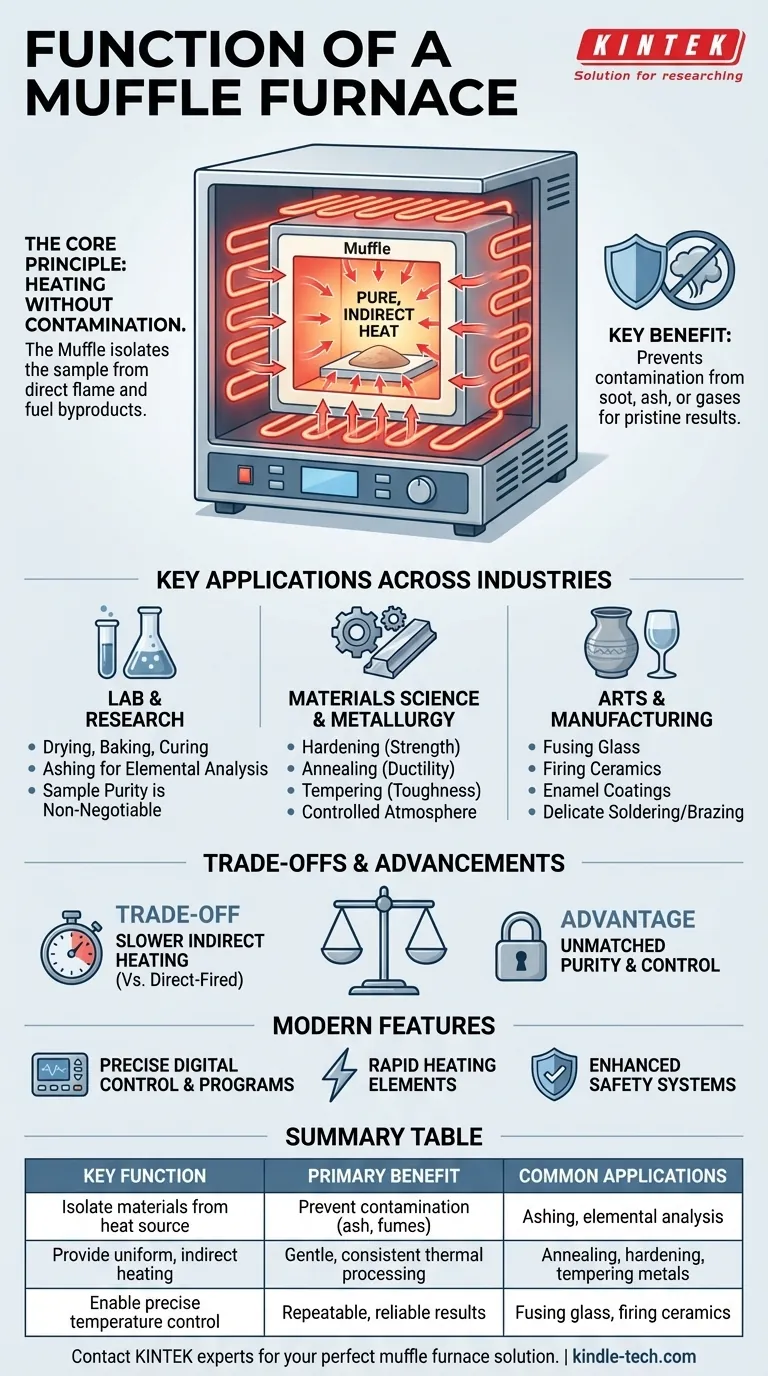
The primary function of a muffle furnace is to provide a highly controlled, high-temperature environment for heating materials while isolating them from the direct heat source and any potential contaminants. This isolation is its defining characteristic, enabling precise processes like heat treatment, material analysis, and chemical alteration without the risk of contamination from fuel byproducts like ash or fumes.
The crucial insight is that a muffle furnace isn't just about reaching high temperatures; it's about providing pure, indirect heat. This clean heating environment is essential for processes where material integrity and composition are paramount.
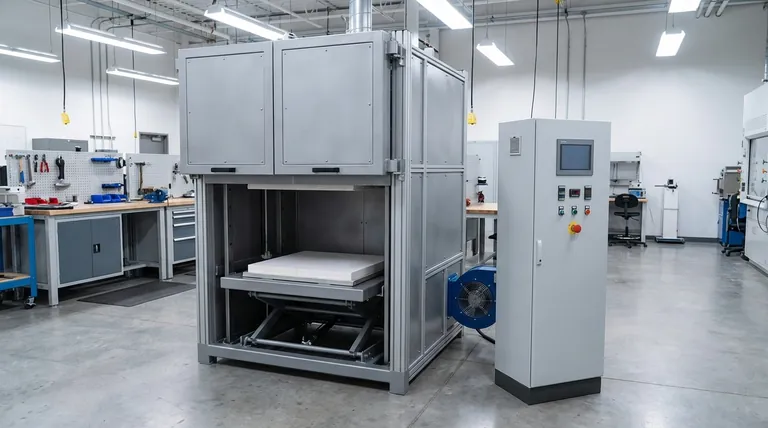

The Core Principle: Heating Without Contamination
The unique function of a muffle furnace stems directly from its core design, which revolves around an internal chamber called the "muffle."
The Role of the "Muffle"
The muffle is a heat-resistant inner container that holds the material being treated. Historically, it was designed to protect samples from the byproducts of fuel combustion, such as soot, ash, or gas fumes.
This separation is the key. The sample never comes into direct contact with the heating elements or flames.
How It Achieves Clean Heating
Instead of direct exposure, the furnace's heating elements (such as resistance wires or silicon-molybdenum rods) heat the chamber's interior.
The muffle then absorbs this energy and radiates heat uniformly onto the sample inside. This ensures gentle, even heating, which is critical for consistent results in sensitive applications.
Modern designs also use mechanical convection to safely direct airflow out of an exhaust, often eliminating the need for a separate fume hood.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to provide a clean, high-temperature environment makes the muffle furnace indispensable in several fields.
Laboratory and Scientific Research
In a lab setting, a muffle furnace performs vital functions where sample purity is non-negotiable. This includes drying (removing all moisture), baking, and curing materials to induce physical or chemical changes.
It is also a standard tool for elemental analysis, such as determining the composition of coal by burning it down to ash in a controlled environment.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
For small-scale industrial applications and materials testing, the furnace is used for the heat treatment of metals.
These processes include hardening (increasing material strength), annealing (reducing hardness and increasing ductility), and tempering (improving toughness). The controlled atmosphere prevents unwanted reactions on the metal's surface.
Arts and Manufacturing
The furnace is widely used for high-temperature applications like fusing glass, creating durable enamel coatings, and firing ceramics.
In these processes, preventing contamination from dust or fumes is essential for achieving a flawless final product. It is also used for delicate soldering and brazing tasks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advancements
While powerful, the muffle furnace design has inherent trade-offs and has evolved significantly over time.
The Trade-off: Indirect vs. Direct Heat
The primary benefit—isolating the sample—is also its main operational trade-off. Because the heat is transferred indirectly, the heating process can be slower compared to furnaces where the sample is exposed directly to the heat source.
This is a necessary compromise to achieve the required level of purity and control for sensitive materials.
Modern Features and Controls
New-generation muffle furnaces have overcome many historical limitations. They often feature a double-shell structure for better insulation and safety.
Advanced digital controllers allow for precise, multi-stage temperature programs, while modern heating elements provide rapid temperature rise. Safety is also paramount, with integrated over-current, over-voltage, and leakage protection systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating instrument depends entirely on the requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination: A muffle furnace is the definitive choice due to its isolating muffle chamber.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable heat treatment of metals: The furnace's uniform, controlled heating makes it ideal for annealing, hardening, and tempering.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating where minor contamination is acceptable: You might consider a direct-fired furnace, which can often reach target temperatures more quickly.
Ultimately, the function of a muffle furnace is to give you absolute control over the thermal processing of a material in a pristine environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Isolate materials from heat source | Prevent contamination (ash, fumes) | Ashing, elemental analysis |
| Provide uniform, indirect heating | Gentle, consistent thermal processing | Annealing, hardening, tempering metals |
| Enable precise temperature control | Repeatable, reliable results | Fusing glass, firing ceramics |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your lab processes?
KINTEK's muffle furnaces are engineered to provide the clean, controlled high-temperature environment essential for accurate material testing, heat treatment, and sample preparation. Whether you're in research, quality control, or materials development, our equipment ensures your results are reliable and repeatable.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation
- What are the classification of refractory materials? A Guide to Chemical and Thermal Selection
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts
- What is muffle furnace working principle and application? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the suitable material of construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature Performance



















