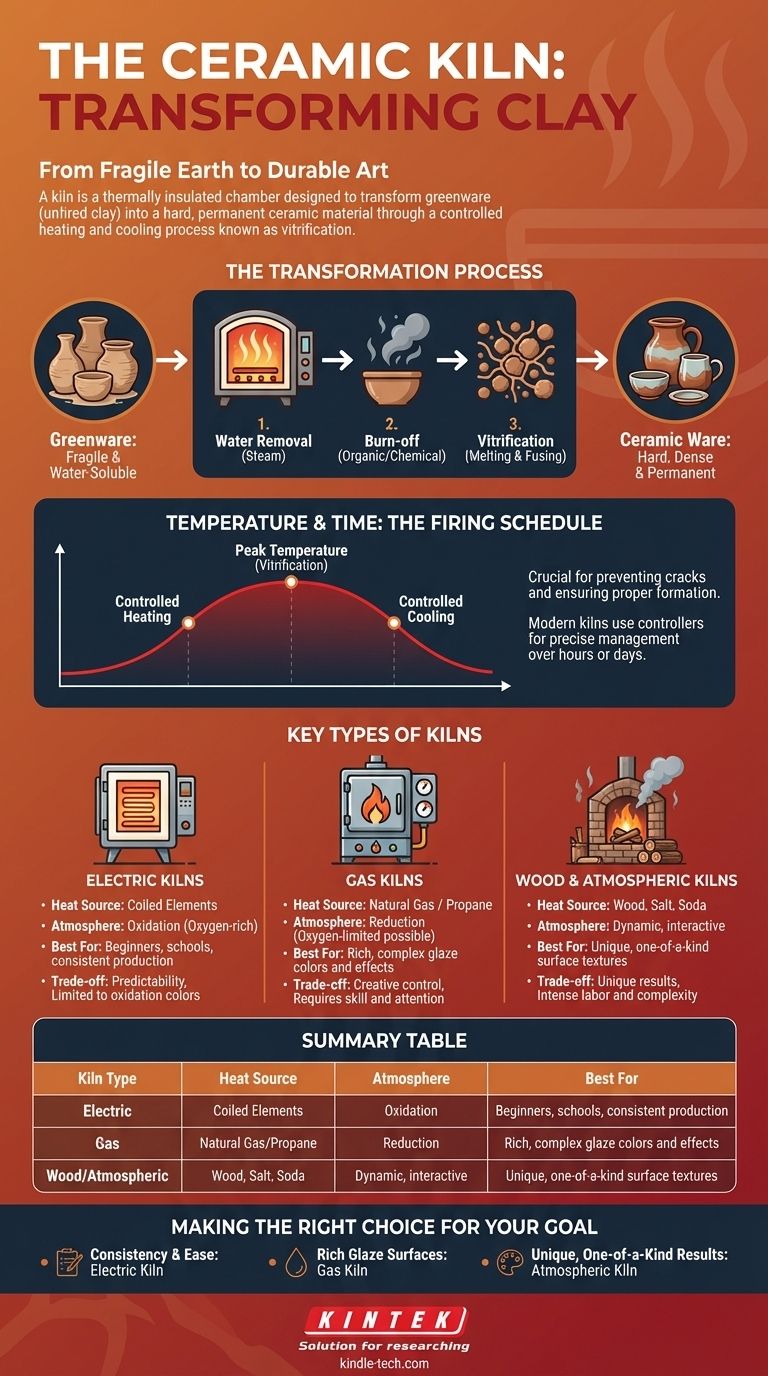
The specialized furnace used for firing ceramics is called a kiln. More than just a high-temperature oven, a kiln is a thermally insulated chamber designed to transform fragile, water-soluble clay into a hard, permanent ceramic material through a carefully controlled heating and cooling process.
A kiln is not simply a device for heating; it is a tool for transformation. Its primary function is to manage temperature over time, initiating the irreversible chemical and physical changes that turn malleable clay into durable ceramic.

From Clay to Ceramic: The Role of the Kiln
Understanding the kiln begins with understanding why clay needs to be fired. The process is fundamental to creating any lasting ceramic object.
Why Firing is Necessary
Unfired clay, known as greenware, is extremely fragile. It will shatter if dropped and dissolve back into mud if exposed to water.
The intense heat inside a kiln creates permanent, crystalline bonds between the clay particles. This process, called vitrification, makes the object hard, dense, and impervious to water.
The Transformation Process
As the kiln's temperature rises, the clay goes through several critical stages. First, any remaining physical water is turned to steam and removed.
Next, organic materials and chemical water within the clay body are burned off. Finally, at peak temperatures, the clay particles begin to melt and fuse together, creating the strong, glass-like bonds that define ceramic ware.
Temperature and Time: The Firing Schedule
A successful firing depends on more than just reaching a high temperature. The rate of temperature increase and decrease, known as the firing schedule, is critical.
Heating too quickly can cause trapped water to turn to steam and explode the piece. Cooling too rapidly can cause thermal shock, leading to cracks. Modern kilns use controllers to precisely manage this schedule over many hours or even days.
Key Types of Ceramic Kilns
While all kilns serve the same basic purpose, their heat source and design create different firing environments, which profoundly impact the final appearance of the pottery.
Electric Kilns
Electric kilns are the most common type for schools, hobbyists, and small studios. They use coiled heating elements to generate radiant heat, much like a conventional oven.
They are prized for their ease of use and predictable, consistent results. They typically fire in an oxidation atmosphere, meaning there is an abundance of oxygen, which produces clear and bright glaze colors.
Gas Kilns
Gas kilns, which run on natural gas or propane, are favored by many professional potters. The flame and airflow can be actively managed by the artist.
This allows for precise control over the kiln's atmosphere. By limiting the oxygen supply, potters can create a reduction atmosphere, which starves the glazes of oxygen and produces deep, rich, and often unpredictable colors not achievable in an electric kiln.
Wood and Atmospheric Kilns
Wood-fired kilns are a traditional method where wood is the fuel source. Other "atmospheric" kilns introduce materials like salt or soda into the chamber during firing.
In these kilns, the fly ash from the wood or the vaporized materials become part of the firing process itself, interacting directly with the pottery to create unique, non-replicable surface textures and patterns. The results are a direct collaboration between the potter, the clay, and the fire.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a firing method involves balancing predictability against creative potential, and convenience against complexity.
Electric Kilns: Predictability vs. Limited Palette
The primary strength of an electric kiln is its reliability. You can expect highly consistent results from one firing to the next, which is ideal for production work.
The trade-off is the limitation to oxidation firing. While many beautiful glazes exist for oxidation, you cannot achieve the unique effects, like copper reds or celadon blues, that depend on a reduction atmosphere.
Fuel-Burning Kilns: Creative Control vs. Complexity
Gas and wood kilns offer unparalleled control over the firing environment, opening up a vast world of rich glaze chemistry and atmospheric effects.
This creative freedom comes at the cost of complexity and labor. Managing a gas kiln requires skill and attention, while firing a wood kiln is an intense, multi-day effort that demands a team of people.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" kiln is the one that aligns with your artistic or practical objectives.
- If your primary focus is consistency and ease of use: An electric kiln is the most practical and reliable choice for beginners, schools, and consistent production.
- If your primary focus is achieving rich, complex glaze surfaces: A gas kiln provides the atmospheric control needed for reduction firing and a broader color palette.
- If your primary focus is embracing unique, one-of-a-kind results: An atmospheric kiln, such as a wood, salt, or soda kiln, offers a dynamic process where the fire itself becomes a creative partner.
Ultimately, understanding the function of the kiln is the first step toward intentionally shaping the outcome of your work.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Type | Heat Source | Atmosphere | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric | Coiled Elements | Oxidation (Oxygen-rich) | Beginners, schools, consistent production |
| Gas | Natural Gas/Propane | Reduction (Oxygen-limited) | Rich, complex glaze colors and effects |
| Wood/Atmospheric | Wood, Salt, Soda | Dynamic, interactive | Unique, one-of-a-kind surface textures |
Ready to choose the perfect kiln for your ceramic projects? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including kilns tailored to your specific needs—whether you're a hobbyist, educator, or professional potter. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to achieve precise temperature control, consistent results, or unique artistic effects. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let KINTEK support your creative and technical success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker















