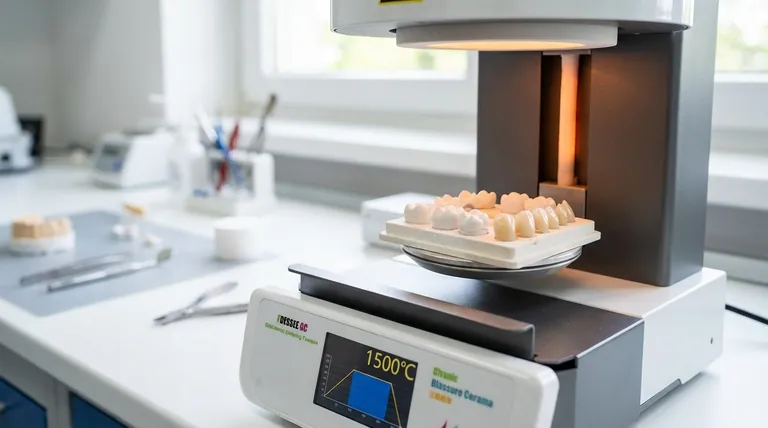
In short, sintering temperature is the single most critical factor determining the final strength, stability, and aesthetic quality of zirconia. Deviating even slightly from the manufacturer's recommended temperature can dramatically weaken the material and compromise its structural integrity.
The core challenge of sintering zirconia is achieving maximum density without causing excessive grain growth. While heat is necessary to fuse particles and eliminate porosity, too much heat enlarges the material's grain structure, which severely reduces its final strength and stability.

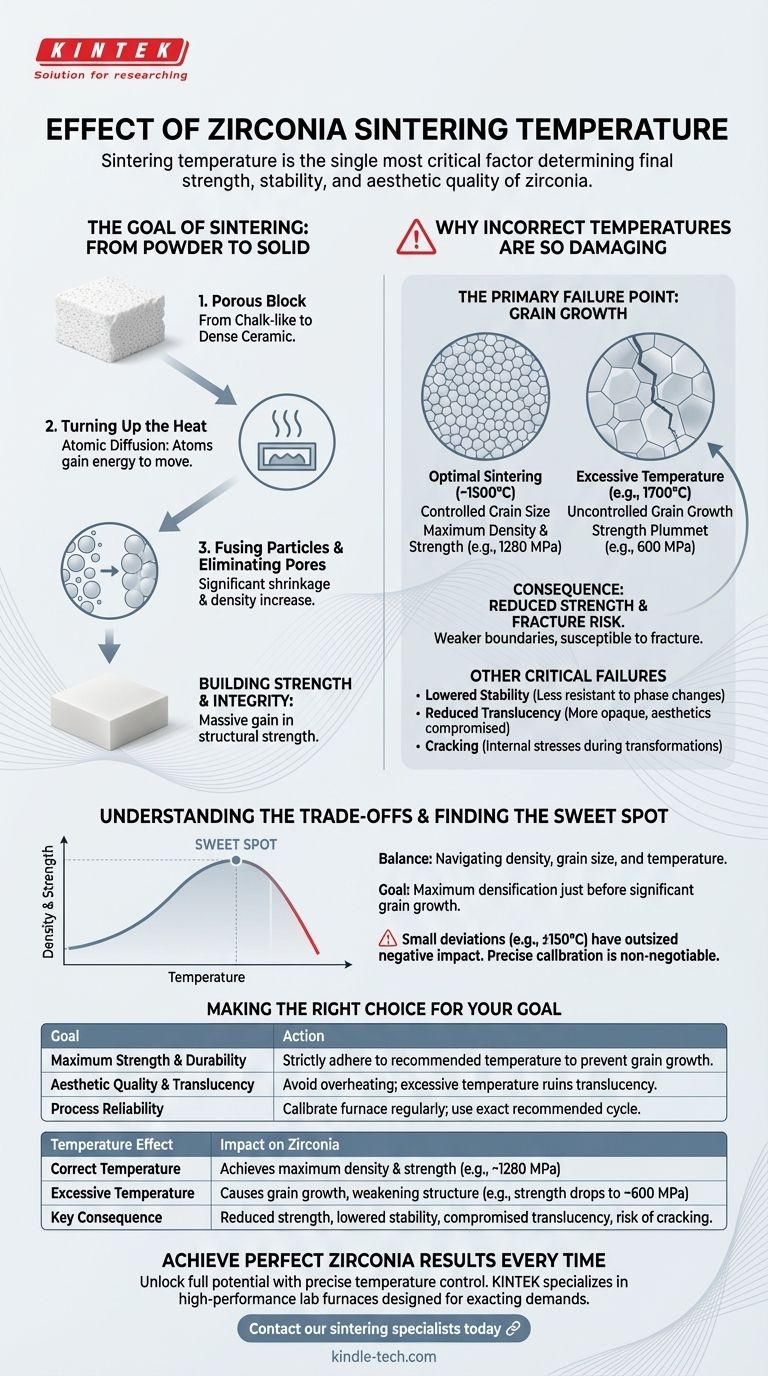
The Goal of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a transformative process that turns a porous, chalk-like zirconia block into a dense, high-strength ceramic. Temperature is the engine that drives this transformation.
Turning Up the Heat
The sintering process uses heat to give atoms the energy they need to move. This atomic movement is known as diffusion.
Fusing Particles and Eliminating Pores
As temperature rises, particles begin to fuse together at their boundaries. This process closes the tiny pores between particles, causing the material to shrink significantly and become much denser.
Building Strength and Integrity
This increase in density is directly responsible for the massive gain in strength and structural integrity that makes zirconia suitable for demanding applications.
Why Incorrect Temperatures Are So Damaging
While heat is necessary, a precise temperature window is essential. Exceeding the recommended temperature initiates a destructive process that undermines the material's properties.
The Primary Failure Point: Grain Growth
The most significant negative effect of excessive temperature is uncontrolled grain growth. The individual crystalline grains that make up the ceramic begin to enlarge and coarsen.
The Consequence of Grain Growth: Reduced Strength
Large grains create weaker boundaries within the material, making it more susceptible to fracture. The loss of strength is not minor; it is a steep decline.
For example, a zirconia material might exhibit a strength of 1280 MPa when sintered correctly at 1500°C. Increasing the temperature to 1600°C can drop the strength to 980 MPa, and a further increase to 1700°C can plummet it to just 600 MPa.
Other Critical Failures
Beyond strength loss, improper high temperatures can also lead to:
- Lowered Stability: The material becomes less resistant to phase changes over time.
- Reduced Translucency: The aesthetic quality is compromised, making the material appear more opaque.
- Cracking: Uncontrolled transformations and internal stresses can cause the part to crack during or after sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The entire sintering process is a delicate balance. You are navigating the relationship between density, grain size, and temperature.
Finding the "Sweet Spot"
The manufacturer's recommended temperature is designed to hit the optimal point where maximum densification is achieved just before significant grain growth begins. It's a narrow window for peak performance.
Why Small Deviations Matter
Processes like atomic diffusion are highly dependent on temperature. This is why a deviation of just 150°C can have such an outsized and negative impact on the final properties. Precise furnace calibration and control are not just best practices; they are fundamental requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve predictable and reliable outcomes, your sintering protocol must be dictated by your primary objective for the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Strictly adhere to the manufacturer's recommended sintering temperature to prevent the grain growth that is the primary cause of strength reduction.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic quality and translucency: Avoid overheating at all costs, as excessive temperatures will reduce translucency and ruin the final appearance of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Calibrate your furnace regularly and use the exact cycle recommended for the specific zirconia you are using, as this is the only way to ensure consistent results.
Ultimately, precise temperature control is the non-negotiable key to unlocking the full potential of your zirconia material.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Impact on Zirconia |
|---|---|
| Correct Temperature | Achieves maximum density and strength (e.g., ~1280 MPa) |
| Excessive Temperature | Causes grain growth, weakening structure (e.g., strength drops to ~600 MPa) |
| Key Consequence | Reduced strength, lowered stability, compromised translucency, risk of cracking |
Achieve Perfect Zirconia Results Every Time
Unlock the full potential of your zirconia materials with precise temperature control. Inconsistent sintering temperatures are a primary cause of weak, unstable, or aesthetically failed dental restorations and lab components.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for the exacting demands of dental labs and materials science. Our sintering furnaces deliver the precise, reliable temperature control you need to ensure maximum strength, stability, and aesthetic quality in every zirconia piece.
Don't let improper sintering compromise your work. Let our experts help you select the right equipment to guarantee consistent, high-quality outcomes.
Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss your lab's needs and find the perfect solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- Are zirconia crowns biocompatible? The Ultimate Guide to Safe, Metal-Free Dental Restorations
- How can consistent heating of ceramic restorations be achieved within a furnace? Master Your Furnace's Heat Dynamics
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconia ceramic? Mastering the 1400°C-1600°C Thermal Profile
- What is the most common dental ceramics? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- What is a sintering furnace for dental? The Key to Durable, High-Strength Ceramic Restorations
- What is sintering in dentistry? Transform Zirconia into High-Strength Dental Restorations
- What is the firing of porcelain in dentistry? The Lab Process for Strong, Life-like Crowns & Veneers
- How hot does a dental sintering furnace get? Unlock the Key to Perfect Restorations



















