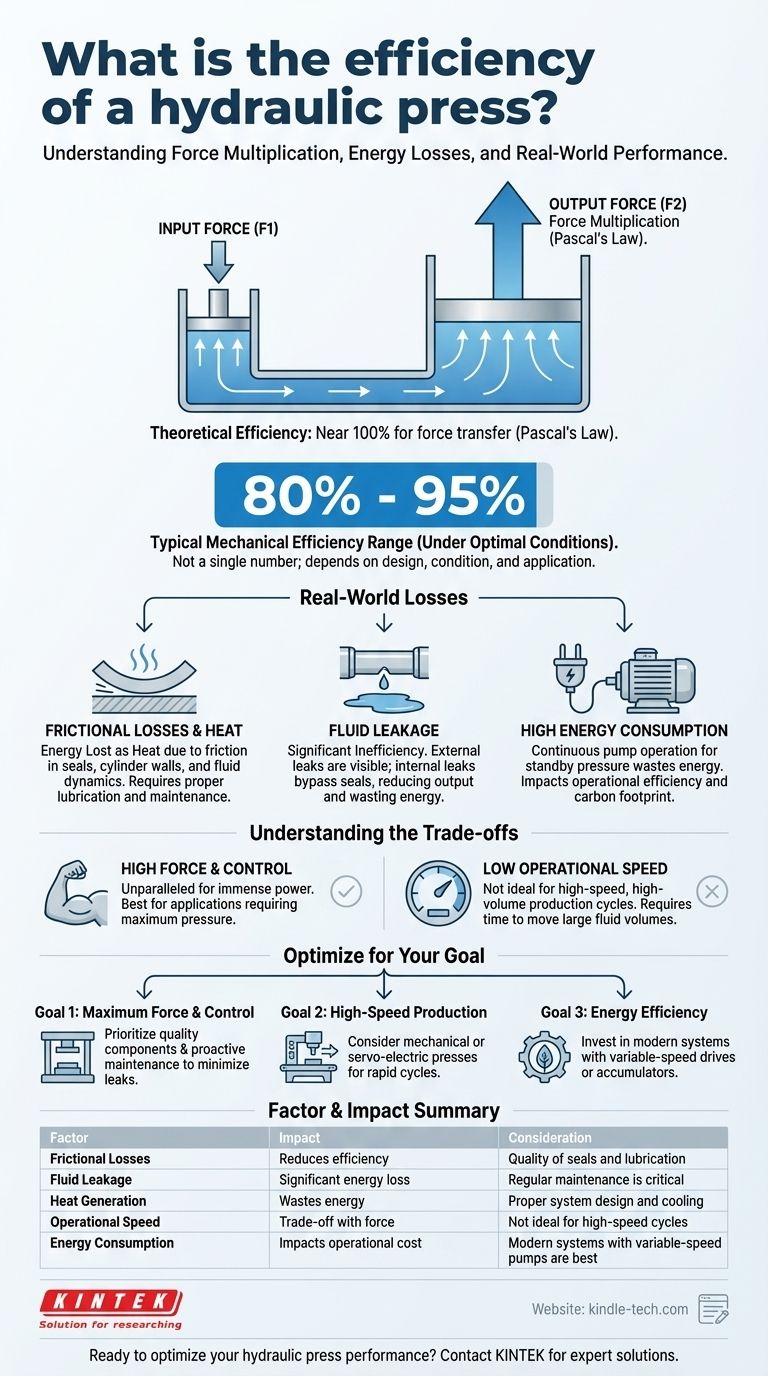
To be precise, there is no single efficiency number for a hydraulic press, as it depends heavily on the machine's design, condition, and specific application. However, hydraulic systems are generally considered highly efficient in their core function of force multiplication, often achieving mechanical efficiencies in the range of 80% to 95% under optimal conditions. This efficiency is degraded by real-world factors like fluid friction, heat generation, and internal or external leaks.
The core principle of a hydraulic press, Pascal's Law, allows for nearly lossless force multiplication in theory. In practice, its overall efficiency is a measure of how well the system minimizes energy losses to friction, heat, and fluid leakage during operation.

The Principle Behind Hydraulic Efficiency: Pascal's Law
A hydraulic press is fundamentally a force multiplier, and its efficiency starts with its operating principle.
How Force is Multiplied
The system operates on Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
A small force applied to a small piston creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid. This pressure then acts on a much larger piston, generating a proportionally larger output force. This is the source of the press's immense power.
The Ideal vs. The Reality
In a perfect, theoretical system with no friction or leaks, the energy transfer would be nearly 100% efficient. However, every real-world hydraulic system experiences energy losses that reduce its overall efficiency.
Key Factors That Reduce Hydraulic Press Efficiency
The difference between theoretical potential and actual performance comes down to several sources of energy loss.
Frictional Losses
Energy is lost as heat due to friction between the system's moving parts. This occurs primarily in the piston seals, rod wipers, and cylinder walls. Well-maintained seals and proper lubrication are critical to minimizing this loss.
Fluid Dynamics and Heat
Simply moving the hydraulic fluid requires energy. As the pump forces fluid through hoses, valves, and fittings, it encounters resistance. This fluid friction generates heat, which represents a direct loss of energy from the system.
Fluid Leakage
Fluid leakage is a primary cause of inefficiency. External leaks are obvious and result in lost fluid and pressure. More subtle are internal leaks, where high-pressure fluid bypasses seals inside a component (like a pump or cylinder), reducing output speed and wasting energy without any visible sign.
High Energy Consumption
Many hydraulic systems consume significant energy even when not actively pressing. If the electric motor and pump run continuously to maintain standby pressure, energy is wasted. This lowers the overall operational efficiency, especially in applications with long idle times.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the hydraulic press comes with inherent characteristics that impact its practical efficiency and suitability for certain tasks.
Speed vs. Power
A key trade-off for hydraulic presses is their relatively low operational speed. Achieving immense force requires moving a large volume of fluid, which takes time. For high-speed, high-volume production, a mechanical press may be a more efficient choice.
Maintenance and Reliability
The potential for fluid leakage necessitates a rigorous maintenance schedule. As mentioned in the references, some hydraulic fluids can be flammable, adding a layer of safety management. A system's efficiency is directly tied to its condition; worn seals and minor leaks can quickly degrade performance.
The Carbon Footprint
The high energy consumption, especially from older or less sophisticated systems where the pump runs constantly, contributes to a larger carbon footprint. This is a growing consideration when evaluating the total lifecycle cost and efficiency of a machine.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing and operating a hydraulic press effectively means matching its characteristics to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and control: The hydraulic press is unparalleled; prioritize high-quality components and proactive maintenance to minimize internal leakage and ensure consistent power delivery.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production cycles: A hydraulic press may not be the most efficient tool; consider a mechanical or servo-electric press that is designed for rapid strokes.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Invest in modern hydraulic systems with variable-speed pump drives or accumulators, which dramatically reduce power consumption during idle periods.
By understanding these factors, you can leverage the immense power of a hydraulic press while optimizing its efficiency for your specific task.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Efficiency | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Frictional Losses | Reduces efficiency | Quality of seals and lubrication |
| Fluid Leakage | Significant energy loss | Regular maintenance is critical |
| Heat Generation | Wastes energy | Proper system design and cooling |
| Operational Speed | Trade-off with force | Not ideal for high-speed cycles |
| Energy Consumption | Impacts operational cost | Modern systems with variable-speed pumps are best |
Ready to optimize your hydraulic press performance? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you require a reliable hydraulic press for maximum force and control or are evaluating more energy-efficient alternatives for high-speed production, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your efficiency and achieve your goals. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















