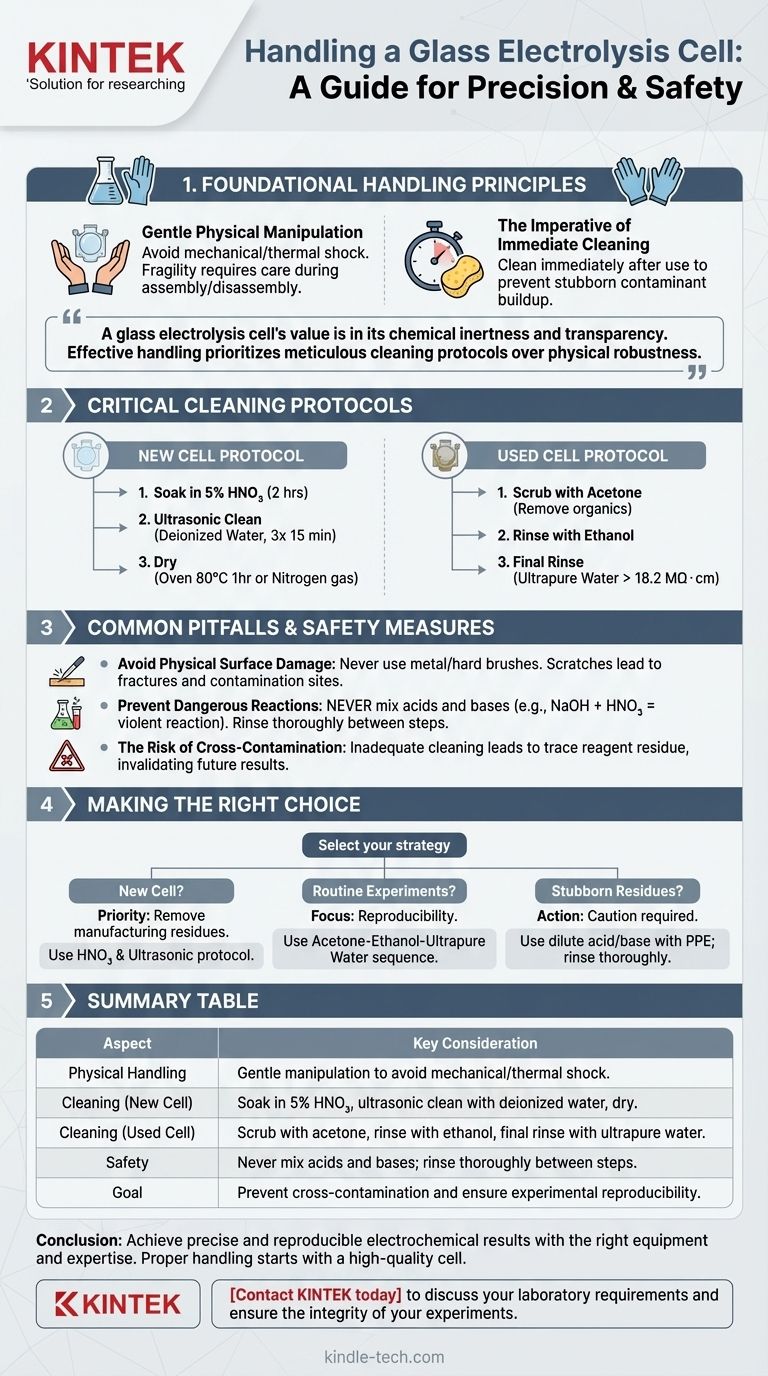
Proper handling of a glass electrolysis cell is centered on three core activities: gentle physical manipulation due to the material's fragility, rigorous and immediate cleaning to prevent contamination, and adherence to crucial safety protocols. Because your experimental results are highly sensitive to surface conditions, your handling procedure directly determines the accuracy of your data and the longevity of the cell.
A glass electrolysis cell's value is not in its durability, but in its chemical inertness and transparency. Therefore, effective handling prioritizes meticulous cleaning protocols over physical robustness to ensure the integrity and reproducibility of your electrochemical experiments.

Foundational Handling Principles
The reliability of your electrolysis setup begins with how you physically interact with the cell before, during, and after an experiment. These foundational habits prevent premature failure and inconsistent results.
Acknowledge Material Fragility
Glass is inherently brittle and susceptible to both mechanical and thermal shock. Always handle the cell gently, avoiding impacts with hard surfaces. When assembling or disassembling your apparatus, ensure all components are properly aligned and supported to prevent applying stress to the glass.
The Imperative of Immediate Cleaning
Residues from an electrochemical reaction can adhere strongly to the glass surface if left to dry. Clean the cell and electrodes immediately after each experiment. This single habit is the most effective way to prevent the buildup of stubborn contaminants that can alter surface chemistry and skew future results.
Critical Cleaning Protocols for Accurate Results
The goal of cleaning is to return the cell to a pristine, chemically inert state. The correct protocol depends on whether the cell is new or has been used for previous experiments.
Protocol for a New Cell
A new cell must be treated to remove any residues from the manufacturing process. First, soak the cell body in a 5% nitric acid (HNO₃) solution for at least two hours. Follow this by ultrasonically cleaning it with deionized water three times for 15 minutes each. Finally, dry it in an oven at 80℃ for one hour or use a stream of nitrogen gas.
Protocol for a Used Cell
For a cell that has been used, the goal is to remove specific experimental residues. Begin by scrubbing the inner wall with a suitable solvent like acetone to dissolve organic materials. Then, rinse thoroughly with ethanol, followed by a final rinse with ultrapure water (resistivity > 18.2 MΩ・cm) to remove all ionic traces.
Common Pitfalls and Safety Measures
Mistakes in handling often lead to either damaged equipment or compromised data. Being aware of common pitfalls is essential for maintaining a safe and effective lab environment.
Avoid Physical Surface Damage
Never use metal or other hard-bristled brushes for cleaning. These tools will create microscopic scratches on the glass surface. Scratches not only become sites for contamination to accumulate but also act as stress concentrators, making the cell significantly more likely to fracture.
Prevent Dangerous Chemical Reactions
A critical safety rule is to never mix acids and bases during a cleaning procedure. For example, adding a sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution to a cell containing residual nitric acid (HNO₃) can cause a violent and dangerous exothermic reaction. Always rinse thoroughly with deionized water between different chemical cleaning steps.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
The ultimate goal of these protocols is to prevent cross-contamination between experiments. Failing to clean properly can leave trace amounts of reagents or products adsorbed to the cell walls, which can catalytically or electrochemically interfere with your next reaction, invalidating your results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your handling and cleaning strategy based on the specific context of your work to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- If you are commissioning a new cell: Your priority is removing manufacturing residues. The nitric acid soak and ultrasonic cleaning protocol is non-negotiable for establishing a pristine baseline.
- If you are performing routine experiments: Your focus is on reproducibility. Clean the cell immediately after each run using the acetone-ethanol-ultrapure water sequence to prevent cross-contamination.
- If you are facing stubborn, unknown residues: You may need a dilute acid or base treatment. However, always proceed with caution, use appropriate PPE, and ensure the cell is thoroughly rinsed before and after.
A disciplined approach to handling transforms your glass cell from a fragile instrument into a reliable tool for precise electrochemical analysis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Physical Handling | Gentle manipulation to avoid mechanical/thermal shock. |
| Cleaning (New Cell) | Soak in 5% HNO₃, ultrasonic clean with deionized water, dry. |
| Cleaning (Used Cell) | Scrub with acetone, rinse with ethanol, final rinse with ultrapure water. |
| Safety | Never mix acids and bases; rinse thoroughly between steps. |
| Goal | Prevent cross-contamination and ensure experimental reproducibility. |
Achieve precise and reproducible electrochemical results with the right equipment and expertise. Proper handling is critical, but it starts with a high-quality cell. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including durable glassware designed for electrochemical applications. Our team can help you select the right cell for your needs and provide guidance on best practices. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory requirements and ensure the integrity of your experiments.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the design of an electrolytic cell influence evaluation of electrochemical catalytic performance? Key Factors
- What is the precaution regarding temperature when using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Essential Thermal Safety Tips
- How should the H-type electrolytic cell be connected? Expert Setup Guide for Precise Electrochemical Experiments
- What checks should be performed on the H-type electrolytic cell before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Data
- What are the advantages of a PTFE-covered glass electrolytic cell? Ensure Precision in CO2-Saturated Testing



















