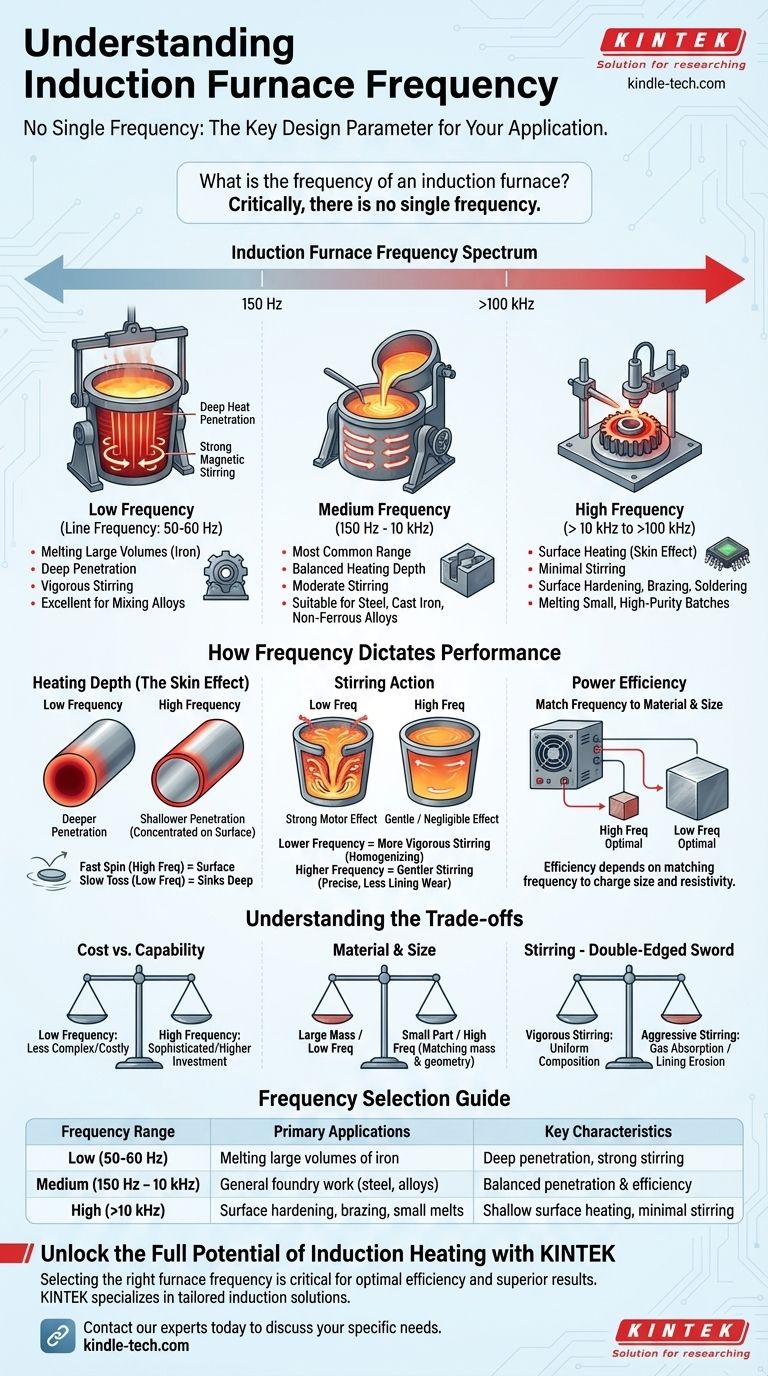
Critically, there is no single frequency for an induction furnace; the operating frequency is a crucial design parameter that is chosen based on the specific application. Induction furnaces operate across a wide spectrum, from line frequencies (50/60 Hz) for large melts to high radio frequencies (over 100 kHz) for surface heating and small, precise applications.
The choice of operating frequency is the single most important factor in an induction furnace's design. It directly dictates the depth of heat penetration and the intensity of the magnetic stirring effect, determining whether the furnace is suitable for melting large volumes, heating small parts, or treating surfaces.

The Fundamental Role of Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current sent through the furnace's copper coil determines how the energy is transferred to the metal charge inside. This relationship is governed by a principle known as the "skin effect."
Low Frequency (Line Frequency)
At standard line frequencies of 50 Hz to 60 Hz, the electromagnetic field penetrates deeply into the molten metal.
This deep penetration is ideal for melting large batches of highly conductive metals like iron. It also generates a very strong stirring action, which is excellent for mixing alloys and ensuring a uniform temperature and composition.
Medium Frequency
This is the most common range for modern foundries, typically operating between 150 Hz and 10,000 Hz (10 kHz).
Medium frequency offers a versatile balance between heating depth and efficiency. It provides good penetration and a moderate stirring action, making it suitable for melting steel, cast iron, and various non-ferrous alloys. The reference to a "medium frequency power supply cabinet" points to the prevalence of this type.
High Frequency (Radio Frequency)
Frequencies above 10,000 Hz (10 kHz) and often extending into the hundreds of kilohertz are considered high frequency.
Here, the skin effect is very pronounced, meaning the current and heat are concentrated in a very thin layer on the surface of the material. This makes high-frequency systems unsuitable for melting large volumes but perfect for applications like surface hardening, brazing, soldering, or melting very small, high-purity batches where minimal stirring is desired.
How Frequency Dictates Performance
Understanding the application requires understanding how frequency directly impacts the physical processes inside the furnace.
Heating Depth (The Skin Effect)
The higher the frequency, the shallower the depth the induced current penetrates.
Think of it like skipping a stone on water. A fast, high-frequency spin keeps the stone right at the surface. A slow, low-frequency toss allows it to sink deeper. This is why high frequency is used for surface treatments and low frequency for through-heating large masses.
Stirring Action
The electromagnetic field creates a motor effect within the molten metal, causing it to stir.
Lower frequencies produce a much more vigorous stirring action. This is beneficial for homogenizing alloys but can be detrimental if it's too aggressive, potentially increasing wear on the refractory lining of the crucible. Higher frequencies induce a much gentler, or almost negligible, stirring effect.
Power Efficiency
The efficiency of the furnace depends on matching the frequency to the size of the material being heated and its electrical resistivity.
The power supply's control system, as noted in the references, constantly adjusts voltage and current to maintain constant power, but the fundamental efficiency is locked in by the choice of frequency for a given task.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a frequency is not just a matter of physics; it involves balancing cost, capability, and operational goals.
Cost vs. Capability
Generally, power supplies for lower frequencies are less complex and costly than those required for high-frequency applications. The sophisticated solid-state electronics needed to generate stable high frequencies add to the initial investment.
Material and Size Constraints
A frequency that is perfect for a one-ton iron melt (low/medium frequency) would be incredibly inefficient for heat-treating a small gear (high frequency). The energy would penetrate too deeply and fail to concentrate where needed. The choice must match the mass and geometry of the charge.
Stirring: A Double-Edged Sword
While stirring is crucial for uniform composition, the vigorous action from a low-frequency furnace can increase gas absorption from the atmosphere and accelerate the erosion of the furnace lining. In contrast, the lack of stirring in a high-frequency furnace may be undesirable if alloying elements need to be mixed thoroughly.
Matching the Frequency to Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct frequency range.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of conductive metals like cast iron: A low-frequency (line frequency) or low-end medium-frequency furnace provides the deep penetration and strong stirring required.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose foundry work for steel, copper, or aluminum alloys: A medium-frequency furnace offers the best all-around balance of heating efficiency, control, and stirring action.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening, brazing, or melting small, high-purity quantities: A high-frequency system is necessary to concentrate heat on the surface or in a small volume precisely.
Ultimately, selecting the correct operating frequency is the key to leveraging the induction furnace's renowned efficiency, speed, and control for your specific process.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Primary Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Low (50-60 Hz) | Melting large volumes of iron | Deep penetration, strong stirring |
| Medium (150 Hz - 10 kHz) | General foundry work (steel, alloys) | Balanced penetration & efficiency |
| High (>10 kHz) | Surface hardening, brazing, small melts | Shallow surface heating, minimal stirring |
Unlock the full potential of induction heating for your lab or foundry. Selecting the right furnace frequency is critical for achieving optimal efficiency, precise temperature control, and superior results in your melting, heat treatment, or brazing processes. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored induction solutions that match your specific material and application needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your operations with the perfect induction furnace.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















