such as unconverted carbonates or hydroxides, and incorrect physical properties.
The Risk of Over-calcination (Sintering)
If the temperature is too high, particles begin to fuse and densify. This phenomenon, sintering, is often the primary enemy of calcination.
Sintering drastically reduces the material's surface area and porosity, which is catastrophic for applications like catalysts, adsorbents, or pigments where high reactivity and surface interaction are essential.
The Impact of Heating Rate
The speed at which the target temperature is reached (the ramp rate) also matters. A ramp rate that is too fast can cause thermal shock, fracturing particles, or creating a non-uniform product where the outside is calcined but the core is not.
Optimizing Temperature for Your Goal
The ideal calcination temperature is not a single value but is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. To determine the correct thermal profile, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and complete decomposition: You must operate above the material's decomposition temperature for a sufficient duration, while carefully remaining below the onset temperature for significant sintering.
- If your primary focus is high surface area and reactivity: Use the lowest possible temperature that still achieves the necessary chemical conversion to minimize particle growth and preserve a porous structure.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific crystal phase: Your process must precisely target the temperature range required for that phase transition without overshooting into a different, undesired crystal structure.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is mastering the precise application of heat to transform a raw material into a final product with carefully engineered properties.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Outcome | Consequence of Poor Control |
|---|---|---|
| Provides Activation Energy | Drives thermal decomposition (e.g., CaCO₃ to CaO) | Incomplete conversion; impure product |
| Controls Reaction Rate | Faster processing at higher temperatures | Inefficient process; inconsistent results |
| Dictates Crystal Phase | Forms specific polymorphs (e.g., Anatase vs. Rutile TiO₂) | Incorrect material structure; failed application |
| Influences Surface Area | Higher temps cause sintering, reducing porosity | Low reactivity; poor performance as catalyst/adsorbent |
Optimize Your Calcination Process with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is not just a detail—it's the difference between a high-performance material and a failed batch. The right thermal profile ensures the purity, crystal structure, and surface area you need for your application.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that empower your research and production. We provide the reliable furnaces and expert support necessary to master calcination, helping you avoid the pitfalls of under-calcination and sintering.
Let us help you achieve:
- Maximum Purity: Ensure complete decomposition without impurities.
- Targeted Crystal Structures: Precisely form the polymorph you need.
- High Surface Area: Preserve porosity and reactivity for catalysts and adsorbents.
Ready to transform your materials with precision? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific calcination challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What does a high ash content mean? A Guide to Material Quality & Contamination
- What is the application of muffle furnace in food industry? Essential for Accurate Food Ash Analysis
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an oven? Choose the Right High-Temperature Tool
- What is the suitable material of construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature Performance



















